(1) 编写一个函数new,对n个字符开辟连续的存储空间,此函数应返回一个指针(地址),指向字符串开始的空间。new(n)表示分配n个字节的内存空间。(2)写一函数free,将前面用new函数占用的空间释放。free(p)表示将p(地址)指向的单元以后的内存段释放。
解题思路: 封装malloc函数申请空间,封装free函数释放空间;
答案:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void *mynew(int n)
{
return malloc(n);
}
void myfree(char *p)
{
return free(p);
}
int main()
{
int num;
char *str = NULL;
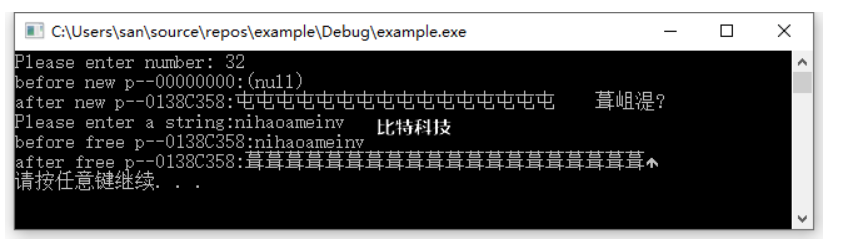
printf("Please enter number: ");
scanf_s("%d", &num);
printf("before new p--%p:%s
", str, str);//申请空间之前,查看指针的地址和指向空间数据
str = (char*)mynew(num);
printf("after new p--%p:%s
", str, str);//申请空间之后,查看指针的地址和指向空间数据
printf("Please enter a string:");
scanf_s("%s", str, num);
printf("before free p--%p:%s
", str, str);//释放空间之前,查看指针的地址和指向空间数据
myfree(str);
printf("after free p--%p:%s
", str, str);//释放空间之后,查看指针的地址和指向空间数据
system("pause");
return 0;
}