1118考试总结
T1
题目大意:
给定一个数列, 求第(k)大值.(n <= 1e7)
一看这数据范围肯定不能用(sort)了, 考场上我用的二分法, 就是二分第(k)大值,看看有多少数比它小, 判断一下是否有(k)个, 复杂度差不多是(O(3e8))的, 勉强过去了.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 1e7 + 5, mod = 1e9;
int n, k, x, ans;
long long y;
int a[N];
int check(int x) {
register int res = 0;
for(register int i = 1;i <= n; ++ i) {
if(a[i] <= x) res ++;
if(res > k) return res;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
n = read(); k = read(), a[1] = x = read(); y = read();
for(register int i = 2;i <= n; ++ i) a[i] = (y * a[i - 1] % mod + x) % mod;
int l = 0, r = 1e9 + 1;
while(l <= r) {
register int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
register int tmp = check(mid);
if(tmp > k) r = mid - 1, ans = mid;
else if(tmp == k) r = mid - 1, ans = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
还有另一种标准(O(n))解法, 用递归求.
直接选取(a[1])作为标准, 然后把这(n)个数按比(a[1])小(d个), 和(a[1])相等(count个), 比(a[1])大分(e个)为三类.
如果说(d < k, d + count >= k), 说明找到了正解.
如果(d >= k),说明当前的标准找大了, 那么就将比(a[1])小的那些数的第一个作为标准, 然后递归.
如果(d < k),说明当前的标准找小了, 那么就将比(a[1])大的那些数的第一个作为标准, 然后递归, 注意下次找第(k - count - d)大的数字.
复杂度经过数学分析是(O(n))的.我不会.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 1e7 + 5, mod = 1e9;
int n, k, x, ans;
long long y;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
void solve(int *a, int *b, int *c, int k, int n) {
int tmp = a[1], count = 0, d = 0, e = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) {
if(a[i] == tmp) count ++;
if(a[i] < tmp) b[++ d] = a[i];
if(a[i] > tmp) c[++ e] = a[i];
}
if(d < k && d + count >= k) { printf("%d", tmp); return ; }
else if(d >= k) solve(b, a, c, k, d);
else solve(c, b, a, k - count - d, e);
}
int main() {
n = read(); k = read(), a[1] = x = read(); y = read();
for(register int i = 2;i <= n; ++ i) a[i] = (y * a[i - 1] % mod + x) % mod;
solve(a, b, c, k, n);
return 0;
}
T2
水题不说了.
T3
题目大意:
一个人有(n)个相同的苹果, 要把这些苹果装到不同的盒子里给另外一个人.这个人可以吃任意个苹果, 这些盒子可以为空, 问总共有多少种方案.
(n, m <= 1e9, p < 2^{31}),p不一定为质数.
组合数 + 扩展卢卡斯定理.
化简完题意后, 我们可以得出答案就是 (displaystyle sum_{i = 0}^{n} C_{i + m - 1}^{m - 1}).
假设这个人吃完苹果后还剩(i)个, 那么方案数就是(C_{i + m - 1}^{m - 1}).可以用隔板法理解, 因为盒子可以空, 我们可以预先在(m)个盒子里都垫上一个苹果, 那么现在就有(i+ m)个苹果, 我们要把它们分到(m)个盒子里, 那么就需要在任意(i + m - 1)个空隙里选出(m - 1)个空隙.
上式还可以化简:(C_{m - 1}^{m - 1} + C_m^{m - 1} + ... + C_{m + n - 1}^{m - 1} = C_{m}^{m} + C_m^{m - 1} + C_{m + 1}^{m - 1 } + ... + C_{n + m - 1}^{m - 1} = C_{m + 1}^{m} + C_{m + 1}^{m - 1} + ... + C_{n + m - 1}^{m - 1}= C_{n + m}^{m}).
然后我们就可以开开心心求组合数.....等等, (p)不是质数, (n,m <= 1e9), woc毒瘤啊!
那怎么办, 我们知道唯一分解定理, 可以把p分解质因数, 然后可以求出组合数模每一个(p_c^{k_c})的值, 然后用中国剩余定理合并.(因为(p_1^{k_1}, p_2^{k_2}...)都两两互质, 所以可以合并).
又发现(n, m)过于大, 我们可以用卢卡斯定理求. 但是卢卡斯定理仅适用于(p)为质数的情况, 对于(p_c^{k_c})这个不一定为质数的模数我们只能用扩展卢卡斯来求.
具体思路就是这样, 由于刚刚学习扩展卢卡斯(其实讲过好几遍了, 刚刚才会...), 我认为有必要写一下证明过程:
我们现在要求:(displaystyle frac{n!}{m!(n - m)!} \% p^k), 由于不是质数, 不能求(m!)的逆元, 我们可以转换一下形式使(n!)这些东西与模数互质, 于是就变成了:(displaystyle frac{frac{n!}{p^x}}{frac{m!}{p^y}frac{(n - m)!}{p^z}} * p^{x - y + z} \% p^k).
那么现在问题转化成了求(displaystyle frac{n!}{p^x}).
(x)很好求, (x=displaystyle sum _{i=1, p^i <= n} lfloor frac{n}{p^i} floor).现在只需求(displaystyle frac{n!}{p^x} \% p^k).就好了.
假设当前(n = 22, p = 3, k = 2, P=p^k), 我们把(n / P)的整块和(n \% p)的残块挑出来:
((1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9) * (10 * 11 * 12 * 13 * 14 * 15 * 16 * 17 * 18) * (19 * 20 * 21 * 22))
然后再把这里面所有(p)的倍数挑出来:
((1 * 2 * 4 * 5 * 7 * 8) * (10 * 11 * 13 * 14 * 16 * 17) * (19 * 20 * 22) * 3^7*(1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7))
我们发现, 设一个整块的乘积是(X), 那么所有整块的乘积与(P)取模的结果就是(X^{n / P} \% P).然后残块暴力算, (3^7)也可与模数消掉, 然后我们发现最后一块又是一个阶乘, 我们可以将其表示为:(displaystyle frac{(n / p)!}{p^x} \% P). 然后递归求解就好了.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n_, m_, P, cnt, M, ans_;
int p[50], d[50], b[50], m[50], k[50], ans[50];
void divide() {
for(int i = 2;i * i <= P; i++) {
if(!(P % i)) {
p[++ cnt] = i;
while(!(P % i)) b[cnt] ++, P /= i;
}
}
if(P > 1) p[++ cnt] = P, b[cnt] = 1;
}
int ksm(int x, int y, int mod) {
int res = 1;
while(y) { if(y & 1) res = 1ll * res * x % mod; x = 1ll * x * x % mod; y >>= 1; }
return res;
}
void ex_gcd(int a, int b, long long &x, long long &y) {
if(!b) { x = 1; y = 0; return ; }
else { ex_gcd(b, a % b, y, x); y -= x * (a / b); return ; }
}
int inv(int a, int b) {
long long x, y;
ex_gcd(a, b, x, y);
return (x + b) % b;
}
void CRT() {
ans_ = 0; M = 1; long long x, y;
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt; i++) M = M * d[i];
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt; i++) m[i] = M / d[i], ex_gcd(d[i], m[i], x, y), k[i] = y;
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt; i++) ans_ = (ans_ + 1ll * ans[i] * m[i] % M * k[i] % M) % M;
ans_ = (ans_ + M) % M;
}
int main() {
n_ = read(); m_ = read(); P = read();
divide();
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt; i++) {
int x[3], y[3], now, P = ksm(p[i], b[i], 1e9);
x[1] = x[2] = x[0] = 0;
for(int j = 0;j < 3; j++) {
j == 0 ? now = n_ + m_ : j == 1 ? now = n_ : now = m_;
int u = p[i]; y[j] = 1;
while(u <= now) { x[j] += now / u; u *= p[i]; }
while(now) {
int tmp = 1;
for(int k = 1;k <= P; k++) if(k % p[i]) tmp = 1ll * tmp * k % P;
int div = now / P, yu = now % P;
y[j] = 1ll * y[j] * ksm(tmp, div, P) % P;
for(int k = P * div + 1;k <= P * div + yu; k++) if(k % p[i]) y[j] = 1ll * y[j] * k % P;
now /= p[i];
}
}
ans[i] = ksm(p[i], x[0] - x[1] - x[2], P);
ans[i] = 1ll * ans[i] * y[0] % P;
ans[i] = 1ll * ans[i] * inv(y[1], P) % P;
ans[i] = 1ll * ans[i] * inv(y[2], P) % P;
d[i] = P;
}
fclose(stdin); fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
T4
题目大意:
小P可以求出任意一个数列的艺术价值,它等于将这个数列 顺次划分为若干个极长单调区间(相邻两个单调区间的单调性必须不相同)后,每个单 调区间中元素总和的平均值。比如对于数列3 7 9 2 4 5,它将被划分为[3 7 9] [2] [4 5], 其艺术价值为(19 +2 + 9)/3 = 10。由于小P特殊的审美观,他还要求划分出的第一个单 调区间必须为单调增区间,也就是说,对于数列10 9 8,它将被划分为[10] [9 8],而不 是[10 9 8]现在小P手里有一个长度为n的序列a,,他想问你,这个序列的所有子序列中,艺术价值最大的是哪个子序列,输出其艺术价值。注意:本题单调数列为严格单调,也就是说数列中的数必须严格上升或严格下降 (n <= 1e5)
最长上升子序列 + 树状数组.
首先我们可以证明最后的结果只有两种形式: 一直单调递增 或者 先单调递增后单调递减 .
如果是这样的:
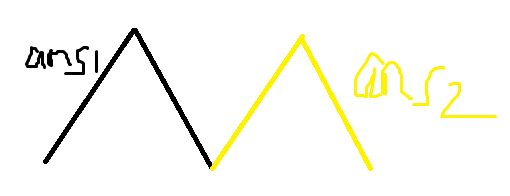
我们可以算出总的答案是:(frac{ans1 + ans2}{2}), 可以发现它小于max(ans1, ans2).
如果是这样的:
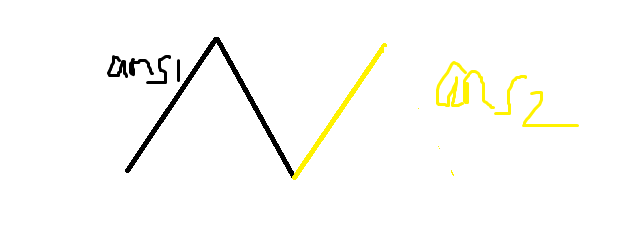
假设(ans1 >ans2), 那么我们会发现(ans1 > frac{2ans1 + ans2}{3}), 也就是(ans1)比总体的答案要优.
假设(ans1 < ans2), 那么我们会发现(ans2 > frac{2ans1 + ans2}{3}),也就是(ans2)比总体的答案要优.
然后我们用(f[i])表示从(1)到(i)的单调递增的总和, (g[i])表示从(i)到(n)的单调递减的总和.就做完啦.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n, a[N], b[N];
long long f[N], g[N], t[N];
double ans;
int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); }
long long query(int x) {
long long res = 0; for( ; x ; x -= lowbit(x)) res = max(res, t[x]); return res;
}
void insert(int x, long long y) {
for( ; x < N ; x += lowbit(x)) t[x] = max(t[x], y);
}
int main() {
n = read();
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) b[i] = a[i] = read();
sort(b + 1, b + n + 1);
int cnt = unique(b + 1, b + n + 1) - b - 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) a[i] = lower_bound(b + 1, b + cnt + 1, a[i]) - b;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) {
f[i] = query(a[i] - 1) + b[a[i]];
insert(a[i], f[i]);
}
memset(t, 0, sizeof(t));
for(int i = n;i >= 1; i--) {
g[i] = query(a[i] - 1) + b[a[i]];
insert(a[i], g[i]);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, 1.0 * f[i]);
if(i != 1) ans = max(ans, 1.0 * (f[i] + g[i] - b[a[i]]) / 2);
}
printf("%.3lf
", ans);
return 0;
}
这种思想的题其实还有好多比如这个:T1
也是通过一些证明得到了一个正确且容易求的结论.
还比如这个:
Makik 有一张详细的城市地图,地图标注了 L 个景区,编号为 1~L。而景区与景区之间建有 单向高速通道。这天,Makik 要去逛景区,他可以任选一个景区开始一天行程,且只能通过单向高速通道进入其他景区。
至少要参观两个景区,游玩最后要回到起始景区。如果 Makik 参观了第 i 个景区,会获得一个乐趣值 (F_i)。且参观过得景区不会再获得乐趣值。对于第 i 条单向高速通道,需要消耗 (T_i) 的时间,能够从 (L1_i) 到达 (L2_i)。为了简化问题,参观景区不需要花费时间,Makik 想要最终单位时间内获得的乐趣值最大。请你写个程序,帮 Makik 计算一下他能得到的最大平均乐趣值。
题目链接
简化题意就是求一个最优的环.
我们设第一个环的总和为(a), 点的个数为(b), 第二个环的总和为(c), 点的个数为(d), 假设这两个环连着并且没用重复的点, 那我们可以得到一条新的总和为(a + c), 点的个数为(b + d)的路径.
显然, 如果说(frac{a}{b} > frac{c}{d}), 那么可以得到(frac{a}{b} > frac{a + c}{b + d} > frac{c}{d}), 证明方法通分一下就好了, 这里就不赘述了.
所以说我们找的最优路径肯定只是单个环, 而不是"环连环". 思想其实和上题差不多的
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long read() {
long long s = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar())) (ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(s = ch ^ 48;isdigit(ch = getchar()); s = (s << 1) + (s << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return s * f;
}
const int N = 1005, M = 5005, inf = 1e9;
int n, m, cnt1, cnt2;
int in[N], num[N], head[N];
long double val[M], dis[N];
int a[N], to[M], next[M];
struct cj { int x, y; double z; } b[M];
struct edge { int to, nxt; double val; } e[M];
void add(int id, double mid) {
e[id].nxt = head[b[id].x];
head[b[id].x] = id;
e[id].to = b[id].y;
e[id].val = a[b[id].y] - mid * b[id].z;
}
int check(double mid) {
queue <int> q;
memset(head, 0, sizeof head);
memset(in, 0, sizeof in);
memset(num, 0, sizeof num);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) dis[i] = -inf;
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++) add(i, mid);
dis[1] = 0; q.push(1); in[1] = 1; num[1] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front(); q.pop(); in[x] = 0;
for(int i = head[x]; i ; i = e[i].nxt) {
int y = e[i].to;
if(dis[y] <= dis[x] + e[i].val) {
dis[y] = dis[x] + e[i].val;
if(!in[y]) in[y] = 1, num[y] ++, q.push(y);
if(num[y] >= n) return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++)
b[i].x = read(), b[i].y = read(), cin >> b[i].z;
double l = 0, r = 1e6;
while(r - l > 0.0001) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
printf("%.2lf", l);
return 0;
}