概述
- 属于行为型
- 程序需要按顺序处理多个请求时
- 程序需要使用不同方式处理不同种类的请求,且请求类型和顺序预先未知时,将多个处理者连成一条链,接到请求后,询问每个处理者是否能对其进行处理
- 沿责任链传递请求,直到有一个对象处理为止。使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系

- 一个请求可能会被多个对象处理,但每个请求在运行时只能有一个接受者,如果显式指定,将必不可少地带来请求者与接受者的紧耦合
- 如何使请求的发送者不需要指定具体的接受者?让请求的接受者自己在运行时决定来处理请求,从而使二者解耦
- 使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系,将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止
- 使用多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系,将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递请求,知道有一个对象处理它为止
- Chain of Responsibility 模式的应用场合在于“一个请求可能有多个接受者,但最后真正的接受者只有一个”,这时候请求发送者与接受者的耦合有可能出现“变化脆弱”的症状,职责链的目的就是将二者解耦,从而更好地应对变化
- 应用了Chain of Responsibility 模式后,对象的职责分派将更具灵活性,可在运行时动态添加/修改请求的处理职责
- 如果请求传递到职责链的末尾仍得不到处理,应该有一个合理的缺省机制,这也是每一个接收对象的职责,而不是发出请求的对象的责任
场景
- 拨打技术支持电话时,多名接听人员接力处理
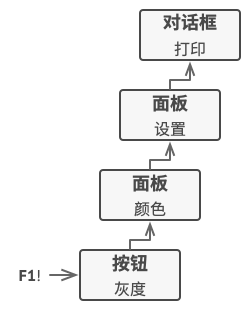
- 为活动的GUI元素显示上下文帮助信息。当用户鼠标移动到某个元素并按下F1键时,程序检测到指针下的组件并对其发送帮助请求,该请求不断向上传递到该元素的所有容器,直到某个元素能显示帮助信息
- Struct2的拦截器
- jsp servlet 的 Filter
- Tomca 对 Encoding 的处理
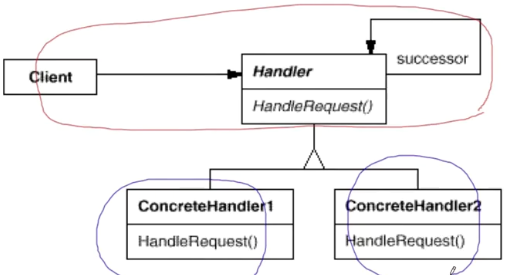
结构
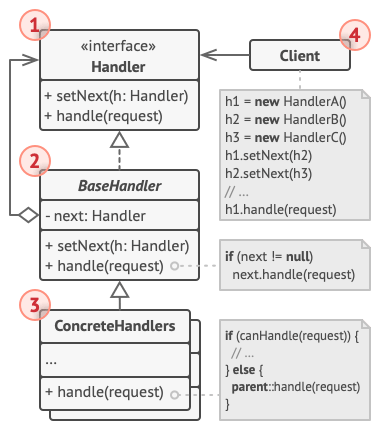
- 处理者:声明了所有具体处理者的通用接口
- 基础处理者:放置所有处理者共用的代码
- 具体处理者:处理请求的实际代码,处理者接到具体请求后,决定是否处理,是否沿着链传递请求
- 客户端:根据程序逻辑一次性或动态地生成链,请求可以发给链上的任一个处理者
示例1
ChainofResponsibility.cpp
 View Code
View Code- 举例:windows界面
- 25行:用链表实现链,基类的多态指针指向自身,形成多态链表
- 38-45行:整体处理
示例2
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Request{ 7 public: 8 string m_strContent; 9 int m_nNumber; 10 }; 11 class Manager{ 12 protected: 13 Manager* manager; 14 string name; 15 public: 16 Manager(string temp){ 17 name = temp; 18 } 19 void SetSuccessor(Manager* temp){ 20 manager = temp; 21 } 22 virtual void GetRequest(Request* request)=0; 23 }; 24 class CommonManager:public Manager{ 25 public: 26 CommonManager(string strTemp):Manager(strTemp){} 27 virtual void GetRequest(Request* request){ 28 if(request->m_nNumber>=0 && request->m_nNumber<10){ 29 cout<<name<<"处理了"<<request->m_nNumber<<"个请求"<<endl; 30 }else{ 31 manager->GetRequest(request); 32 } 33 } 34 }; 35 class MajorDomo:public Manager{ 36 public: 37 MajorDomo(string name):Manager(name){} 38 virtual void GetRequest(Request* request){ 39 if(request->m_nNumber>=10){ 40 cout<<name<<"处理了"<<request->m_nNumber<<"个请求"<<endl; 41 } 42 } 43 }; 44 int main(){ 45 Manager* common = new CommonManager("张经理"); 46 Manager* major = new MajorDomo("李总监"); 47 common->SetSuccessor(major); 48 Request* req = new Request(); 49 50 req->m_nNumber = 33; 51 common->GetRequest(req); 52 53 req->m_nNumber=3; 54 common->GetRequest(req); 55 56 return 0; 57 }

示例3


1 // 处理者接口声明了一个创建处理者链的方法。还声明了一个执行请求的方法。 2 interface ComponentWithContextualHelp is 3 method showHelp() 4 5 6 // 简单组件的基础类。 7 abstract class Component implements ComponentWithContextualHelp is 8 field tooltipText: string 9 10 // 组件容器在处理者链中作为“下一个”链接。 11 protected field container: Container 12 13 // 如果组件设定了帮助文字,那它将会显示提示信息。如果组件没有帮助文字 14 // 且其容器存在,那它会将调用传递给容器。 15 method showHelp() is 16 if (tooltipText != null) 17 // 显示提示信息。 18 else 19 container.showHelp() 20 21 22 // 容器可以将简单组件和其他容器作为其子项目。链关系将在这里建立。该类将从 23 // 其父类处继承 showHelp(显示帮助)的行为。 24 abstract class Container extends Component is 25 protected field children: array of Component 26 27 method add(child) is 28 children.add(child) 29 child.container = this 30 31 32 // 原始组件应该能够使用帮助操作的默认实现... 33 class Button extends Component is 34 // ... 35 36 // 但复杂组件可能会对默认实现进行重写。如果无法以新的方式来提供帮助文字, 37 // 那组件总是还能调用基础实现的(参见 Component 类)。 38 class Panel extends Container is 39 field modalHelpText: string 40 41 method showHelp() is 42 if (modalHelpText != null) 43 // 显示包含帮助文字的模态窗口。 44 else 45 super.showHelp() 46 47 // ...同上... 48 class Dialog extends Container is 49 field wikiPageURL: string 50 51 method showHelp() is 52 if (wikiPageURL != null) 53 // 打开百科帮助页面。 54 else 55 super.showHelp() 56 57 58 // 客户端代码。 59 class Application is 60 // 每个程序都能以不同方式对链进行配置。 61 method createUI() is 62 dialog = new Dialog("预算报告") 63 dialog.wikiPageURL = "http://..." 64 panel = new Panel(0, 0, 400, 800) 65 panel.modalHelpText = "本面板用于..." 66 ok = new Button(250, 760, 50, 20, "确认") 67 ok.tooltipText = "这是一个确认按钮..." 68 cancel = new Button(320, 760, 50, 20, "取消") 69 // ... 70 panel.add(ok) 71 panel.add(cancel) 72 dialog.add(panel) 73 74 // 想象这里会发生什么。 75 method onF1KeyPress() is 76 component = this.getComponentAtMouseCoords() 77 component.showHelp()
示例4

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 /** 5 * The Handler interface declares a method for building the chain of handlers. 6 * It also declares a method for executing a request. 7 */ 8 class Handler { 9 public: 10 virtual Handler *SetNext(Handler *handler) = 0; 11 virtual std::string Handle(std::string request) = 0; 12 }; 13 /** 14 * The default chaining behavior can be implemented inside a base handler class. 15 */ 16 class AbstractHandler : public Handler { 17 /** 18 * @var Handler 19 */ 20 private: 21 Handler *next_handler_; 22 23 public: 24 AbstractHandler() : next_handler_(nullptr) { 25 } 26 Handler *SetNext(Handler *handler) override { 27 this->next_handler_ = handler; 28 // Returning a handler from here will let us link handlers in a convenient 29 // way like this: 30 // $monkey->setNext($squirrel)->setNext($dog); 31 return handler; 32 } 33 std::string Handle(std::string request) override { 34 if (this->next_handler_) { 35 return this->next_handler_->Handle(request); 36 } 37 38 return {}; 39 } 40 }; 41 /** 42 * All Concrete Handlers either handle a request or pass it to the next handler 43 * in the chain. 44 */ 45 class MonkeyHandler : public AbstractHandler { 46 public: 47 std::string Handle(std::string request) override { 48 if (request == "Banana") { 49 return "Monkey: I'll eat the " + request + ". "; 50 } else { 51 return AbstractHandler::Handle(request); 52 } 53 } 54 }; 55 class SquirrelHandler : public AbstractHandler { 56 public: 57 std::string Handle(std::string request) override { 58 if (request == "Nut") { 59 return "Squirrel: I'll eat the " + request + ". "; 60 } else { 61 return AbstractHandler::Handle(request); 62 } 63 } 64 }; 65 class DogHandler : public AbstractHandler { 66 public: 67 std::string Handle(std::string request) override { 68 if (request == "MeatBall") { 69 return "Dog: I'll eat the " + request + ". "; 70 } else { 71 return AbstractHandler::Handle(request); 72 } 73 } 74 }; 75 /** 76 * The client code is usually suited to work with a single handler. In most 77 * cases, it is not even aware that the handler is part of a chain. 78 */ 79 void ClientCode(Handler &handler) { 80 std::vector<std::string> food = {"Nut", "Banana", "Cup of coffee"}; 81 for (const std::string &f : food) { 82 std::cout << "Client: Who wants a " << f << "? "; 83 const std::string result = handler.Handle(f); 84 if (!result.empty()) { 85 std::cout << " " << result; 86 } else { 87 std::cout << " " << f << " was left untouched. "; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 /** 92 * The other part of the client code constructs the actual chain. 93 */ 94 int main() { 95 MonkeyHandler *monkey = new MonkeyHandler; 96 SquirrelHandler *squirrel = new SquirrelHandler; 97 DogHandler *dog = new DogHandler; 98 monkey->SetNext(squirrel)->SetNext(dog); 99 100 /** 101 * The client should be able to send a request to any handler, not just the 102 * first one in the chain. 103 */ 104 std::cout << "Chain: Monkey > Squirrel > Dog "; 105 ClientCode(*monkey); 106 std::cout << " "; 107 std::cout << "Subchain: Squirrel > Dog "; 108 ClientCode(*squirrel); 109 110 delete monkey; 111 delete squirrel; 112 delete dog; 113 114 return 0; 115 }
Chain: Monkey > Squirrel > Dog Client: Who wants a Nut? Squirrel: I'll eat the Nut. Client: Who wants a Banana? Monkey: I'll eat the Banana. Client: Who wants a Cup of coffee? Cup of coffee was left untouched. Subchain: Squirrel > Dog Client: Who wants a Nut? Squirrel: I'll eat the Nut. Client: Who wants a Banana? Banana was left untouched. Client: Who wants a Cup of coffee? Cup of coffee was left untouched.
参考
https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/chain-of-responsibility
