Hadoop设计模式–抽象类
在过去我们进行类的衍生中,使用的比较多的是接口。
接口的自由性和拓展性都是接口的比较重要的优势,因为耦合性的关系,我们都在尽量避免继承,但无可否认,抽象类在一定情况下同样拥有良好的使用效果。正如《JAVA编程思想》所述,每一个JAVA的特性都会拥有用武之地。
抽象层 重载
在抽象层进行类的重载可以有效减少在实现层进行重载的代码量,特别是对于抽象层延展比较多的代码。以下Demon截取自Hadoop HDFS FileSystem
public abstract class FileSystem extends Configured implements Closeable {
public abstract FSDataOutputStream create(Path f, //提取抽象方法,完整参数列表
FsPermission permission,
boolean overwrite,
int bufferSize,
short replication,
long blockSize,
Progressable progress) throws IOException;
public FSDataOutputStream create(Path f, //重载,调用抽象方法
boolean overwrite,
int bufferSize,
short replication,
long blockSize,
Progressable progress
) throws IOException {
return this.create(f, FsPermission.getDefault(),
overwrite, bufferSize, replication,
blockSize, progress);
}
public FSDataOutputStream create(Path f, ////重载,调用
boolean overwrite,
int bufferSize,
short replication,
long blockSize
) throws IOException {
return create(f, overwrite, bufferSize, replication, blockSize, null);
}
FileSystem下属子类应用于不同环境下的FileSystem
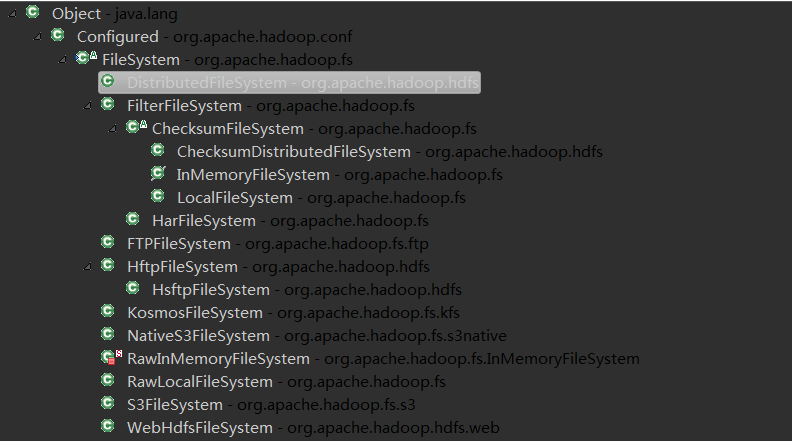
但对于Create方法FileSystem所有子类只需要实现在所属环境下的create完整参数方法,而不需要对create方法进行重载。
截取DistributeFileSystem
Public class DistributeFileSystem extends FileSystem { //子类只需要实现抽象方法
public FSDataOutputStream create(Path f, FsPermission permission,
boolean overwrite,
int bufferSize, short replication, long blockSize,
Progressable progress) throws IOException {
statistics.incrementWriteOps(1);
return new FSDataOutputStream
(dfs.create(getPathName(f), permission,
overwrite, true, replication, blockSize, progress, bufferSize),
statistics);
}
}