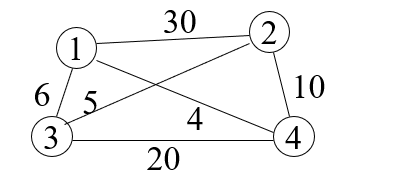
问题描述:
某售货员要到若干城市去推销商品,已知各城市之间的路程,他要选定一条从驻地出发,经过每个城市一遍,最后回到住地的路线,使总的路程最短。
算法描述:
回溯法,序列树, 假设起点为 1。
算法开始时 x = [1, 2, 3, ..., n]
x[1 : n]有两重含义 x[1 : i]代表前 i 步按顺序走过的城市, x[i + 1 : n]代表还未经过的城市。利用Swap函数进行交换位置。
若当前搜索的层次i = n 时,处在排列树的叶节点的父节点上,此时算法检查图G是否存在一条从顶点x[n-1] 到顶点x[n] 有一条边,和从顶点x[n] 到顶点x[1] 也有一条边。若这两条边都存在,则发现了一个旅行售货员的回路即:新旅行路线),算法判断这条回路的费用是否优于已经找到的当前最优回路的费用bestcost,若是,则更新当前最优值bestcost和当前最优解bestx。
若i < n 时,检查x[i - 1]至x[i]之间是否存在一条边, 若存在,则x [1 : i ] 构成了图G的一条路径,若路径x[1: i] 的耗费小于当前最优解的耗费,则算法进入排列树下一层,否则剪掉相应的子树。
代码实现:

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int max_ = 0x3f3f3f; const int NoEdge = -1; int citynum; int edgenum; int currentcost; int bestcost; int Graph[100][100]; int x[100]; int bestx[100]; void InPut() { int pos1, pos2, len; scanf("%d %d", &citynum, &edgenum); memset(Graph, NoEdge, sizeof(Graph)); for(int i = 1; i <= edgenum; ++i) { scanf("%d %d %d", &pos1, &pos2, &len); Graph[pos1][pos2] = Graph[pos2][pos1] = len; } } void Initilize() { currentcost = 0; bestcost = max_; for(int i = 1; i <= citynum; ++i) { x[i] = i; } } void Swap(int &a, int &b) { int temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } void BackTrack(int i) //这里的i代表第i步去的城市而不是代号为i的城市 { if(i == citynum) { if(Graph[x[i - 1]][x[i]] != NoEdge && Graph[x[i]][x[1]] != NoEdge && (currentcost + Graph[x[i - 1]][x[i]] + Graph[x[i]][x[1]] < bestcost || bestcost == max_)) { bestcost = currentcost + Graph[x[i - 1]][x[i]] + Graph[x[i]][x[1]]; for(int j = 1; j <= citynum; ++j) bestx[j] = x[j]; } } else { for(int j = i; j <= citynum; ++j) { if(Graph[x[i - 1]][x[j]] != NoEdge && (currentcost + Graph[x[i - 1]][x[j]] < bestcost || bestcost == max_)) { Swap(x[i], x[j]); //这里i 和 j的位置交换了, 所以下面的是currentcost += Graph[x[i - 1]][x[i]]; currentcost += Graph[x[i - 1]][x[i]]; BackTrack(i + 1); currentcost -= Graph[x[i - 1]][x[i]]; Swap(x[i], x[j]); } } } } void OutPut() { cout << "路线为:" << endl; for(int i = 1; i <= citynum; ++i) cout << bestx[i] << " "; cout << "1" << endl; } int main() { InPut(); Initilize(); BackTrack(2); OutPut(); }
测试样例:
实现结果:
参考:王晓东《算法设计与分析》