首先得先感谢 海边沫沫 的这篇文章,由于一些网站常常被关闭,在这里先收藏了。
SpringSide 3.1.4.3
是目前
SpringSide
的最新版本,也是完成度比较高的一个版本,用来做实际项目的开发应该丝毫不成问题。这里写一下使用该版本开发一个简单
Web
项目的全过程,当然,最重要的是我自己的一些心得体会。我的文章很长,只有耐下性子细看,才能体会个中三味。
第一步、下载
SpringSide 3.1.4.3 all-in-one
版。
这个过程太简单了,
SpringSide
的官方网站是
www.springside.org.cn
,去那里就可以下载了,
all-in-one
版当然是懒人们的不二选择。这里有一点很搞笑,该版本标的是
SpringSide 3.1.4.3
,但是下载后解压缩,解压缩出来的文件是
springside-3.1.4.2
,这可能是江南白衣的一点小小的失误,据我猜测,
3.1.4.3
较
3.1.4.1
的进步应该是加入了
jsp-api.jar
这一个库,希望白衣这次不要为了更改这个版本号上的失误而再推出一个新版本,如果真要推出新版本,怎么样也应该把我最近研究出来的多数据库的配置加进去。
第二步、安装
SpringSide
。
如果安装过
SpringSide
以前的版本,最好把用户目录下的
.m2
文件夹删掉,这个文件夹是
Maven
的本地仓库所在地,虽说
Maven
可以有效保证库文件不会发生版本冲突,但是删除这个文件夹会使安装过程加快,否则,
SpringSide
的安装过程会不停询问你是否覆盖某某文件。删除
.m2
文件夹后,运行
springside-3.1.4.2
目录下的
bin
目录中的
quickstart.bat
即可(前提条件是已经安装好了
JDK5
或以上版本,如果你的电脑中连
JDK
都没有,就别来趟
SpringSide
的浑水了)。
等待这个文件运行完,就可以看到
SpringSide 3
提供的三个示例项目
mini-web
、
mini-service
、
showcase
都运行起来了,这时你可以细细体会一下
SpringSide
实现的各种特性。
仔细察看
SpringSide
的
bin
目录,发现该版本提供的脚本更加明确和有用,如
start-db.bat
可以用来启动
Derby
数据库,
start-selenium.bat
用来启动
selenium server
,而
start-tomcat.bat
那就别说了,地球人都知道。
如果要想使用
SpringSide
来生成项目,还有一点点小工作要做,就是把
Maven
的
bin
目录加入到
PATH
环境变量中,如下图:

第三步,使用
SpringSide
生成项目。
运行
bin
目录下的
new-project.bat
即可,如下图:
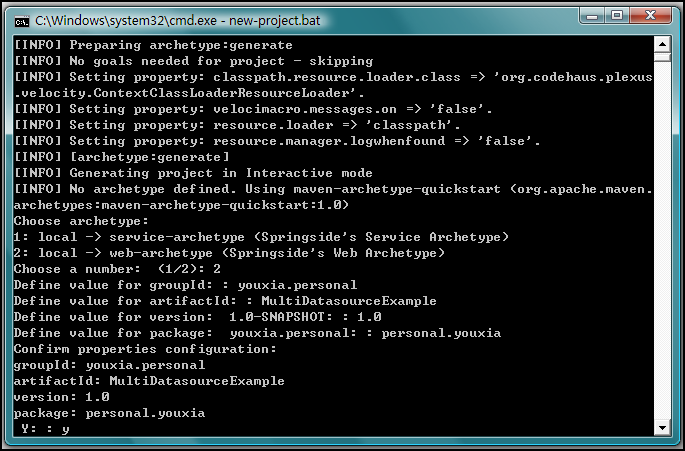
在创建项目的过程中,该脚本会提出一些问题,其中
groupId
指的是你的组织的名称,由于该项目由我私人贡献,纯属示范用,所以我填了
youxia.personal
,因此,在第
5
个问题上,我选择了
personal.you
作为我项目中的
package
的名字,这也是符合国际惯例的;
artifactId
指的是项目的名字,这里为
MultiDatasourceExample
,名字有点长,从名字就可以看出来我要示范多个数据源的配置。
第四步、启动
Eclipse
,导入项目。
生成的项目位于
SpringSide
目录下的
tools/generator/generated-project
目录下,下面是
Eclipse
的截图:
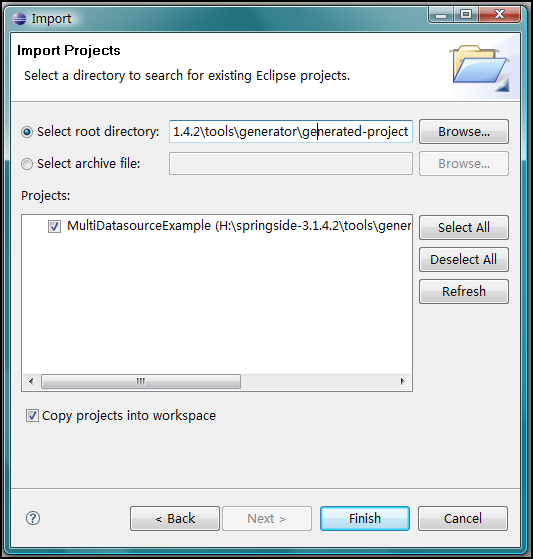
项目导入成功后,
Eclispe
资源管理器的截图:

可以看到,该项目一经导入,立即可用,一个烦人的红叉都没有,这也正说明了该版本是
SpringSide 3
的一个革命性版本,从该版本开始,
SpringSide 3
的易用性提高了不止一个档次。
Eclipse
推荐使用
3.4
及以上版本,因为在该版本中,对
Tomcat
服务器的管理更加方便,只需要在项目的快捷菜单中选择
Run On Server
,即可自动打开
Tomcat
服务器并部署项目,如下图:
这里有一点一定要注意,由于
SpringSide
生成的项目默认使用的是
Derby
数据库,所以要想成功运行项目,必须先启动
Derby
数据库,还记得前面提到的
start-db.bat
吗?运行它!然后运行该项目的
bin
目录下的
init-db.jar
,在数据库中放入该项目的初始化数据。
然后就可以点
Run On Server
来启动项目了,让大家见识一下
Eclipse
的嵌入式浏览器、
Tomcat
服务器视图、
Console
视图。真的是太方便了:
第五步、将数据库迁移到
MySQL
中。
在项目中,创建数据库和初始化数据库的语句都是以
SQL
文件存在的,如下图:
但是该语句都是针对
Derby
的,如果要应用于
MySQL
,还必须得要做一些修改才行,先修改
schema.sql
,如下:
drop
table
if
exists
RESOURCES_AUTHORITIES;
drop
table
if
exists
ROLES_AUTHORITIES;
drop
table
if
exists
USERS_ROLES;
drop
table
if
exists
RESOURCES;
drop
table
if
exists
AUTHORITIES;
drop
table
if
exists
USERS;
drop
table
if
exists
ROLES;
create
table
USERS (
ID integer
primary
key
auto_increment,
LOGIN_NAME varchar
(
20
)
not
null
unique
,
PASSWORD varchar
(
20
),
NAME varchar
(
20
),
EMAIL varchar
(
30
)
);
create
unique
index
USERS_LOGIN_NAME_INDEX
on
USERS(LOGIN_NAME);
create
table
ROLES (
ID integer
primary
key
auto_increment,
NAME varchar
(
20
)
not
null
unique
);
create
table
USERS_ROLES (
USER_ID
integer
not
null
,
ROLE_ID integer
not
null
,
FOREIGN
KEY
(ROLE_ID)
references
ROLES(ID),
FOREIGN
KEY
(
USER_ID
)
references
USERS(ID)
);
CREATE
TABLE
AUTHORITIES (
ID integer
primary
key
auto_increment,
NAME varchar
(
20
)
not
null
,
DISPLAY_NAME varchar
(
20
)
not
null
);
create
table
ROLES_AUTHORITIES (
ROLE_ID integer
not
null
,
AUTHORITY_ID integer
not
null
,
FOREIGN
KEY
(ROLE_ID)
references
ROLES(ID),
FOREIGN
KEY
(AUTHORITY_ID)
references
AUTHORITIES(ID)
);
CREATE
TABLE
RESOURCES (
ID integer
primary
key
auto_increment,
RESOURCE_TYPE varchar
(
20
)
not
null
,
VALUE varchar
(
255
)
not
null
,
ORDER_NUM float
not
null
);
create
table
RESOURCES_AUTHORITIES (
AUTHORITY_ID integer
not
null
,
RESOURCE_ID integer
not
null
,
FOREIGN
KEY
(AUTHORITY_ID)
references
AUTHORITIES(ID),
FOREIGN
KEY
(RESOURCE_ID)
references
RESOURCES(ID)
);
该修改主要包含两个地方,一个是在
drop table
后面加上了
if exists
,一个是把
GENERATED ALWAYS as IDENTITY
修改为
auto_increment
。而
load-data.sql
不需要修改。
然后,启动
MySQL
,在
MySQL
中使用上面的两个
sql
文件创建数据库和添加初始化数据,如下图:
然后更改数据库连接,修改项目的
application.properties
文件,如下:
#jdbc settings
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MultiDatasourceExample?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.username=youxia
jdbc.password=******
#hibernate settings
hibernate.show_sql=false
hibernate.format_sql=false
hibernate.ehcache_config_file=/ehcache/ehcache-hibernate-local.xml
修改项目的
applicationContext.xml
文件,这里要修改两个地方,一个为
DriverClassName
,一个为
hibernate.dilect
,如下:
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<
beans
xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jee
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:tx
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"
default-lazy-init
="true">
<
description
>
Spring
公共配置文件
</
description
>
<!--
定义受环境影响易变的变量
-->
<
bean
class
="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<
property
name
="systemPropertiesModeName"
value
="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE"
/>
<
property
name
="ignoreResourceNotFound"
value
="true"
/>
<
property
name
="locations">
<
list
>
<!--
标准配置
-->
<
value
>
classpath*:/application.properties
</
value
>
<!--
本地开发环境配置
-->
<
value
>
classpath*:/application.local.properties
</
value
>
<!--
服务器生产环境配置
-->
<!-- <value>file:/var/myapp/application.server.properties</value> -->
</
list
>
</
property
>
</
bean
>
<!--
使用
annotation
自动注册
bean,
并保证
@Required,@Autowired
的属性被注入
-->
<
context:component-scan
base-package
="personal.youxia"
/>
<!--
数据源配置
,
使用应用内的
DBCP
数据库连接池
-->
<
bean
id
="dataSource"
class
="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method
="close">
<!-- Connection Info -->
<
property
name
="driverClassName"
value
="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
/>
<
property
name
="url"
value
="${jdbc.url}"
/>
<
property
name
="username"
value
="${jdbc.username}"
/>
<
property
name
="password"
value
="${jdbc.password}"
/>
<!-- Connection Pooling Info -->
<
property
name
="initialSize"
value
="5"
/>
<
property
name
="maxActive"
value
="100"
/>
<
property
name
="maxIdle"
value
="30"
/>
<
property
name
="maxWait"
value
="1000"
/>
<
property
name
="poolPreparedStatements"
value
="true"
/>
<
property
name
="defaultAutoCommit"
value
="false"
/>
</
bean
>
<!--
数据源配置
,
使用应用服务器的数据库连接池
-->
<!--<jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="java:comp/env/jdbc/ExampleDB" />-->
<!-- Hibernate
配置
-->
<
bean
id
="sessionFactory"
class
="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<
property
name
="dataSource"
ref
="dataSource"
/>
<
property
name
="namingStrategy">
<
bean
class
="org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy"
/>
</
property
>
<
property
name
="hibernateProperties">
<
props
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.show_sql">
${hibernate.show_sql}
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.format_sql">
${hibernate.format_sql}
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.cache.provider_class">
org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.cache.provider_configuration_file_resource_path">
${hibernate.ehcache_config_file}
</
prop
>
</
props
>
</
property
>
<
property
name
="packagesToScan"
value
="personal.youxia.entity.*"
/>
</
bean
>
<!--
事务管理器配置
,
单数据源事务
-->
<
bean
id
="transactionManager"
class
="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<
property
name
="sessionFactory"
ref
="sessionFactory"
/>
</
bean
>
<!--
事务管理器配置
,
多数据源
JTA
事务
-->
<!--
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager or
WebLogicJtaTransactionManager" />
-->
<!--
使用
annotation
定义事务
-->
<
tx:annotation-driven
transaction-manager
="transactionManager"
/>
</
beans
>
由于
SpringSide
不提供
Mysql
的
jdbc
驱动,所以需要自己去
MySQL
的官方网站下载,将下载到的
mysql-connector-5.*.jar
复制到项目的
WEB-INF
中的
lib
目录中。然后运行项目,成功。至此,成功将项目迁移到
MySQL
中。
第六步、添加数据表、编写
Entity
类、编写
Dao
类、
Manager
类,并进行单元测试。
还是以前几篇文章中提到的文章发布系统为例,每一篇文章对应多篇评论,所以说据库中需创建
articles
和
comments
两个数据表,如下:
create
table
articles(
id int
primary
key
auto_increment,
subject varchar
(
20
)
not
null
,
content text
);
create
table
comments(
id int
primary
key
auto_increment,
content varchar
(
255
),
article_id int
not
null
,
foreign
key
(article_id)
references
articles(id)
);
在编写
Java
代码之前,我还要做一点小工作,什么工作呢?那就是要为我自己的项目创建一个单独的源文件夹,因为
src/main/java
这个文件夹已经被江南白衣放入了太多的
package
,而且因为涉及到
security
,所以层次也不明显,操作起来不方便,找起代码来也不够快。下面是我创建了自己的源文件夹后的截图:
在我自己的源文件夹中,只创建了四个
package
,刚好代表从底到上的四个层次,这样,找起代码来要方便得多。
先来
Entity
层,
Article.java
的代码如下:
package
personal.youxia.entity;
import
java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import
java.util.Set;
import
javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import
javax.persistence.Entity;
import
javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import
javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import
javax.persistence.OrderBy;
import
javax.persistence.Table;
import
org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import
org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
import
org.hibernate.annotations.Fetch;
import
org.hibernate.annotations.FetchMode;
@Entity
//
表名与类名不相同时重新定义表名
.
@Table(name = "articles")
//
默认的缓存策略
.
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
public
class
Article
extends
IdEntity
{
private
String subject;
private
String content;
private
Set<Comment> comments =
new
LinkedHashSet<Comment>();
public
String getSubject()
{
return
subject;
}
public
void
setSubject(String subject)
{
this
.subject = subject;
}
public
String getContent()
{
return
content;
}
public
void
setContent(String content)
{
this
.content = content;
}
@OneToMany(cascade =
{ CascadeType.ALL })
@JoinColumn(name = "article_id")
// Fecth
策略定义
@Fetch(FetchMode.SUBSELECT)
//
集合按
id
排序
.
@OrderBy("id")
//
集合中对象
id
的缓存
.
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
public
Set<Comment> getComments()
{
return
comments;
}
public
void
setComments(Set<Comment> comments)
{
this
.comments = comments;
}
}
Comment.java
如下:
package
personal.youxia.entity.entities;
import
javax.persistence.Column;
import
javax.persistence.Entity;
import
javax.persistence.Table;
import
org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import
org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
import
personal.youxia.entity.IdEntity;
@Entity
//
表名与类名不相同时重新定义表名
.
@Table(name = "comments")
//
默认的缓存策略
.
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
public
class
Comment
extends
IdEntity {
private
String content;
private
Long articleId;
public
String getContent() {
return
content;
}
public
void
setContent(String content) {
this
.content = content;
}
@Column(name = "article_id")
public
Long getArticleId() {
return
articleId;
}
public
void
setArticleId(Long articleId) {
this
.articleId = articleId;
}
}
编写
Dao
层代码,
ArticleDao.java
如下:
package
personal.youxia.dao;
import
org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import
personal.youxia.entity.Article;
public
class
ArticleDao
extends
HibernateDao<Article, Long>
{
}
CommentDao.java
如下:
package
personal.youxia.dao;
import
org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import
personal.youxia.entity.Comment;
public
class
CommentDao
extends
HibernateDao<Comment, Long>
{
}
可以看出,以上代码都从
HibernateDao
继承,得益于泛型支持,基本不需要编写一行代码。
编写
Bussiness
层代码,这一层,白衣使用的包名为
service
,而类名的后缀都是
Manager
,我就跟他学算了,懒得改了。
ArticleManager.java
如下:
package
personal.youxia.service;
import
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import
org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import
personal.youxia.dao.ArticleDao;
import
personal.youxia.entity.Article;
public
class
ArticleManager
extends
EntityManager<Article, Long>
{
@Autowired
private
ArticleDao articleDao;
public
void
setArticleDao(ArticleDao articleDao)
{
this
.articleDao = articleDao;
}
@Override
protected
HibernateDao<Article, Long> getEntityDao()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return
articleDao;
}
}
CommentManager.java
如下:
package
personal.youxia.service;
import
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import
org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import
personal.youxia.dao.CommentDao;
import
personal.youxia.entity.Comment;
public
class
CommentManager
extends
EntityManager<Comment, Long>
{
@Autowired
private
CommentDao commentDao;
public
void
setCommentDao(CommentDao commentDao)
{
this
.commentDao = commentDao;
}
@Override
protected
HibernateDao<Comment, Long> getEntityDao()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return
commentDao;
}
}
以上代码大同小异,都是从
EntityManager
继承,并使用
Spring
的
IoC
特性,将
Dao
类注入到
Manager
类之中,并重载
getEntityDao
方法来使用该注入的
Dao
。这个时候,为了验证这些数据访问相关的层能否正常运行,可以编写单元测试。
代码如下:
package
personal.youxia.test;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import
org.springside.modules.test.junit4.SpringTxTestCase;
import
personal.youxia.entity.entities.Article;
import
personal.youxia.entity.entities.Comment;
import
personal.youxia.service.ArticleManager;
import
personal.youxia.service.CommentManager;
public
class
DataAccessTest
extends
SpringTxTestCase
{
@Autowired
private
ArticleManager articleManager;
@Autowired
private
CommentManager commentManager;
public
void
setArticleManager(ArticleManager articleManager)
{
this
.articleManager = articleManager;
}
@Test
public
void
addArticle()
{
Comment comment =
new
Comment();
Article article =
new
Article();
article.setSubject("test");
article.setContent("test");
articleManager.save(article);
comment.setArticleId(article.getId());
commentManager.save(comment);
}
}
单元测试一运行,发现了三个问题,先是出现
Manager
类没有注入成功的错误,经检查发现
所有的
Manager
类都应该使用
@Service
注解
,再出现的错误是提示
Dao
类没有注入成功,经检查发现
所有的
Dao
类须使用
@Repository
注解
,最后出现的错误是找不到
Entity
类的错误,经检查发现
Entity
类不能位于
personal.youxia.entity
包中,必须位于其子包中
,这是由
applicationContext.xml
文件中的配置决定的,更改包名为
personal.youxia.entity.entities
后,问题解决。
下一步就应该是编写
Action
和
JSP
了,由于文章太长,在
Blogjava
的编辑器中编辑已经非常缓慢了,所以只有将该文章分为上中下三部分。且看下回分解!
http://blog.csdn.net/cuker919/archive/2011/04/20/6336630.aspx
使用SpringSide 3.1.4.3开发Web项目的全过程(中下)