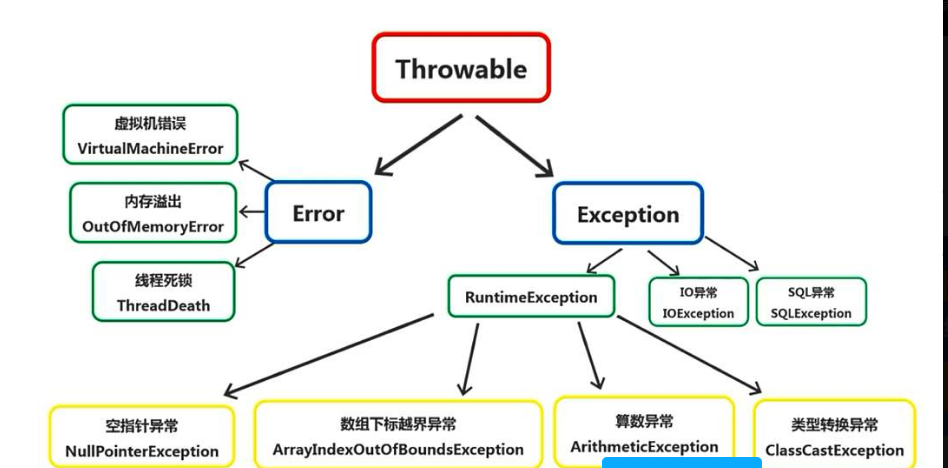
常见的异常图
异常语法(jdk1.7以后):
1 1: 2 try{}catch(ex1 ){}catch(ex2 ){} 3 4 2: 5 try{}catch(ex1 | ex2){} 6 3: 7 try(XX x = new XX()){}catch(){}
子类父类抛出异常问题:
方法重写的时候,如果父类没有抛出任何异常,那么子类只可以抛出运行时异常,不可以抛出编译时异常。
如果父类的方法抛出了一个异常,那么子类在方法重写的时候不能抛出比被重写方法申明更加宽泛的编译时异常。
子类重写方法的时候可以随时抛出运行时异常,包括空指针异常,数组越界异常等。处理异常代码:
1 package com.lv.study.pm.first; 2 3 4 /* 5 * 6 * 多重catch语句 针对不同的异常做不同的处理 7 * 8 * 9 */ 10 public class TestTryCatchCatch { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 14 System.out.println("打卡"); 15 test1(null); 16 System.out.println("赏月"); 17 } 18 19 public static void test1(Object str) { 20 21 try { 22 23 System.out.println(str.getClass()); 24 Integer it = (Integer) str; 25 System.out.println(it); 26 27 /* 28 * 如果代码发生了空指针异常打印 小喵崴泥 29 * 30 * 代码发生了类型转换异常打印 lalal 31 * 32 */ 33 34 //catch 只会走一个 多重catch一定是子类在前父类在后或者所有的异常都是平级的 35 } catch (NullPointerException e) {//只会处理这个个异常去处理 36 System.out.println("小喵崴泥"); 37 } catch (ClassCastException e) { 38 System.out.println("lalal"); 39 } catch (Exception e) {//以防万一 40 System.out.println("系统异常"); 41 } 42 } 43 44 }
补充:
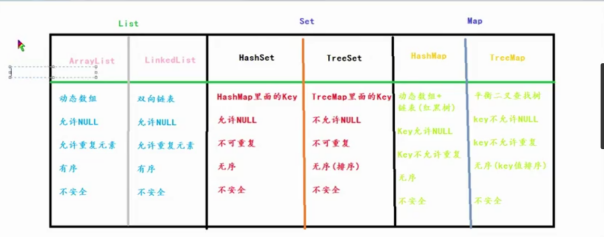
Hashmap的原理
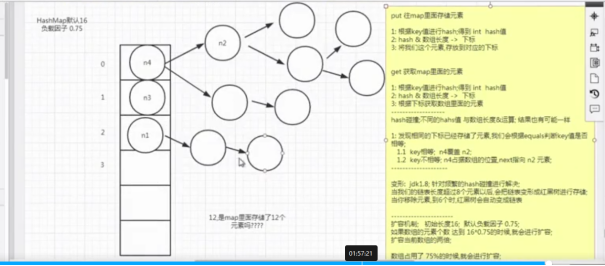
jdk1.7以前是进去:node,把前面的挤走,自己上位,但是1.7之后就在后面连着了
异常语法