时空限制
Time Limit:1000ms
Resident Memory Limit:1024KB
Output Limit:1024B
题目内容
Given a positive integer n, print out the positions of all 1’s in its binary representation. The position of the least significant bit is 0.≤d
Example
The positions of 1’s in the binary representation of 13 are 0, 2, 3.
Task
Write a program which for each data set: reads a positive integer n, computes the positions of 1’s in the binary representation of n, writes the result.
Input
The first line of the input contains exactly one positive integer d equal to the number of data sets, 1≤d≤10. The data sets follows. Each data set consists of exactly one line containing exactly one intger n, 1≤n≤106.
Output
The output should consists of exactly d lines, one line for each data set. Line i, 1≤i≤d, should contain increasing sequence of integers separated by single spaces——the positions of 1’s in the binary representation of the i-th input number.
题目来源
Central Europe 2001, Practice
解题思路
本题主要考查十进制到二进制的转换。十进制整整数转换为二进制整数的方法是不断除2取余,而被除数则不断除2取整,知道被除数变为0.把各位余数按相反的顺序连接起来,正好是该整整数的二进制表示。
本题要求打印一个正整数的二进制中1的位置,所以,只要把每位二进制位存入向量中即可,最后,再在向量中进行处理,这样很省事。
本题格式上,要求两位输出之间用一个空格隔开,而每行的最后不能有空格。这点要特别注意。
流程分析
(1)定义一个整型向量容器存储整数对应的二进制;定义一个整型变量作为输入整数的个数;定义一个整型变量作为每次输入的整数;定义一个整型变量作为是否输出空格的标志
(2)从键盘读入输入的整数个数
(3)对输入的每个整数,先将向量容器清空,
(4)对输入的每个整数,对其每次除2的商,不断对2取余并将取余结果插入向量容器
(5)对输入的每个整数,对其二进制的每一位,首先判断是不是第一次输出,若是则直接输出其位置,即在向量容器中的下标;若不是第一次输出,则先输出空格再输出其位置
参考代码
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char * argv[])
{
vector<int> v;
int n,a;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a;
v.clear();
for(int j=a;j;j=j/2)
{
v.push_back(j%2?1:0);
}
int p=0;
for(int k=0;k<v.size();k++)
{
if(v[k]==1)
{
if(p==0) cout<<k;
else cout<<" "<<k;
p=1;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
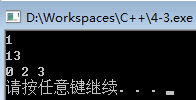
运行结果