说明:
本例程使用YOLOv3进行昆虫检测。例程分为数据处理、模型设计、损失函数、训练模型、模型预测和测试模型六个部分。本篇为第五部分,使用非极大值抑制来消除预测出的重叠面积过大的边框,然后显示预测结果图像。
实验代码:
模型预测:
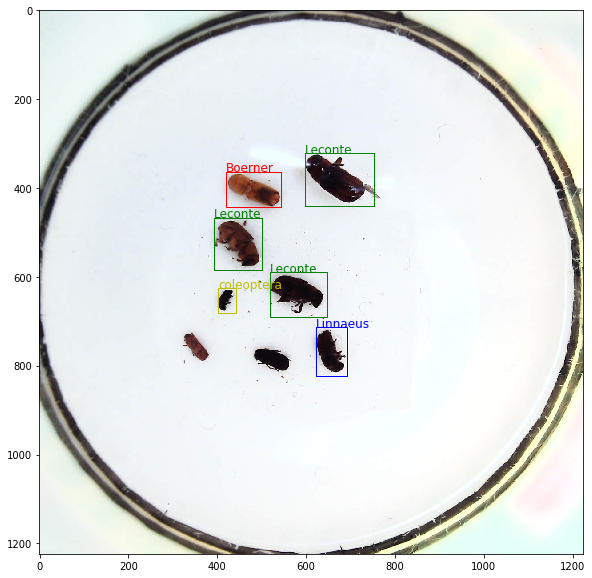
import paddle.fluid as fluid from paddle.fluid.dygraph.base import to_variable from source.data import single_test_reader, display_infer from source.model import YOLOv3 from source.infer import get_nms_infer num_classes = 7 # 类别数量 anchor_size = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326] # 锚框大小 anchor_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]] # 锚框掩码 downsample_ratio = 32 # 下采样率 image_path = './dataset/test/images/1872.jpeg' # 预测图像路径 model_path = './output/darknet53-yolov3' # 网络权重路径 sco_threshold = 0.70 # 预测得分阈值:根据测试的平均精度在准确率和召回率之间取一个平衡值 nms_threshold = 0.45 # 非极大值阈值 with fluid.dygraph.guard(): # 读取图像 image, image_size = single_test_reader(image_path) # 读取图像 image = to_variable(image) # 转换格式 image_size = to_variable(image_size) # 转换格式 # 加载模型 model = YOLOv3(num_classes=num_classes, anchor_mask=anchor_mask) # 加载模型 model_dict, _ = fluid.load_dygraph(model_path) # 加载权重 model.load_dict(model_dict) # 设置权重 model.eval() # 设置验证 # 前向传播 infer = model(image) # 获取结果 infer = get_nms_infer(infer, image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask, downsample_ratio, sco_threshold, nms_threshold) # 显示结果 print('image infer:', infer[0].shape[0]) # 显示图像预测结果数量 display_infer(infer[0], image_path) # 显示一张图像预测结果
结果:
image infer: 6
infer.py文件
import numpy as np def sigmoid(x): """ 功能: 计算sigmoid函数 输入: x - 输入数值 输出: y - 输出数值 """ return 0.5 * (1.0 + np.tanh(0.5 * x)) # def sigmoid(x): # return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x)) def get_infer(infer, image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask, downsample_ratio): """ 功能: 计算每个特征图像的预测边框和得分 输入: infer - 特征图像 image_size - 图像高宽 num_classes - 类别数量 anchor_size - 锚框大小 anchor_mask - 锚框掩码 downsample_ratio - 下采样率 输出: pdbox - 预测边框 pdsco - 预测得分 """ # 调整特征形状 batch_size = infer.shape[0] # 特征批数 num_rows = infer.shape[2] # 特征行数 num_cols = infer.shape[3] # 特征列数 num_anchor = len(anchor_mask) # 锚框数量 infer = infer.numpy() infer = infer.reshape([-1, num_anchor, 5 + num_classes, num_rows, num_cols]) # 转换特征形状 # 计算预测边框 pdloc = infer[:, :, 0:4, :, :] # 获取预测位置:[b,c,4,n,m] pdbox = np.zeros(pdloc.shape) # 预测边框数组:[b,c,4,n,m] image_h = num_rows * downsample_ratio # 预测图像高度 image_w = num_cols * downsample_ratio # 预测图像宽度 for m in range(batch_size): # 遍历图像 for i in range(num_rows): # 遍历行数 for j in range(num_cols): # 遍历列数 for k in range(num_anchor): # 遍历锚框 # 获取边框大小 anchor_w = anchor_size[2 * anchor_mask[k]] # 锚框宽度 anchor_h = anchor_size[2 * anchor_mask[k] + 1] # 锚框高度 # 设置预测边框 pdbox[m, k, 0, i, j] = j # 预测边框cx pdbox[m, k, 1, i, j] = i # 预测边框cy pdbox[m, k, 2, i, j] = anchor_w # 预测边框pw pdbox[m, k, 3, i, j] = anchor_h # 预测边框ph pdbox[:, :, 0, :, :] = (pdbox[:, :, 0, :, :] + sigmoid(pdloc[:, :, 0, :, :])) / num_cols # 预测边框x=cx + dx pdbox[:, :, 1, :, :] = (pdbox[:, :, 1, :, :] + sigmoid(pdloc[:, :, 1, :, :])) / num_rows # 预测边框y=cy + dy pdbox[:, :, 2, :, :] = (pdbox[:, :, 2, :, :] * np.exp(pdloc[:, :, 2, :, :])) / image_w # 预测边框w=pw * exp(tw) pdbox[:, :, 3, :, :] = (pdbox[:, :, 3, :, :] * np.exp(pdloc[:, :, 3, :, :])) / image_h # 预测边框h=ph * exp(th) pdbox = np.clip(pdbox, 0.0, 1.0) # 限制预测边框范围为[0,1] pdbox = pdbox.transpose((0, 1, 3, 4, 2)) # 调整数据维度:[b,c,n,m,4] pdbox = pdbox.reshape((pdbox.shape[0], -1, pdbox.shape[-1])) # 调整数据形状:[b,c*n*m,4] # 调整坐标格式 pdbox[:, :, 0] = pdbox[:, :, 0] - pdbox[:, :, 2] / 2.0 # 预测边框x1 pdbox[:, :, 1] = pdbox[:, :, 1] - pdbox[:, :, 3] / 2.0 # 预测边框y1 pdbox[:, :, 2] = pdbox[:, :, 0] + pdbox[:, :, 2] # 预测边框x2 pdbox[:, :, 3] = pdbox[:, :, 1] + pdbox[:, :, 3] # 预测边框y2 # 计算原图坐标 scale = image_size.numpy() # 原图高宽 for m in range(batch_size): pdbox[m, :, 0] = pdbox[m, :, 0] * scale[m, 1] # 预测边框x1 pdbox[m, :, 1] = pdbox[m, :, 1] * scale[m, 0] # 预测边框y1 pdbox[m, :, 2] = pdbox[m, :, 2] * scale[m, 1] # 预测边框x2 pdbox[m, :, 3] = pdbox[m, :, 3] * scale[m, 0] # 预测边框y2 # 计算预测得分 pdobj = sigmoid(infer[:, :, 4, :, :]) # 预测物体概率:[b,c,n,m],对损失函数计算结果求sigmoid pdcls = sigmoid(infer[:, :, 5:5+num_classes, :, :]) # 预测类别概率:[b,c,7,n,m],对损失函数计算结果求sigmoid pdobj = np.expand_dims(pdobj, axis=2) # 添加数据维度:[b,c,1,n,m] pdsco = pdobj * pdcls # 计算预测得分:[b,c,7,n,m] pdsco = pdsco.transpose((0, 1, 3, 4, 2)) # 调整数据维度:[b,c,n,m,7] pdsco = pdsco.reshape((pdsco.shape[0], -1, pdsco.shape[-1])) # 调整数据形状:[b,c*n*m,7] pdsco = pdsco.transpose((0, 2, 1)) # 调整数据维度:[b,7,c*n*m] return pdbox, pdsco # def get_infer(infer, image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask, downsample_ratio): # # 获取锚框大小 # anchor_list = [] # 锚框列表 # for i in anchor_mask: # 遍历锚框 # anchor_list.append(anchor_size[2 * i]) # 锚框宽度 # anchor_list.append(anchor_size[2 * i + 1]) # 锚框高度 # # 计算预测结果 # pdbox, pdsco = fluid.layers.yolo_box( # x=infer, # img_size=image_size, # class_num=num_classes, # anchors=anchor_list, # conf_thresh=0.01, # downsample_ratio=downsample_ratio) # pdsco = fluid.layers.transpose(pdsco, perm=[0, 2, 1]) # return pdbox.numpy(), pdsco.numpy() def get_sum_infer(infer, image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask, downsample_ratio): """ 功能: 计算三个输出的预测结果的边框和得分 输入: infer - 特征列表 image_size - 图像高宽 num_classes - 类别数量 anchor_size - 锚框大小 anchor_mask - 锚框掩码 downsample_ratio - 下采样率 输出: pdbox - 预测边框 pdsco - 预测得分 """ # 计算预测结果 pdbox_list = [] # 预测边框列表 pdsco_list = [] # 预测得分列表 for i in range(len(infer)): # 遍历特征列表 pdbox, pdsco = get_infer(infer[i], image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask[i], downsample_ratio) pdbox_list.append(pdbox) # 添加边框列表 pdsco_list.append(pdsco) # 添加得分列表 # 减小下采样率 downsample_ratio //= 2 # 减小下采样率 # 合并预测结果 pdbox = np.concatenate(pdbox_list, axis=1) # 连接预测边框列表第一维 pdsco = np.concatenate(pdsco_list, axis=2) # 连接预测得分列表第二维 return pdbox, pdsco ############################################################################################################## def get_box_iou_xyxy(box1, box2): """ 功能: 计算边框交并比值 输入: box1 - 边界框1 box2 - 边界框2 输出: iou - 交并比值 """ # 计算交集面积 x1_min, y1_min, x1_max, y1_max = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3] x2_min, y2_min, x2_max, y2_max = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3] x_min = np.maximum(x1_min, x2_min) y_min = np.maximum(y1_min, y2_min) x_max = np.minimum(x1_max, x2_max) y_max = np.minimum(y1_max, y2_max) w = np.maximum(x_max - x_min + 1.0, 0) h = np.maximum(y_max - y_min + 1.0, 0) intersection = w * h # 交集面积 # 计算并集面积 s1 = (y1_max - y1_min + 1.0) * (x1_max - x1_min + 1.0) s2 = (y2_max - y2_min + 1.0) * (x2_max - x2_min + 1.0) union = s1 + s2 - intersection # 并集面积 # 计算交并比 iou = intersection / union return iou def get_nms_index(pdbox, pdsco, sco_threshold, nms_threshold): """ 功能: 获取非极大值抑制预测索引 输入: pdbox - 预测边框 pdsco - 预测得分 sco_threshold - 预测得分阈值 nms_threshold - 非极大值阈值 输出: nms_index - 预测索引 """ # 获取得分索引 sco_index = np.argsort(pdsco)[::-1] # 对得分逆向排序,获取预测得分索引 # 非极大值抑制 nms_index = [] # 预测索引列表 while(len(sco_index) > 0): # 如果剩余得分索引数量大于0,则进行非极大值抑制 # 获取最大得分 max_index = sco_index[0] # 获取最大得分索引 max_score = pdsco[max_index] # 获取最大得分 if max_score < sco_threshold: # 如果最大得分小于预测得分阈值,则不处理剩余得分索引 break # 设置保留标识 keep_flag = True # 保留标识为真 for i in nms_index: # 遍历保留索引 # 计算交并比值 box1 = pdbox[max_index] # 第一个边框坐标 box2 = pdbox[i] # 保留的边框坐标 iou = get_box_iou_xyxy(box1, box2) # 计算交并比值 if iou > nms_threshold: # 如果交并比值大于非极大值阈值,则不处理剩余保留索引 keep_flag = False # 保留标识为假 break # 添加保留索引 if keep_flag: # 如果保留标识为真,则添加预测索引 nms_index.append(max_index) # 添加预测索引列表 # 获取剩余索引 sco_index = sco_index[1:] # 转换数据格式 nms_index = np.array(nms_index) return nms_index def get_nms_class(pdbox, pdsco, sco_threshold, nms_threshold): """ 功能: 获取非极大值抑制的预测结果 输入: pdbox - 预测边框 pdsco - 预测得分 sco_threshold - 预测得分阈值 nms_threshold - 非极大值阈值 输出: infer_list - 预测结果列表 """ # 获取批次结果 batch_size = pdbox.shape[0] # 预测批数数量 class_numb = pdsco.shape[1] # 总的类别数量 infer_list = [] # 预测结果列表 for i in range(batch_size): # 遍历批次 # 获取预测结果 infer = [] # 每批预测列表 for c in range(class_numb): # 遍历类别 # 获取预测索引 nms_index = get_nms_index(pdbox[i], pdsco[i][c], sco_threshold, nms_threshold) if len(nms_index) < 1: # 如果预测索引为0,则计算下一个类别索引 continue # 设置预测结果 nms_pdsco = pdsco[i][c][nms_index] # 预测得分 nms_pdbox = pdbox[i][nms_index] # 预测边框 nms_infer = np.zeros([nms_pdsco.shape[0], 6]) # 预测结果 nms_infer[:, 0] = c # 设置预测类别 nms_infer[:, 1] = nms_pdsco[:] # 设置预测得分 nms_infer[:, 2:6] = nms_pdbox[:, :] # 设置预测边框 infer.append(nms_infer) # 添加每类结果 # 添加预测列表 if len(infer) > 0: infer = np.concatenate(infer, axis=0) # 合并各批预测结果 infer_list.append(infer) # 添加预测结果列表 else: infer_list.append(infer) # 添加空的预测结果 return infer_list ############################################################################################################## def get_nms_infer(infer, image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask, downsample_ratio, sco_threshold, nms_threshold): """ 功能: 获取三个输出的非极大值抑制的预测结果 输入: infer - 特征列表 image_size - 原图高宽 num_classes - 类别数量 anchor_size - 锚框大小 anchor_mask - 锚框掩码 downsample_ratio - 下采样率 sco_threshold - 预测得分阈值 nms_threshold - 非极大值阈值 输出: infer - 预测结果 """ # 计算预测结果 pdbox, pdsco = get_sum_infer(infer, image_size, num_classes, anchor_size, anchor_mask, downsample_ratio) # 非极大值抑制 infer = get_nms_class(pdbox, pdsco, sco_threshold, nms_threshold) return infer
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/litt1e/article/details/88814417
https://blog.csdn.net/litt1e/article/details/88852745
https://blog.csdn.net/litt1e/article/details/88907542
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/742781
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/672017
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/868589
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/122277