深度神经网络计算过程

提前加载包
1 import numpy as np 2 import h5py 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from testCases_v2 import * 5 from dnn_utils import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward 6 from scipy import ndimage 7 import lr_utils
初始化模型参数
两层结构:
1 def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y): 2 """ 3 Argument: 4 n_x -- size of the input layer 5 n_h -- size of the hidden layer 6 n_y -- size of the output layer 7 8 Returns: 9 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters: 10 W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x) 11 b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1) 12 W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h) 13 b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1) 14 """ 15 np.random.seed(1) 16 17 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code) 18 W1=np.random.randn(n_h,n_x)*0.01 19 W2=np.random.randn(n_y,n_h)*0.01 20 b1=np.zeros((n_h,1)) 21 b2=np.zeros((n_y,1)) 22 ### END CODE HERE ### 23 24 assert(W1.shape == (n_h, n_x)) 25 assert(b1.shape == (n_h, 1)) 26 assert(W2.shape == (n_y, n_h)) 27 assert(b2.shape == (n_y, 1)) 28 29 parameters = {"W1": W1, 30 "b1": b1, 31 "W2": W2, 32 "b2": b2} 33 34 return parameters
L层结构:
1 def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims): 2 """ 3 Arguments: 4 layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network 5 6 Returns: 7 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL": 8 Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) 9 bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1) 10 """ 11 np.random.seed(3) 12 parameters = {} 13 L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network 14 15 for l in range(1, L): 16 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 17 parameters['W' + str(l)]=np.random.randn(layer_dims[l],layer_dims[l-1])/np.sqrt(layers_dims[l - 1]) 18 parameters['b' + str(l)]=np.zeros((layer_dims[l],1)) 19 ### END CODE HERE ### 20 21 assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1])) 22 assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1)) 23 return parameters
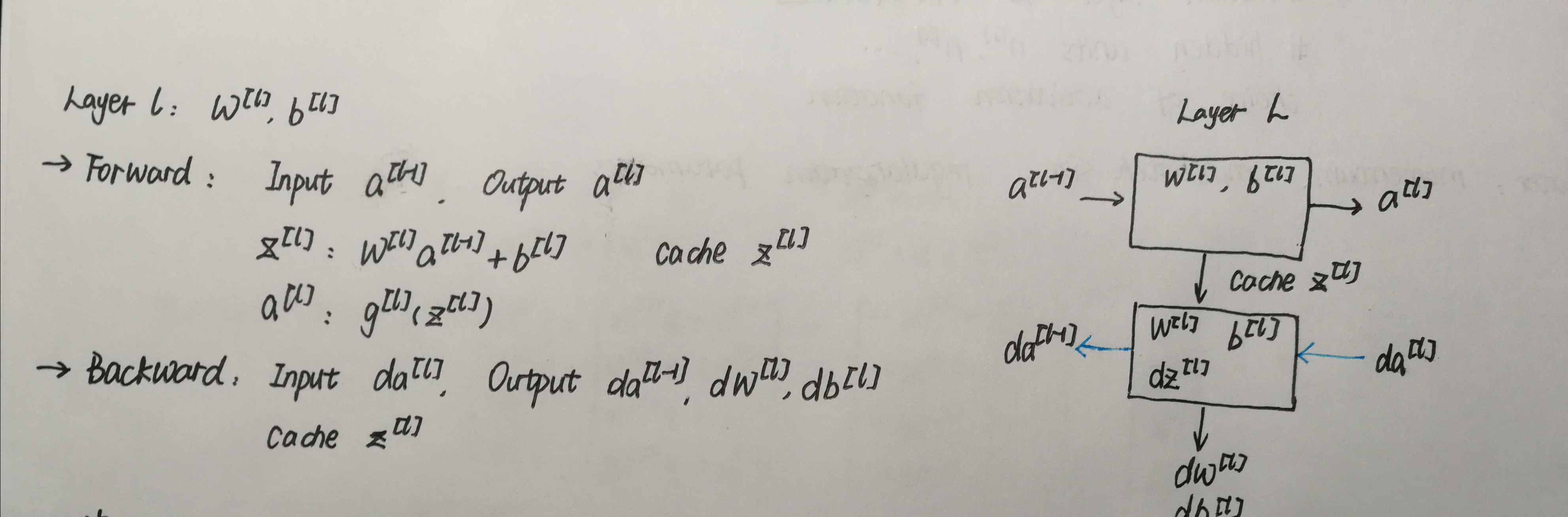
Forward propagation 前向传播
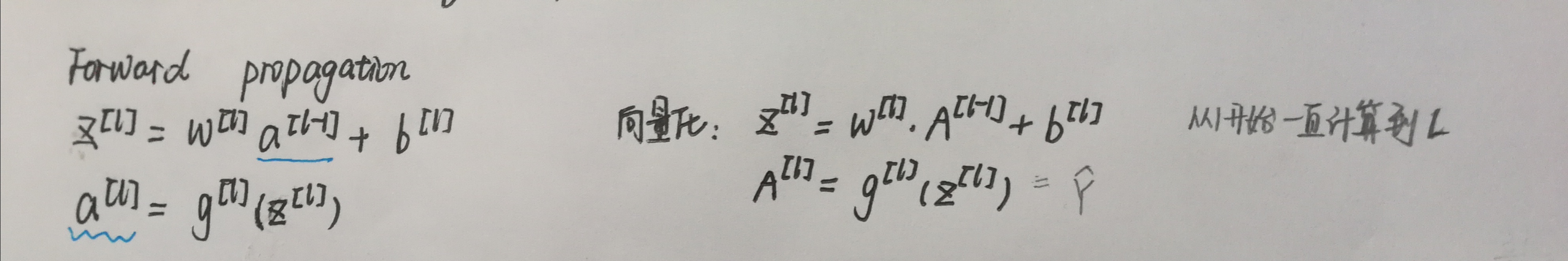
线性部分:
1 def linear_forward(A, W, b):
2 """
3 Implement the linear part of a layer's forward propagation.
4
5 Arguments:
6 A -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
7 W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
8 b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
9
10 Returns:
11 Z -- the input of the activation function, also called pre-activation parameter
12 cache -- a python dictionary containing "A", "W" and "b" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
13 """
14 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
15 Z=np.dot(W,A)+b
16 ### END CODE HERE ###
17
18 assert(Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
19 cache = (A, W, b)
20 return Z, cache
线性激活部分:
1 def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation): 2 """ 3 Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer 4 5 Arguments: 6 A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples) 7 W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer) 8 b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1) 9 activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu" 10 11 Returns: 12 A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value 13 cache -- a python dictionary containing "linear_cache" and "activation_cache"; 14 stored for computing the backward pass efficiently 15 """ 16 17 if activation == "sigmoid": 18 # Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache". 19 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 20 Z,linear_cache=linear_forward(A_prev, W, b) 21 A,activation_cache=sigmoid(Z) 22 ### END CODE HERE ### 23 24 elif activation == "relu": 25 # Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache". 26 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 27 Z,linear_cache=linear_forward(A_prev, W, b) 28 A,activation_cache=relu(Z) 29 ### END CODE HERE ### 30 31 assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1])) 32 cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache) 33 34 return A, cache
多层模型前向传播:
1 def L_model_forward(X, parameters): 2 """ 3 Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computation 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples) 7 parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep() 8 9 Returns: 10 AL -- last post-activation value 11 caches -- list of caches containing: 12 every cache of linear_relu_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-2) 13 the cache of linear_sigmoid_forward() (there is one, indexed L-1) 14 """ 15 caches = [] 16 A = X 17 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network 18 19 # Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list. 20 for l in range(1, L): 21 A_prev = A 22 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 23 A,cache=linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W'+str(l)], parameters['b'+str(l)], "relu") 24 caches.append(cache) 25 ### END CODE HERE ### 26 27 # Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list. 28 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 29 AL,cache=linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W'+str(L)], parameters['b'+str(L)], 'sigmoid') 30 caches.append(cache) 31 ### END CODE HERE ### 32 33 assert(AL.shape == (1, X.shape[1])) 34 35 return AL, caches
计算损失
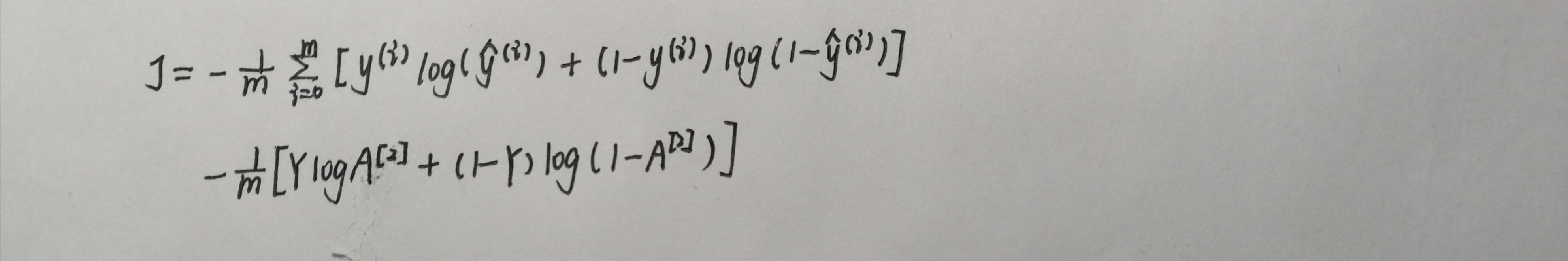
1 def compute_cost(AL, Y): 2 """ 3 Implement the cost function defined by equation (7). 4 5 Arguments: 6 AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples) 8 9 Returns: 10 cost -- cross-entropy cost 11 """ 12 m = Y.shape[1] 13 14 # Compute loss from aL and y. 15 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 lines of code) 16 cost =-np.sum(np.multiply(np.log(AL),Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - AL), 1 - Y)) / m 17 ### END CODE HERE ### 18 19 cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17). 20 assert(cost.shape == ()) 21 return cost
Backward propagation反向传播
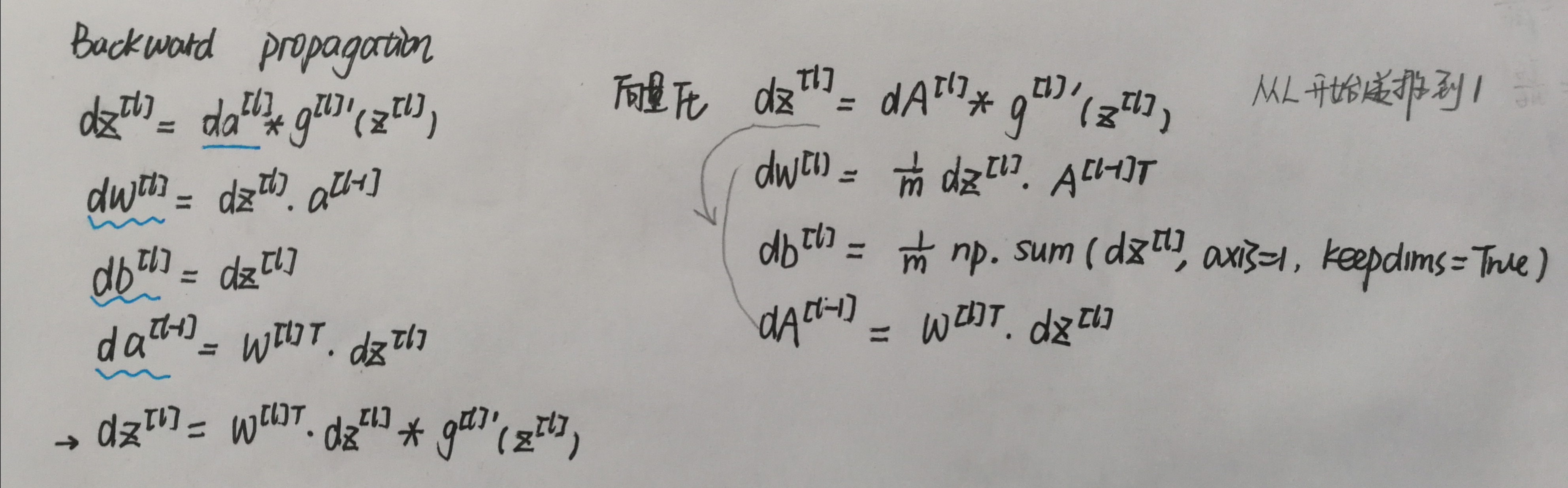
线性部分:
1 def linear_backward(dZ, cache): 2 """ 3 Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l) 4 5 Arguments: 6 dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l) 7 cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layer 8 9 Returns: 10 dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev 11 dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W 12 db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b 13 """ 14 A_prev, W, b = cache 15 m = A_prev.shape[1] 16 17 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code) 18 dW=np.dot(dZ,A_prev.T)/m 19 db=np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True)/m 20 dA_prev=np.dot(W.T, dZ) 21 ### END CODE HERE ### 22 23 assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape) 24 assert (dW.shape == W.shape) 25 assert (db.shape == b.shape) 26 27 return dA_prev, dW, db
线性激活部分:
1 def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer. 4 5 Arguments: 6 dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l 7 cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficiently 8 activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu" 9 10 Returns: 11 dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev 12 dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W 13 db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b 14 """ 15 linear_cache, activation_cache = cache 16 17 if activation == "relu": 18 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 19 dZ=relu_backward(dA, activation_cache) 20 dA_prev,dW,db=linear_backward(dZ,linear_cache) 21 ### END CODE HERE ### 22 23 elif activation == "sigmoid": 24 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 25 dZ=sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache) 26 dA_prev,dW,db=linear_backward(dZ,linear_cache) 27 ### END CODE HERE ### 28 29 dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache) 30 return dA_prev, dW, db
多层模型向后传播函数:
1 def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID group 4 5 Arguments: 6 AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward()) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat) 8 caches -- list of caches containing: 9 every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (it's caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2) 10 the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (it's caches[L-1]) 11 12 Returns: 13 grads -- A dictionary with the gradients 14 grads["dA" + str(l)] = ... 15 grads["dW" + str(l)] = ... 16 grads["db" + str(l)] = ... 17 """ 18 grads = {} 19 L = len(caches) # the number of layers 20 m = AL.shape[1] 21 Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL 22 23 # Initializing the backpropagation 24 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code) 25 dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL)) 26 current_cache = caches[L-1] 27 ### END CODE HERE ### 28 29 # Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"] 30 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 31 grads["dA" + str(L-1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, "sigmoid") 32 ### END CODE HERE ### 33 34 for l in reversed(range(L-1)): 35 # lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients. 36 # Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], caches". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)] 37 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines) 38 current_cache = caches[l] 39 dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache, "relu") 40 grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp 41 grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp 42 grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp 43 ### END CODE HERE ### 44 45 return grads
更新参数
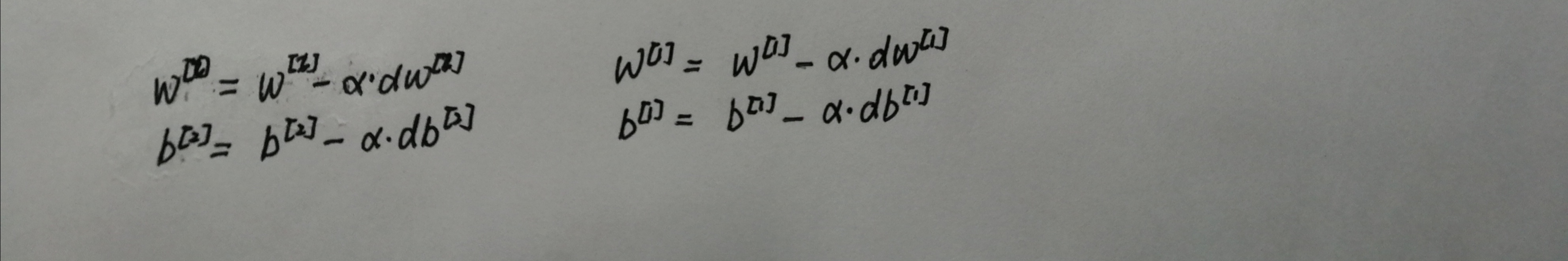
1 def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate): 2 """ 3 Update parameters using gradient descent 4 5 Arguments: 6 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters 7 grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backward 8 9 Returns: 10 parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters 11 parameters["W" + str(l)] = ... 12 parameters["b" + str(l)] = ... 13 """ 14 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network 15 16 # Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop. 17 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code) 18 for l in range(L): 19 parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*grads['dW'+str(l+1)] 20 parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*grads['db'+str(l+1)] 21 ### END CODE HERE ### 22 23 return parameters
搭建两层神经网络
1 def two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False): 2 """ 3 Implements a two-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID. 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- input data, of shape (n_x, number of examples) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples) 8 layers_dims -- dimensions of the layers (n_x, n_h, n_y) 9 num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop 10 learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule 11 print_cost -- If set to True, this will print the cost every 100 iterations 12 13 Returns: 14 parameters -- a dictionary containing W1, W2, b1, and b2 15 """ 16 np.random.seed(1) 17 grads = {} 18 costs = [] # to keep track of the cost 19 m = X.shape[1] # number of examples 20 (n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims 21 22 # Initialize parameters dictionary, by calling one of the functions you'd previously implemented 23 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code) 24 parameters=initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y) 25 ### END CODE HERE ### 26 27 # Get W1, b1, W2 and b2 from the dictionary parameters. 28 W1 = parameters["W1"] 29 b1 = parameters["b1"] 30 W2 = parameters["W2"] 31 b2 = parameters["b2"] 32 33 # Loop (gradient descent) 34 for i in range(0, num_iterations): 35 36 # Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Inputs: "X, W1, b1". Output: "A1, cache1, A2, cache2". 37 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 38 A1,cache1=linear_activation_forward(X, W1, b1, 'relu') 39 A2,cache2=linear_activation_forward(A1, W2, b2, 'sigmoid') 40 ### END CODE HERE ### 41 42 # Compute cost 43 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code) 44 cost=compute_cost(A2, Y) 45 ### END CODE HERE ### 46 47 # Initializing backward propagation 48 dA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - A2)) 49 50 # Backward propagation. Inputs: "dA2, cache2, cache1". Outputs: "dA1, dW2, db2; also dA0 (not used), dW1, db1". 51 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 52 dA1,dW2,db2=linear_activation_backward(dA2, cache2, 'sigmoid') 53 dA0,dW1,db1=linear_activation_backward(dA1, cache1, 'relu') 54 ### END CODE HERE ### 55 56 # Set grads['dWl'] to dW1, grads['db1'] to db1, grads['dW2'] to dW2, grads['db2'] to db2 57 grads['dW1'] = dW1 58 grads['db1'] = db1 59 grads['dW2'] = dW2 60 grads['db2'] = db2 61 62 # Update parameters. 63 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line of code) 64 parameters=update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate) 65 ### END CODE HERE ### 66 67 # Retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2 from parameters 68 W1 = parameters["W1"] 69 b1 = parameters["b1"] 70 W2 = parameters["W2"] 71 b2 = parameters["b2"] 72 73 # Print the cost every 100 training example 74 if print_cost and i % 100 == 0: 75 print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost))) 76 costs.append(cost) 77 78 # plot the cost 79 plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs)) 80 plt.ylabel('cost') 81 plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') 82 plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate)) 83 plt.show() 84 return parameters
搭建多层神经网络
1 def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False): #lr was 0.009 2 """ 3 Implements a L-layer neural network: [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID. 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- data, numpy array of shape (number of examples, num_px * num_px * 3) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples) 8 layers_dims -- list containing the input size and each layer size, of length (number of layers + 1). 9 learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule 10 num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop 11 print_cost -- if True, it prints the cost every 100 steps 12 13 Returns: 14 parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict. 15 """ 16 np.random.seed(1) 17 costs = [] # keep track of cost 18 19 # Parameters initialization. 20 ### START CODE HERE ### 21 parameters=initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims) 22 ### END CODE HERE ### 23 24 # Loop (gradient descent) 25 for i in range(0, num_iterations): 26 27 # Forward propagation: [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. 28 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code) 29 AL,caches=L_model_forward(X, parameters) 30 ### END CODE HERE ### 31 32 # Compute cost. 33 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code) 34 cost=compute_cost(AL, Y) 35 ### END CODE HERE ### 36 37 # Backward propagation. 38 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code) 39 grads=L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches) 40 ### END CODE HERE ### 41 42 # Update parameters. 43 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code) 44 parameters=update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate) 45 ### END CODE HERE ### 46 47 # Print the cost every 100 training example 48 if print_cost and i % 100 == 0: 49 print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" % (i, cost)) 50 costs.append(cost) 51 52 # plot the cost 53 plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs)) 54 plt.ylabel('cost') 55 plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') 56 plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate)) 57 plt.show() 58 59 return parameters
预测
1 def predict(X, y, parameters): 2 """ 3 该函数用于预测L层神经网络的结果,当然也包含两层 4 参数: 5 X - 测试集 6 y - 标签 7 parameters - 训练模型的参数 8 返回: 9 p - 给定数据集X的预测 10 """ 11 m = X.shape[1] 12 n = len(parameters) // 2 # 神经网络的层数 13 p = np.zeros((1,m)) 14 15 #根据参数前向传播 16 probas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters) 17 18 for i in range(0, probas.shape[1]): 19 p[0,i] = 1 if probas[0,i] > 0.5 else 0 20 21 print("准确度为: " + str(float(np.sum((p == y))/m))) 22 return p
对搭建的神经网络进行预测:
1 #准备数据 2 train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_data() 3 4 # Reshape the training and test examples 5 train_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T # The "-1" makes reshape flatten the remaining dimensions 6 test_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T 7 8 # Standardize data to have feature values between 0 and 1. 9 train_x = train_x_flatten / 255 10 test_x = test_x_flatten / 255
1 #对两层神经网络进行预测 2 parameters1 = two_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims = (12288, 7, 1), num_iterations = 2500, print_cost=True) 3 pred_test1=predict(test_x, test_y, parameters1) 4 5 #对多层神经网络进行预测 6 parameters2 = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims=(12288,20,7,5,1), num_iterations=250, print_cost=True) 7 pred_test2=predict(test_x, test_y, parameters2)
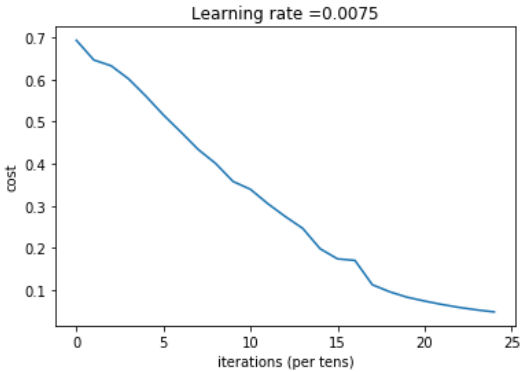
两层神经网络,精确率72%
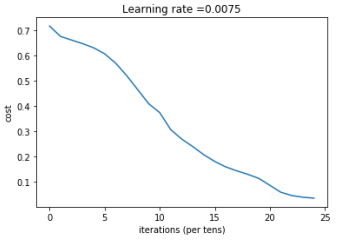
多层神经网络,精确率78%