Github项目地址:https://github.com/siberia0015/PersonProject-Java
PSP表格:
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 20 |
| • Estimate | • 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 600 | 630 |
| Development | 开发 | 530 | 695 |
| • Analysis | • 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 60 |
| • Design Spec | • 生成设计文档 | 10 | 5 |
| • Design Review | • 设计复审 | 10 | 20 |
| • Coding Standard | • 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 60 | 140 |
| • Design | • 具体设计 | 120 | 150 |
| • Coding | • 具体编码 | 180 | 180 |
| • Code Review | • 代码复审 | 30 | 40 |
| • Test | • 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 100 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 40 | 50 |
| • Test Repor | • 测试报告 | 15 | 15 |
| • Size Measurement | • 计算工作量 | 10 | 20 |
| • Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | • 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 15 | 15 |
| 合计 | 600 | 765 |
计算模块接口的设计与实现过程:
出于开发项目和今后发展考虑,从这次作业起我将学习使用java编程。首先,题目要求程序能够接收一个文件,文件名由控制台输入,因此需要一个方法能够接收控制台输入的值作为文件的地址参数。因为题目还需要求把不同功能的模块封装成独立的模块,因此我把接收文件的代码段直接放在各个方法里。然后,题目要求代码至少要对数据进行四种统计,统计字符出现次数、单词(符合要求的)出现次数、有效行数以及出现频率最高的十个单词。我使用BufferedReader来依次读取文件的每一行,对于行数统计,我在读取的同时会记下长度不为0的行的个数;对于字符统计,我用一个StringBuffer记下每行的内容,然后把它转为String,由于此方法无法记下换行符,所以我最后用这个String的长度加上总行数(包括空白行)-1作为字符数;对于单词(有效)统计,我前面的方法同上,之后用split()方法将String分成一个String数组,通过一系列方法筛选出符合条件的元素,统计个数;对于词频统计,我用一个HashMap存放获得的符合条件的单词及其出现次数,然后对其进行排序并返回。最后,用一个输出函数接收之前方法返回的参数并新建一个新的result.txt输出。
流程图

关键代码说明:
- 主函数 WordCount.java:
用一个变量pathname记下控制台传入的参数,其意义是文件的绝对地址,它将作为计数函数的参数。创建数个变量分别记下字符数,单词数,有效行数以及储存单词与出现次数关系的map。,它们的值分别与计数函数的返回值一一对应。最后,把这些值传入printFile函数中,打印并创建result.txt。
7 public class WordCount { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 String pathname = args[0]; 10 int characters = 0; 11 int words = 0; 12 int lines = 0; 13 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); 14 /*查询&统计*/ 15 characters = lib.countChar(pathname); 16 words = lib.countWord(pathname); 17 lines = lib.countLines(pathname); 18 map = lib.countFrequency(pathname); 19 /*输出结果*/ 20 lib.printFile(characters, words, lines, map); 21 System.out.println("completed"); 22 } 23 }
- 读入文件通用
每个计数函数中通用的打开文件代码。
try { String encoding = "UTF-8"; File file = new File(filePath); if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) { InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding); [计数函数内容] read.close(); } else { System.out.println("找不到指定的文件"); }
[计数函数内容] } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("读取文件内容出错"); e.printStackTrace(); }
- 统计字符数 countChar:
用bufferedreader按行读取文件内容并记下总行数,用stringbuffer转载每行数据并转换成string统计长度,字符数即为长度加上总行数减一(第一行不需要换行符)。
int totalLine=0; /*读取文件数据*/ StringBuffer sb=null; BufferedReader br1; try{ br1=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String temp=br1.readLine(); sb=new StringBuffer(); while(temp!=null){ sb.append(temp); /*统计总行数*/ totalLine++; temp=br1.readLine(); } } catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } /*读取的内容*/ String info=sb.toString(); /*统计字符个数*/ characters=info.length()+totalLine-1;
- 统计单词数 countWord:
同上个方法得到包含文件内容的string,用split方法把字符串分割为一个个单词,将字符串前四个字符切割并把所有字母替换成 “” ,若字符串长度仍大于等于4,则判定为合格字符。
/*读取文件数据*/ StringBuffer sb = null; BufferedReader br1; try { br1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String temp = br1.readLine(); sb = new StringBuffer(); while (temp != null) { sb.append(temp); sb.append(" ");//每行结束多读一个空格 temp = br1.readLine(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } String info = sb.toString(); String s[] = info.split(",|\\.| |\\?|\\!|\\'|\t"); /*统计单词个数*/for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { if (s[i].length() >= 4) { String temp = s[i].substring(0, 4); temp = temp.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", ""); if (temp.length() >= 4) { words++; } } }
- 统计有效行数 countLines:
比较简单,没什么好说的,就是读取时判断如果每行不为空则计数器+1。
br1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String temp = br1.readLine(); while (temp != null) { /*统计有效行数*/ if (!temp.isEmpty()) { lines++; } temp = br1.readLine(); }
- 统计单词出现次数 countFrequency:
本次作业难点之一。先把记录文件内容的string分割为一个个单词并判断是否合法,方法同上。之后建立一个map用来存放单词与其出现次数,若遇到map中没有出现的单词则将单词加入map,若已存在则value+1。全部单词录入完成后对map进行排序,将排序后的map返回。
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
String info=sb.toString(); String s[]=info.split(",|\\.| |\\?|\\!|\\'|\t"); /*统计单词个数*/ for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++){ if(s[i].length()>=4) { String temp = s[i].substring(0, 4); temp=temp.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", ""); if (temp.length() >= 4) { if (map.containsKey(s[i].toLowerCase())) {//判断Map集合对象中是否包含指定的键名 map.put(s[i].toLowerCase(), Integer.parseInt(map.get(s[i].toLowerCase())) + 1 + ""); } else { map.put(s[i].toLowerCase(), 1 + ""); } } } } /*map排序*/ map=sortMapByValue(map);
- 创建新文件 printFile:
通过传入的int characters, int words, int lines, Map<String, String> map,以特定格式在当前目录下新建/更新result.txt。
代码略。
- map排序
因为java的map和c++不同,貌似不会自动排序,因此只好自己写排序函数。
/*map排序*/ public static Map<String, String> sortMapByValue(Map<String, String> oriMap) { if (oriMap == null || oriMap.isEmpty()) { return null; } Map<String, String> sortedMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); List<Map.Entry<String, String>> entryList = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, String>>( oriMap.entrySet()); Collections.sort(entryList, new MapValueComparator()); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iter = entryList.iterator(); Map.Entry<String, String> tmpEntry = null; while (iter.hasNext()) { tmpEntry = iter.next(); sortedMap.put(tmpEntry.getKey(), tmpEntry.getValue()); } return sortedMap; }
- 比较器MapValueComparator:
1 import java.util.Comparator; 2 import java.util.Map; 3 4 public class MapValueComparator implements Comparator<Map.Entry<String, String>> { 5 6 @Override 7 public int compare(Map.Entry<String, String> me1, Map.Entry<String, String> me2) { 8 int flag=me2.getValue().compareTo(me1.getValue()); 9 if(flag==0){ 10 flag=me1.getKey().compareTo(me2.getKey()); 11 } 12 return flag; 13 //return me1.getValue().compareTo(me2.getValue()); 14 } 15 }
计算模块接口部分的性能改进:
因为一开始写的时候比较随意,把几个统计方法都揉在一个方法里写了,这样复用效率不高,因此我将原先的大方法里的各个代码块独立出来,形成了最终的方法。并把开发过程中的一些冗余代码进行了删减。
计算模块部分单元测试展示:
测试用例1

测试结果1


测试用例2
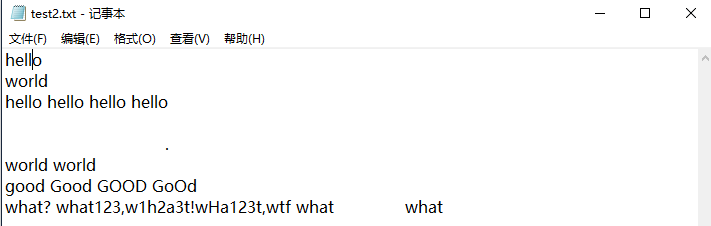
测试结果2

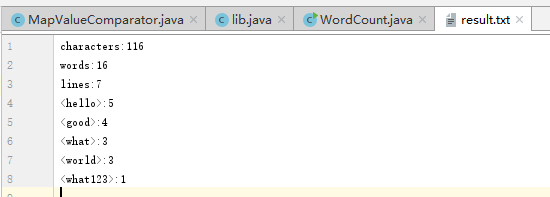
计算模块部分异常处理说明:
通过try catch语句处理异常,在程序出错时方便查找出错点。当路径出错时,提示找不到指定文件;当无法打开文件时,提示无法打开文件。因为我对这方面知识较少,因此不太掌握这方面的知识,不是特别理解。
感想:
经过这次实践,我认识到了准备工作和自学能力的重要性。开始编写时没有做清楚计划,写完程序后代码揉成一团,之后找出关键语句单独封装耗费了很多时间。在开发过程中遇到很多复杂的问题,如果没有掌握自学能力的话学起来非常耗时且困难。第一次按照较规范化的格式编写代码,有很多地方代码冗余或者缺乏注释,我以后会逐渐改正的。