导包
1 import math 2 import numpy as np 3 import h5py 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 import scipy 6 from PIL import Image 7 from scipy import ndimage 8 import tensorflow as tf 9 from tensorflow.python.framework import ops 10 from cnn_utils import * 11 12 np.random.seed(1)
训练数据
1 # Loading the data (signs) 2 X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset() 3 4 X_train = X_train_orig/255. #(1080,64,64,3) 5 X_test = X_test_orig/255. #(120,64,64,3) 6 Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6).T #(1080,6) 7 Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6).T #(120,6)
创建placeholders
1 def create_placeholders(n_H0, n_W0, n_C0, n_y): 2 """ 3 Creates the placeholders for the tensorflow session. 4 5 Arguments: 6 n_H0 -- scalar, height of an input image 7 n_W0 -- scalar, width of an input image 8 n_C0 -- scalar, number of channels of the input 9 n_y -- scalar, number of classes 10 11 Returns: 12 X -- placeholder for the data input, of shape [None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0] and dtype "float" 13 Y -- placeholder for the input labels, of shape [None, n_y] and dtype "float" 14 """ 15 16 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈2 lines) 17 X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0],name='X') 18 Y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None, n_y],name='Y') 19 ### END CODE HERE ### 20 21 return X, Y
初始化参数
1 def initialize_parameters(): 2 """ 3 Initializes weight parameters to build a neural network with tensorflow. The shapes are: 4 W1 : [4, 4, 3, 8] 5 W2 : [2, 2, 8, 16] 6 Returns: 7 parameters -- a dictionary of tensors containing W1, W2 8 """ 9 10 tf.set_random_seed(1) # so that your "random" numbers match ours 11 12 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines of code) 13 W1=tf.get_variable("W1",[4,4,3,8], initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=0)) 14 W2=tf.get_variable("W2",[2,2,8,16], initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=0)) 15 ### END CODE HERE ### 16 17 parameters = {"W1": W1, 18 "W2": W2} 19 return parameters
前向传播
1 def forward_propagation(X, parameters): 2 """ 3 Implements the forward propagation for the model: 4 CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> FULLYCONNECTED 5 6 Arguments: 7 X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples) 8 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "W2" 9 the shapes are given in initialize_parameters 10 11 Returns: 12 Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit 13 """ 14 15 # Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters" 16 W1 = parameters['W1'] 17 W2 = parameters['W2'] 18 19 ### START CODE HERE ### 20 # CONV2D: stride of 1, padding 'SAME' 21 Z1=tf.nn.conv2d(X,W1, strides = [1,1,1,1], padding = 'SAME') 22 # RELU 23 A1=tf.nn.relu(Z1) 24 # MAXPOOL: window 8x8, sride 8, padding 'SAME' 25 P1=tf.nn.max_pool(A1,ksize=[1,8,8,1],strides=[1,8,8,1],padding="SAME") 26 # CONV2D: filters W2, stride 1, padding 'SAME' 27 Z2=tf.nn.conv2d(P1,W2,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME") 28 # RELU 29 A2=tf.nn.relu(Z2) 30 # MAXPOOL: window 4x4, stride 4, padding 'SAME' 31 P2=tf.nn.max_pool(A2,ksize=[1,4,4,1],strides=[1,4,4,1],padding='SAME') 32 # FLATTEN 33 F=tf.contrib.layers.flatten(P2) 34 # FULLY-CONNECTED without non-linear activation function (not not call softmax). 35 # 6 neurons in output layer. Hint: one of the arguments should be "activation_fn=None" 36 Z3=tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(F,6,activation_fn=None) 37 ### END CODE HERE ### 38 39 return Z3
计算成本
1 def compute_cost(Z3, Y): 2 """ 3 Computes the cost 4 5 Arguments: 6 Z3 -- output of forward propagation (output of the last LINEAR unit), of shape (6, number of examples) 7 Y -- "true" labels vector placeholder, same shape as Z3 8 9 Returns: 10 cost - Tensor of the cost function 11 """ 12 13 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code) 14 cost=tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = Z3, labels = Y) 15 cost=tf.reduce_mean(cost) 16 ### END CODE HERE ### 17 18 return cost
构建模型
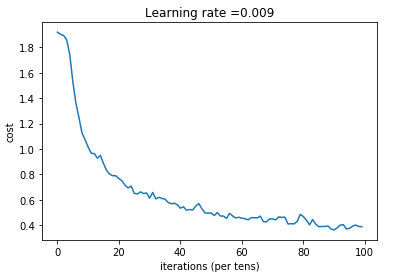
1 def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.009, 2 num_epochs = 100, minibatch_size = 64, print_cost = True): 3 """ 4 Implements a three-layer ConvNet in Tensorflow: 5 CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> FULLYCONNECTED 6 7 Arguments: 8 X_train -- training set, of shape (None, 64, 64, 3) 9 Y_train -- test set, of shape (None, n_y = 6) 10 X_test -- training set, of shape (None, 64, 64, 3) 11 Y_test -- test set, of shape (None, n_y = 6) 12 learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization 13 num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop 14 minibatch_size -- size of a minibatch 15 print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs 16 17 Returns: 18 train_accuracy -- real number, accuracy on the train set (X_train) 19 test_accuracy -- real number, testing accuracy on the test set (X_test) 20 parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict. 21 """ 22 23 ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables 24 tf.set_random_seed(1) # to keep results consistent (tensorflow seed) 25 seed = 3 # to keep results consistent (numpy seed) 26 (m, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0) = X_train.shape 27 n_y = Y_train.shape[1] 28 costs = [] # To keep track of the cost 29 30 # Create Placeholders of the correct shape 31 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 32 X,Y=create_placeholders(n_H0,n_W0,n_C0,n_y) 33 ### END CODE HERE ### 34 35 # Initialize parameters 36 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 37 parameters=initialize_parameters() 38 ### END CODE HERE ### 39 40 # Forward propagation: Build the forward propagation in the tensorflow graph 41 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 42 Z3=forward_propagation(X,parameters) 43 ### END CODE HERE ### 44 45 # Cost function: Add cost function to tensorflow graph 46 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 47 cost=compute_cost(Z3,Y) 48 ### END CODE HERE ### 49 50 # Backpropagation: Define the tensorflow optimizer. Use an AdamOptimizer that minimizes the cost. 51 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 52 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost) 53 ### END CODE HERE ### 54 55 # Initialize all the variables globally 56 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() 57 58 # Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph 59 with tf.Session() as sess: 60 61 # Run the initialization 62 sess.run(init) 63 64 # Do the training loop 65 for epoch in range(num_epochs): 66 67 minibatch_cost = 0. 68 num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # number of minibatches of size minibatch_size in the train set 69 seed = seed + 1 70 minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed) 71 72 for minibatch in minibatches: 73 74 # Select a minibatch 75 (minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch 76 # IMPORTANT: The line that runs the graph on a minibatch. 77 # Run the session to execute the optimizer and the cost, the feedict should contain a minibatch for (X,Y). 78 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) 79 _ , temp_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y}) 80 ### END CODE HERE ### 81 82 minibatch_cost += temp_cost / num_minibatches 83 84 # Print the cost every epoch 85 if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0: 86 print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, minibatch_cost)) 87 if print_cost == True and epoch % 1 == 0: 88 costs.append(minibatch_cost) 89 90 # plot the cost 91 plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs)) 92 plt.ylabel('cost') 93 plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') 94 plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate)) 95 plt.show() 96 97 # Calculate the correct predictions 98 predict_op = tf.argmax(Z3, 1) 99 correct_prediction = tf.equal(predict_op, tf.argmax(Y, 1)) 100 101 # Calculate accuracy on the test set 102 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) 103 print(accuracy) 104 train_accuracy = accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train}) 105 test_accuracy = accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test}) 106 print("Train Accuracy:", train_accuracy) 107 print("Test Accuracy:", test_accuracy) 108 109 return train_accuracy, test_accuracy, parameters
调用
_, _, parameters = model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)
Tensor("Mean_1:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
Train Accuracy: 0.868519
Test Accuracy: 0.733333
相比之下,卷积神经网络比普通的神经网络有更高的准确率。