要求
- 给定一个仅包含数字
2-9的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合 - 1 不对应任何字母
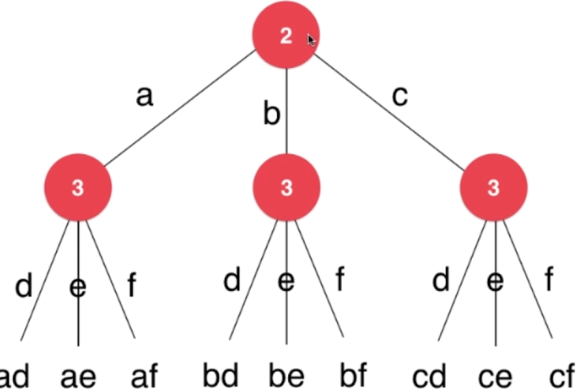

示例
- 输入:“23”
- 输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"]
思路
- 递归向后一位一位生成所有可能字符串
- s(digits)是digits所能生成的字符串
- letter(digits[0])是按键digits[0]对应的字符

实现
- res作为类的私有成员变量
- 调试代码:30,36,45,49

1 #include <vector> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <assert.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 class Solution { 9 10 private: 11 const string letterMap[10] = { 12 " ", 13 "", 14 "abc", 15 "def", 16 "ghi", 17 "jkl", 18 "mno", 19 "pqrs", 20 "tuv", 21 "wxyz" 22 }; 23 24 vector<string> res; 25 // 处理第index位数字 26 // s保存digits[0...index-1]生成的字符串 27 // 找到和digits[index]匹配的字母,获得digits[0...index]生成的解 28 void findCombination(const string &digits, int index, const string &s){ 29 30 cout<<index<<" : "<<s<<endl; 31 32 // 终止条件 33 if( index == digits.size() ){ 34 // s是一个解,保存 35 res.push_back(s); 36 cout<<"get "<<s<<" , return"<<endl; 37 return; 38 } 39 40 char c = digits[index]; 41 assert( c >= '0' && c <= '9' && c != '1' ); 42 string letters = letterMap[c-'0']; 43 44 for( int i = 0 ; i < letters.size() ; i ++ ){ 45 cout<<"digits["<<index<<"] = "<<c<<" , use "<<letters[i]<<endl; 46 // 处理第index+1位数字 47 findCombination(digits, index + 1, s + letters[i] ); 48 } 49 cout<<"digits["<<index<<"] = "<<c<<" complete, return"<<endl; 50 return; 51 } 52 public: 53 vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) { 54 55 // 初始化 56 res.clear(); 57 // 边界情况 58 if( digits == "" ) 59 return res; 60 61 findCombination(digits, 0, ""); 62 63 return res; 64 } 65 }; 66 67 int main(){ 68 69 vector<string> res = Solution().letterCombinations("23"); 70 for( int i = 0 ; i < res.size() ; i ++ ) 71 cout<<res[i]<<endl; 72 73 return 0; 74 }
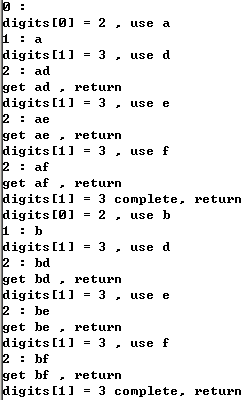
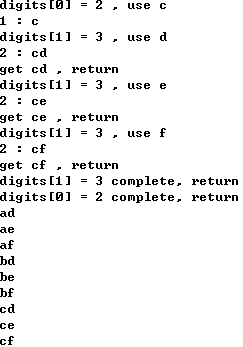
总结
- 本质是回溯(递归调用到底后,返回上一层,继续调用,直到根节点的所有可能性调用完成)
- 回溯是一种算法思想,可通过递归实现
- 和多重循环的区别在于,要处理的字符长度未知
- 动态规划的本质是在回溯的基础上进行改进,提高效率
- 复杂度:3^n(指数级O(2^n),n个字母,每个数字3个字母)
- 暴力枚举解法,效率低,家用计算机n<20
相关
- 93 Restore IP Addresses
- 131 Palindrome Partitioning
参考
递归与回溯有什么区别?怎么区分?
