概述
MDN文档 Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
跨域的英文是Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS),直译过来就是:跨越了来源的源资共享。当浏览器上的页面资源(http://www.a.com/xxx.html)试图访问其他域(http://www.b.com/xxx.html)时,浏览器会检查两个url的协议、域名、端口。其中任意一项不一致,都有可能产生跨域。
如上面例子中,http://www.a.com/xxx.html 和 http://www.b.com/xxx.html 的域名不同,就有可能会触发跨域。
简单请求
为什么说有可能会触发,这是因为简单请求不会触发跨域。简单请求是同时满足以下条件的请求:
Some requests don't trigger a CORS preflight. Those are called simple requests, though the Fetch spec (which defines CORS) doesn't use that term. A simple request is one that meets all the following conditions:
One of the allowed methods:
Apart from the headers automatically set by the user agent (for example,
Connection,User-Agent, or the other headers defined in the Fetch spec as a forbidden header name), the only headers which are allowed to be manually set are those which the Fetch spec defines as a CORS-safelisted request-header, which are:
AcceptAccept-LanguageContent-LanguageContent-Type(but note the additional requirements below)The only allowed values for the
Content-Typeheader are:
application/x-www-form-urlencodedmultipart/form-datatext/plainIf the request is made using an
XMLHttpRequestobject, no event listeners are registered on the object returned by theXMLHttpRequest.uploadproperty used in the request; that is, given anXMLHttpRequestinstancexhr, no code has calledxhr.upload.addEventListener()to add an event listener to monitor the upload.No
ReadableStreamobject is used in the request.
注意,不同浏览器对简单请求的判断条件会有细微不一致(不过这对后端开发人员来说,并不重要了)。
跨域解决方案
概述
在前后端分离的情景下,跨域是很常见的情景。前端部署在一台服务器(10.3.12.31)上,后端部署在另一台服务器(10.3.12.32)上,当用户在浏览器中获取并打开前端服务器的网页资源后,若用户通过网页发任意请求到后端服务器,浏览器会检测到网页资源的域和请求资源的域不同,就有可能触发跨域。
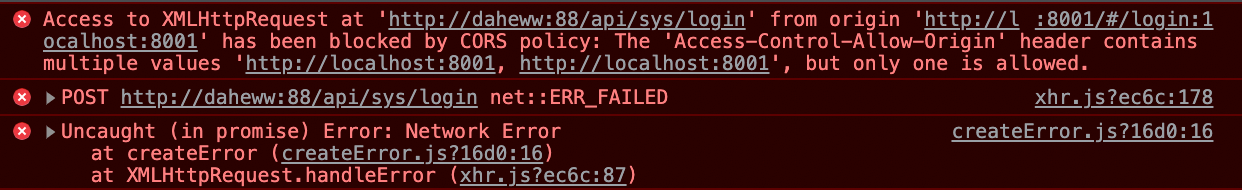
此时,浏览器若判定当前情景跨域,则会先发送一个预检请求(preflight)给后端服务器,该请求的类型为OPTION。预检请求会告诉后端服务器真实请求的各种信息,来让后端服务器判断是否让这个真实请求获取资源。
预检请求示例:

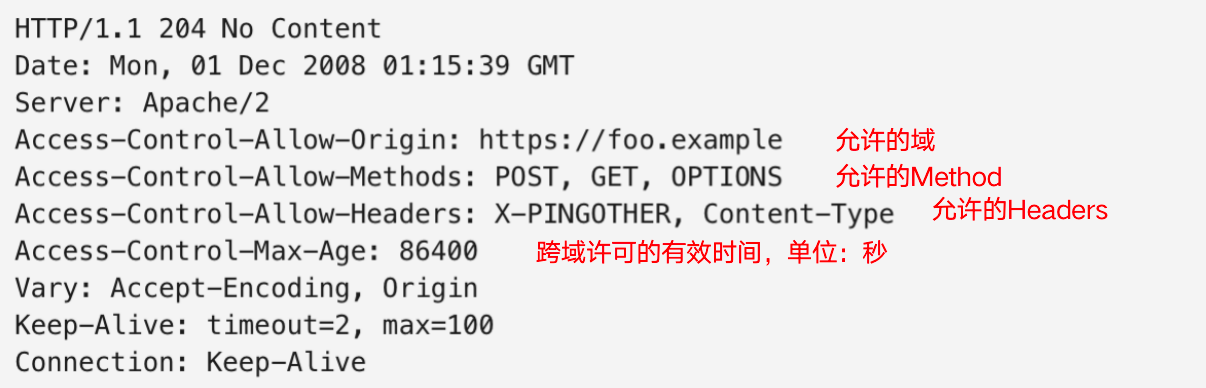
预检请求响应示例:
真实请求示例:
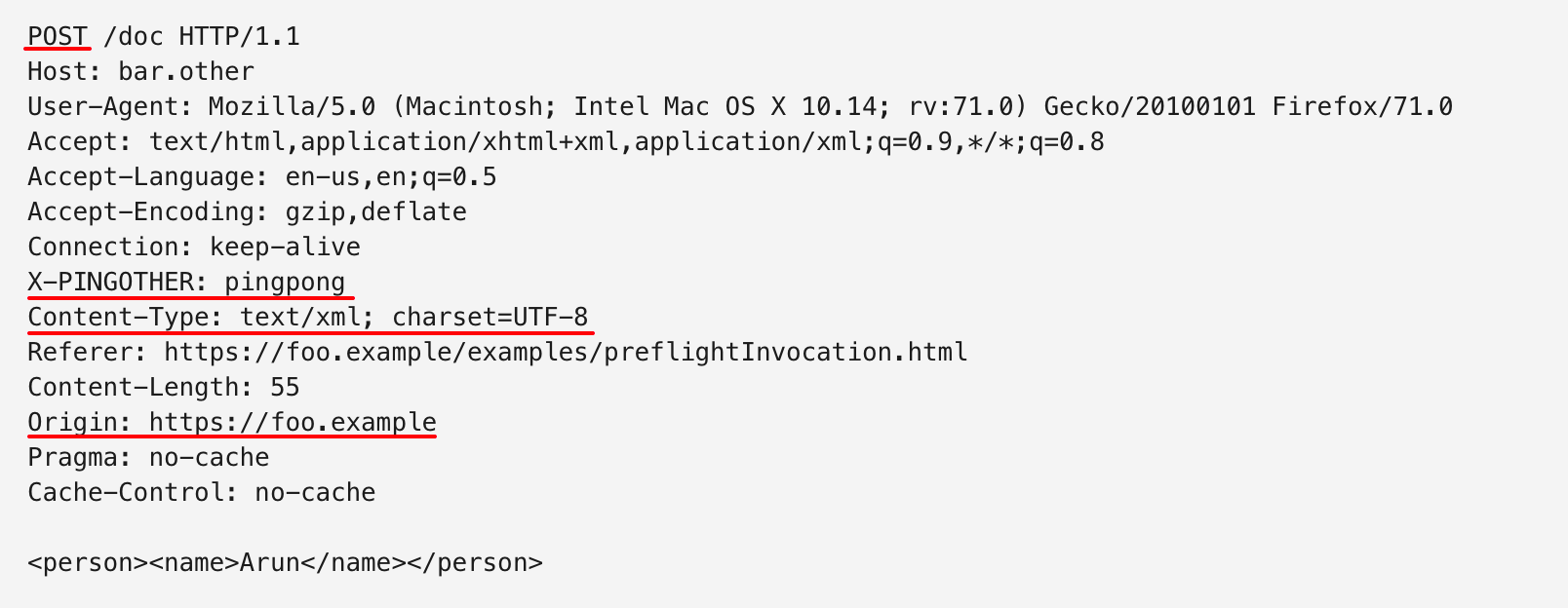
在本示例中,后端服务器允许了预检请求中的各种条件,所以真实请求能够顺利地发送给后端服务器并得到响应。更详细的跨域请求Headers、响应Headers参考见MDN文档 Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS).
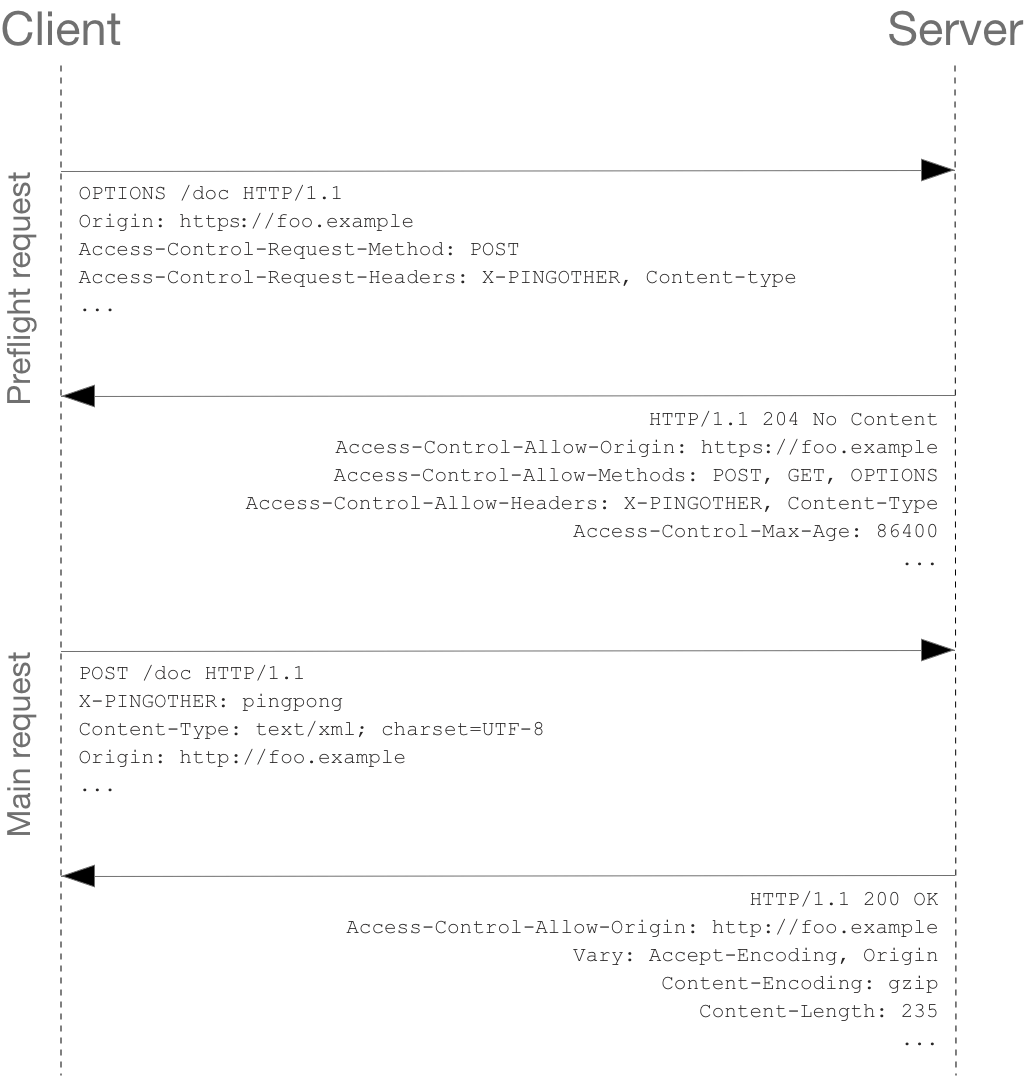
整体流程如下:
SpringBoot配置
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public CorsWebFilter corsWebFilter() {
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = new CorsConfiguration();
corsConfiguration.addAllowedHeader("*");
corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod("*");
corsConfiguration.addAllowedOrigin("*");
corsConfiguration.setAllowCredentials(true);
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**",corsConfiguration);
return new CorsWebFilter(source);
}
}
Nginx配置
若前端并不是将请求直接发送给后端,而是先发送给Nginx服务器,然后再由Nginx将请求转发给后端,则应该给Nginx增加跨域配置。
转自:我也说说Nginx解决前端跨域问题,正确的Nginx跨域配置(后端Nginx CORS跨域配置、CORS设置,后端允许跨域请求)
location /aoda-web {
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'DNT,web-token,app-token,Authorization,Accept,Origin,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Mx-ReqToken,X-Data-Type,X-Auth-Token,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Range';
add_header 'Access-Control-Expose-Headers' 'Content-Length,Content-Range';
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 204;
}
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_connect_timeout 5;
}
跨域相关的配置,主要是下面这部分:
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'DNT,web-token,app-token,Authorization,Accept,Origin,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Mx-ReqToken,X-Data-Type,X-Auth-Token,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Range';
add_header 'Access-Control-Expose-Headers' 'Content-Length,Content-Range';
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 204;
}
下面简单讲解一下,以便大家配置成功!
1、Access-Control-Allow-Origin,这里使用变量 $http_origin取得当前来源域,大家说用“*”代表允许所有,我实际使用并不成功,原因未知;
2、Access-Control-Allow-Credentials,为 true 的时候指请求时可带上Cookie,自己按情况配置吧;
3、Access-Control-Allow-Methods,OPTIONS一定要有的,另外一般也就GET和POST,如果你有其它的也可加进去;
4、Access-Control-Allow-Headers,这个要注意,里面一定要包含自定义的http头字段(就是说前端请求接口时,如果在http头里加了自定义的字段,这里配置一定要写上相应的字段),从上面可看到我写的比较长,我在网上搜索一些常用的写进去了,里面有“web-token”和“app-token”,这个是我项目里前端请求时设置的,所以我在这里要写上;
5、Access-Control-Expose-Headers,可不设置,看网上大致意思是默认只能获返回头的6个基本字段,要获取其它额外的,先在这设置才能获取它;
6、语句“ if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') { ”,因为浏览器判断是否允许跨域时会先往后端发一个 options 请求,然后根据返回的结果判断是否允许跨域请求,所以这里单独判断这个请求,然后直接返回。