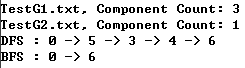- 应用:交通运输、社交网络、互联网、工作安排、程序状态执行
- 分类:无向图、有向图;无权图,有权图
- 简单图:没有自环边、平行边
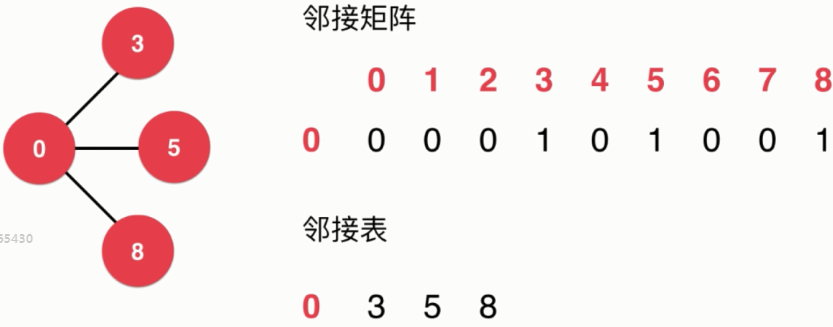
- 表示方式:邻接表(适合稀疏图)、邻接矩阵(适合稠密图)
- 遍历临边:邻接表直接得到,邻接矩阵O(v),v为顶点个数
main.cpp

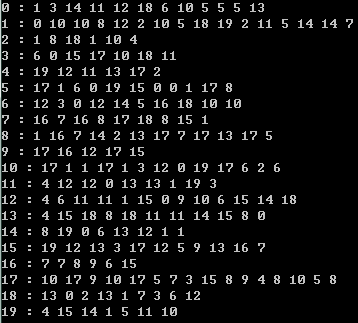
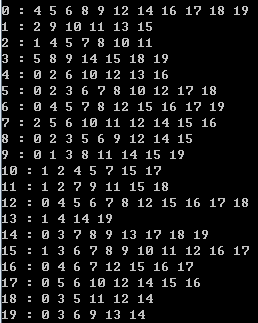
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SparseGraph.h" 3 #include "DenseGraph.h" 4 #include <sys/time.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int main(){ 9 int N = 20; 10 int M = 100; 11 srand( time(NULL) ); 12 13 // Sparse Graph 14 SparseGraph g1(N, false); 15 for( int i = 0 ; i < M ; i ++ ){ 16 int a = rand()%N; 17 int b = rand()%N; 18 g1.addEdge( a , b ); 19 } 20 // O(E) 21 for( int v = 0 ; v < N ; v ++ ){ 22 cout << v << " : "; 23 SparseGraph::adjIterator adj( g1 , v ); 24 for( int w = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; w = adj.next() ) 25 cout << w << " "; 26 cout << endl; 27 } 28 cout << endl; 29 30 // Dense Graph 31 DenseGraph g2(N, false); 32 for( int i = 0 ; i < M ; i ++ ){ 33 int a = rand()%N; 34 int b = rand()%N; 35 g2.addEdge( a , b ); 36 } 37 // O(V^2) 38 for( int v = 0 ; v < N ; v ++ ){ 39 cout << v << " : "; 40 DenseGraph::adjIterator adj( g2, v ); 41 for( int w = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; w = adj.next() ) 42 cout<<w<<" "; 43 cout<<endl; 44 } 45 return 0; 46 }
SparseGraph.h(稀疏图)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cassert> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 // 稀疏图 - 邻接表 8 class SparseGraph{ 9 private: 10 int n,m; 11 bool directed; 12 vector<vector<int> > g; 13 14 public: 15 SparseGraph( int n, bool directed ){ 16 assert( n >= 0 ); 17 this->n = n; 18 this->m = 0; 19 this->directed = directed; 20 // g初始化为n个空的vector,表示每个g[i]都为空,即没有任何边 21 g = vector<vector<int> >(n,vector<int>()); 22 } 23 24 ~SparseGraph(){ } 25 26 int V(){ return n;} 27 int E(){ return m;} 28 29 void addEdge( int v, int w){ 30 assert( v >= 0 && v < n ); 31 assert( w >= 0 && w < n ); 32 33 g[v].push_back(w); 34 // 避免自环边,允许有平行边 35 if( v != w && !directed ) 36 g[w].push_back(v); 37 m ++; 38 } 39 40 // O(n) 41 bool hasEdge( int v , int w ){ 42 assert( v >= 0 && v < n ); 43 assert( w >= 0 && w < n ); 44 for( int i = 0 ; i < g[v].size() ; i ++ ) 45 if( g[v][i] == w ) 46 return true; 47 return false; 48 } 49 // 临边迭代器,传入一个图和一个顶点 50 // 迭代在这个图中和这个顶点相连的所有顶点 51 class adjIterator{ 52 private: 53 SparseGraph &G; 54 int v; 55 int index; 56 57 public: 58 adjIterator(SparseGraph &graph, int v):G(graph){ 59 this->v = v; 60 this->index = 0; 61 } 62 int begin(){ 63 index = 0; 64 if( G.g[v].size() ) 65 return G.g[v][index]; 66 return -1; 67 } 68 int next(){ 69 index ++; 70 if( index < G.g[v].size() ) 71 return G.g[v][index]; 72 return -1; 73 } 74 bool end(){ 75 return index >= G.g[v].size(); 76 } 77 }; 78 };
DenseGraph.h(稠密图)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cassert> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 // 稠密图 - 邻接矩阵 8 class DenseGraph{ 9 private: 10 int n,m; 11 bool directed; 12 vector<vector<bool> > g; 13 14 public: 15 DenseGraph( int n , bool directed ){ 16 this->n = n; 17 this->m = 0; 18 this->directed = directed; 19 for( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) 20 g.push_back( vector<bool>(n,false) ); 21 } 22 ~DenseGraph(){ 23 24 } 25 int V(){ return n;} 26 int E(){ return m;} 27 28 void addEdge( int v , int w ){ 29 assert( v >= 0 && v < n ); 30 assert( w >= 0 && w < n ); 31 if( hasEdge( v,w ) ) 32 return; 33 g[v][w] = true; 34 if( !directed ) 35 g[w][v] = true; 36 m ++; 37 } 38 39 bool hasEdge( int v , int w ){ 40 assert( v >= 0 && v < n ); 41 assert( w >= 0 && w < n ); 42 return g[v][w]; 43 } 44 // 临边迭代器,传入一个图和一个顶点 45 // 迭代在这个图中和这个顶点相连的所有顶点 46 class adjIterator{ 47 private: 48 DenseGraph &G; 49 int v; 50 int index; 51 public: 52 adjIterator(DenseGraph &graph, int v):G(graph){ 53 assert( v >= 0 && v < G.n ); 54 this->v = v; 55 this->index = -1; 56 } 57 ~adjIterator(){} 58 // 返回图G中与顶点v相连的第一个顶点 59 int begin(){ 60 // 索引从-1开始,因为每次遍历都需要调用一次next() 61 index = -1; 62 return next(); 63 } 64 // 返回图G中与顶点v相连接的下一个顶点 65 int next(){ 66 // 从当前index开始向后搜索,直到找到一个g[v][index]为true 67 for( index += 1 ; index < G.V() ; index ++ ) 68 if( G.g[v][index] ) 69 return index; 70 return -1; 71 } 72 // 查看是否已经迭代完了图G中与v相连的所有顶点 73 bool end(){ 74 return index >= G.V(); 75 } 76 }; 77 };
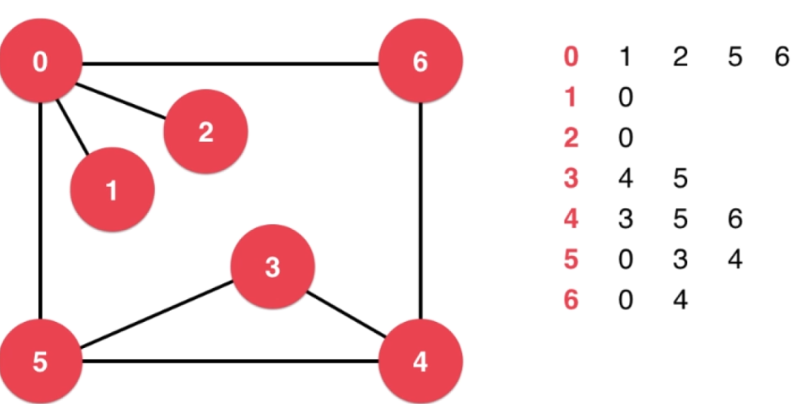
- 遍历:
- 深度优先:0-1-2-5-3-4-6,通过深度优先遍历可求图的连通分量
- 广度优先:0-1-2-5-6-3-4,通过广度优先遍历可求图的最短路径
main.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SparseGraph.h" 3 #include "DenseGraph.h" 4 #include "ReadGraph.h" 5 #include "Component.h" 6 #include "Path.h" 7 #include "ShortestPath.h" 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 int main(){ 12 // TestG1.txt 13 string filename1 = "testG1.txt"; 14 SparseGraph g1 = SparseGraph( 13 , false ); 15 ReadGraph<SparseGraph> readGraph1( g1, filename1); 16 Component<SparseGraph> component1(g1); 17 cout<<"TestG1.txt, Component Count: "<<component1.count()<<endl; 18 19 // TestG2.txt 20 string filename2 = "testG2.txt"; 21 DenseGraph g2 = DenseGraph( 7 , false ); 22 ReadGraph<DenseGraph> readGraph2( g2, filename2); 23 Component<DenseGraph> component2(g2); 24 cout<<"TestG2.txt, Component Count: "<<component2.count()<<endl; 25 26 Path<DenseGraph> dfs(g2,0); 27 cout<<"DFS : "; 28 dfs.showPath(6); 29 30 ShortestPath<DenseGraph> bfs(g2,0); 31 cout<<"BFS : "; 32 bfs.showPath(6); 33 34 return 0; 35 }
Path.h(寻路)

1 #include <vector> 2 #include <stack> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cassert> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 template <typename Graph> 9 class Path{ 10 private: 11 Graph &G; 12 int s; 13 bool* visited; 14 int* from; 15 16 void dfs( int v ){ 17 // 记录是否被遍历过 18 visited[v] = true; 19 // adjIterator是Graph中的类型,而非成员变量 20 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G, v); 21 for( int i = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; i = adj.next() ){ 22 if( !visited[i] ){ 23 from[i] = v; 24 dfs(i); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 public: 30 Path(Graph &graph, int s):G(graph){ 31 32 assert( s >= 0 && s < G.V() ); 33 34 visited = new bool[G.V()]; 35 from = new int[G.V()]; 36 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){ 37 visited[i] = false; 38 from[i] = -1; 39 } 40 this->s = s; 41 // 寻路算法 42 dfs(s); 43 } 44 ~Path(){ 45 delete [] visited; 46 delete [] from; 47 } 48 // s到w是否有路径 49 bool hasPath(int w){ 50 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 51 return visited[w]; 52 } 53 // s到w的具体路径 54 void path(int w, vector<int> &vec){ 55 // 倒推,用栈 56 stack<int> s; 57 int p = w; 58 while( p != -1){ 59 s.push(p); 60 p = from[p]; 61 } 62 vec.clear(); 63 while( !s.empty()){ 64 vec.push_back( s.top() ); 65 s.pop(); 66 } 67 } 68 // 显示路径 69 void showPath(int w){ 70 vector<int> vec; 71 path( w , vec ); 72 for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){ 73 cout<<vec[i]; 74 if( i == vec.size() -1 ) 75 cout<<endl; 76 else 77 cout<<" -> "; 78 } 79 } 80 };
component.h(求连通分量)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cassert> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 // 求无权图的连通分量 7 template <typename Graph> 8 class Component{ 9 private: 10 Graph &G; 11 bool *visited; 12 int ccount; 13 // 是否连通 14 int *id; 15 16 // 图的深度优先遍历 17 // 邻接表:O(V+E) 18 // 邻接矩阵:O(V^2) 19 void dfs( int v ){ 20 // 记录是否被遍历过 21 visited[v] = true; 22 id[v] = ccount; 23 // adjIterator是Graph中的类型,而非成员变量 24 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G, v); 25 for( int i = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; i = adj.next() ){ 26 if( !visited[i] ) 27 dfs(i); 28 } 29 } 30 31 public: 32 // 求出无权图的连通分量 33 Component(Graph &graph):G(graph){ 34 // 初始化 35 visited = new bool[G.V()]; 36 id = new int[G.V()]; 37 ccount = 0; 38 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){ 39 visited[i] = false; 40 id[i] = -1; 41 } 42 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ) 43 if( !visited[i] ){ 44 dfs(i); 45 // 记录连通分量 46 ccount ++; 47 } 48 } 49 ~Component(){ 50 delete[] visited; 51 delete[] id; 52 } 53 54 // 返回图的连通分量 55 int count(){ 56 return ccount; 57 } 58 59 // 查询点v和点w是否连通 60 bool isConnected( int v , int w ){ 61 // 是否越界 62 assert( v >= 0 && v < G.V() ); 63 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 64 return id[v] == id[w]; 65 } 66 };
ShortestPath.h(最短路径)

1 #include <vector> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <cassert> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 template <typename Graph> 10 class ShortestPath{ 11 private: 12 Graph &G; // 图的引用 13 int s; // 起始点 14 bool *visited; // 记录遍历过程中节点是否被访问 15 int *from; // 记录路径,from[i]表示查找路径上i的上一个节点 16 int *ord; // 从s到每个节点的最短距离 17 18 public: 19 ShortestPath(Graph &graph, int s):G(graph){ 20 assert( s >= 0 && s < graph.V() ); 21 visited = new bool[graph.V()]; 22 from = new int[graph.V()]; 23 ord = new int[graph.V()]; 24 for( int i = 0 ; i < graph.V() ; i ++ ){ 25 visited[i] = false; 26 from[i] = -1; 27 ord[i] = -1; 28 } 29 this -> s = s; 30 31 // 无向图最短路径算法,从s开始广度优先遍历整张图 32 // 按距离初始节点的距离遍历(层序遍历) 33 // 邻接表:O(V+E) 34 // 邻接矩阵:O(V^2) 35 queue<int> q; 36 q.push( s ); 37 visited[s] = true; 38 ord[s] = 0; 39 while( !q.empty() ){ 40 int v = q.front(); 41 q.pop(); 42 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G, v); 43 for( int i = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; i = adj.next() ) 44 // 已经加入过队列的元素,不需重复入队 45 if( !visited[i] ){ 46 q.push(i); 47 // 维护i节点的信息 48 visited[i] = true; 49 from[i] = v; 50 ord[i] = ord[v] + 1; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 ~ShortestPath(){ 56 delete [] visited; 57 delete [] from; 58 delete [] ord; 59 } 60 61 // 查询s到w是否有路径 62 bool hasPath(int w){ 63 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 64 return visited[w]; 65 } 66 67 // 查询s到w点的路径,存放在vec中 68 void path(int w , vector<int> &vec){ 69 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 70 stack<int> s; 71 // 通过from数组逆向查找从s到w的路径,存放在栈中 72 int p = w; 73 while( p != -1 ){ 74 s.push(p); 75 p = from[p]; 76 } 77 vec.clear(); 78 while( !s.empty()){ 79 vec.push_back( s.top() ); 80 s.pop(); 81 } 82 } 83 84 // 打印出从s到w的路径 85 void showPath(int w){ 86 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 87 88 vector<int> vec; 89 path(w, vec); 90 for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){ 91 cout<<vec[i]; 92 if( i == vec.size()-1 ) 93 cout<<endl; 94 else 95 cout<<" -> "; 96 } 97 } 98 99 // 查看从s到w的路径长度 100 int length(int w){ 101 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 102 return ord[w]; 103 } 104 };
ReadGraph.h(读文件)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <fstream> 4 #include <sstream> 5 #include <cassert> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 template <typename Graph> 10 class ReadGraph{ 11 public: 12 // 从文件filename中读取图的信息,存进graph中 13 ReadGraph(Graph &graph, const string &filename){ 14 ifstream file(filename); 15 string line; 16 int V,E; 17 18 assert(file.is_open()); 19 20 // 读取图中第一行节点数和边数 21 assert(getline(file,line)); 22 stringstream ss(line); 23 ss>>V>>E; 24 25 assert( V == graph.V() ); 26 27 // 读取每一条边的信息 28 for( int i = 0 ; i < E ; i ++ ){ 29 30 assert( getline(file, line) ); 31 stringstream ss(line); 32 33 int a,b; 34 ss>>a>>b; 35 assert( a >= 0 && a < V ); 36 assert( b >= 0 && b < V ); 37 graph.addEdge( a , b ); 38 } 39 } 40 };
testG1.txt
13 13
0 5
4 3
0 1
9 12
6 4
5 4
0 2
11 12
9 10
0 6
7 8
9 11
5 3
testG2.txt
7 8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
3 4
3 5
4 5
4 6