@Conditional:Spring4.0 介绍了一个新的注解@Conditional,它的逻辑语义可以作为"If…then…else…"来对bean的注册起作用。
@Contidional 介绍
Conditional 是由 SpringFramework 提供的一个注解,位于 org.springframework.context.annotation 包内,定义如下。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Conditional {
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
SpringBoot 模块大量的使用@Conditional 注释,我们可以将Spring的@Conditional注解用于以下场景:
- 可以作为类级别的注解直接或者间接的与@Component相关联,包括@Configuration类;
- 可以作为元注解,用于自动编写构造性注解;
- 作为方法级别的注解,作用在任何@Bean方法上。
Condition 接口
我们需要一个类实现Spring提供的Condition接口,它会匹配@Conditional所符合的方法,然后我们可以使用我们在@Conditional注解中定义的类来检查。
public interface Condition {
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}
Spring @Conditional注解实例
作用在方法上
先来看一个简单一些的示例,我们假设有三个角色老师Teacher、学生Student和父母Parent,三种环境Linux、Windows和MacOSX,如果是Linux环境,就注册Teacher,如果是Windows环境就注册Parent,如果是Mac 环境就注册Student。代码示例如下:
- 首先创建Teacher和Student对象,没有任何的属性和方法,只是一个空类
//如果当前工程运行在Windows系统下,就注册Student
public class Student {}
//如果当前工程运行在Linux系统下,就注册Teacher
public class Teacher {}
// 如果是Mac OSX 系统,就注册Parent
public class Parent {}
- 创建一个LinuxCondition和一个WindowsCondition,LinuxCondition能够匹配Linux环境,WindowsCondition能够匹配Windows环境,MacOSX 系统匹配mac环境。
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 获取系统环境的属性
String systemName = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
if(systemName.contains("Linux")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//自定义一个判断条件
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
/*
* ConditionContext context: spring容器上下文环境
* AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata :@Conditional修饰类型信息
*/
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
String systemName = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
if(systemName.contains("Windows")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class OsxCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
String property = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
if(property.equals("Mac OS X")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
- 下面来新建匹配注册环境,如果系统是Linux环境,就注册Teacher,如果系统是Windows,就注册Parent,如果是Mac 系统,就注册Student
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Conditional(OsxCondition.class)
@Bean
public Student student(){
return new Student();
}
@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)
@Bean
public Teacher teacher(){
return new Teacher();
}
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)
@Bean
public Parent parent(){
return new Parent();
}
}
- 新建测试类进行测试
public class ConditionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
String[] names = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(String name : names){
System.out.println("name = " + name);
}
}
}
由输出可以看出,name = student 被输出到控制台,也就是说,我当前所用的系统环境是MacOSX环境,所以注册的是OSXCondition,也就是student的bean。
手动设置系统环境
也可以进行手动修改vm.options,把当前的系统环境变为Linux 或者Windows,以Idea为例:

在Edit Configurations中找到vm.options 选项,把系统环境改为 Linux,如下:
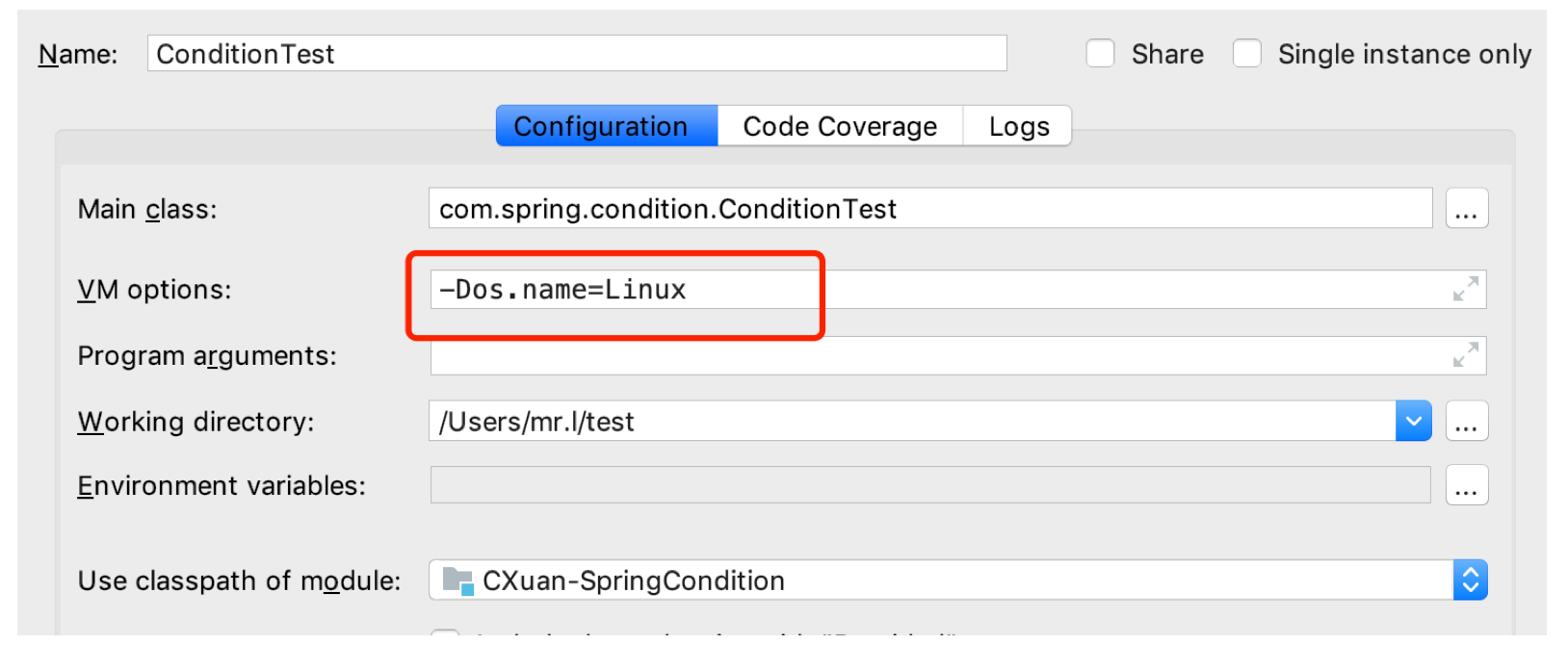
然后重新启动测试,发现Teacher 被注入进来了,修改当前环境为Windows,观察Parent也被注入进来并输出了。
作用在类上
@Conditional 注解可以作用在类上,表示此类下面所有的bean满足条件后都可以进行注入,通常与@Configuration注解一起使用。
- 新建一个
AppClassConfig,在类上标注@Conditional()注解,并配置相关bean,如下:
@Conditional(value = OsxCondition.class)
上文表示如果是OsxCondition.class 的话,就注册student、teacher、parent
- 测试类不用修改,直接用原测试类进行测试,发现student、 teacher、 parent 都被注册进来了
多个条件类
因为@Conditional注解的value 方法默认传递一个数组,所以可以接受多个condition,为了测试如下情况,
新建一个 TestCondition类,如下:
// 单纯为了测试
public class TestCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 返回false,表示不匹配
return false;
}
}
修改一下AppClassConfig
@Conditional(value = {OsxCondition.class,TestCondition.class})
也就是给@Conditional 多加了一个参数 TestCondition.class
启动之前的测试类,发现上述的bean都没有注入,也就是说,只有在满足OsxCondition.class 和 TestCondition.class 都为true的情况下,才会注入对应的bean,修改TestCondition.class的matches方法的返回值为true,重新观察返回结果,发现上述bean都被注入了。
@Conditional 与@Profile 的对比
@Spring3.0 也有一些和@Conditional 相似的注解,它们是Spring SPEL 表达式和Spring Profiles 注解 Spring4.0的@Conditional 注解要比@Profile 注解更加高级。@Profile 注解用来加载应用程序的环境。@Profile注解仅限于根据预定义属性编写条件检查。 @Conditional注释则没有此限制。
Spring中的@Profile 和 @Conditional 注解用来检查"If…then…else"的语义。然而,Spring4 @Conditional是@Profile 注解的更通用法。
- Spring 3中的 @Profiles仅用于编写基于Environment变量的条件检查。 配置文件可用于基于环境加载应用程序配置。
- Spring 4 @Conditional注解允许开发人员为条件检查定义用户定义的策略。 @Conditional可用于条件bean注册。
