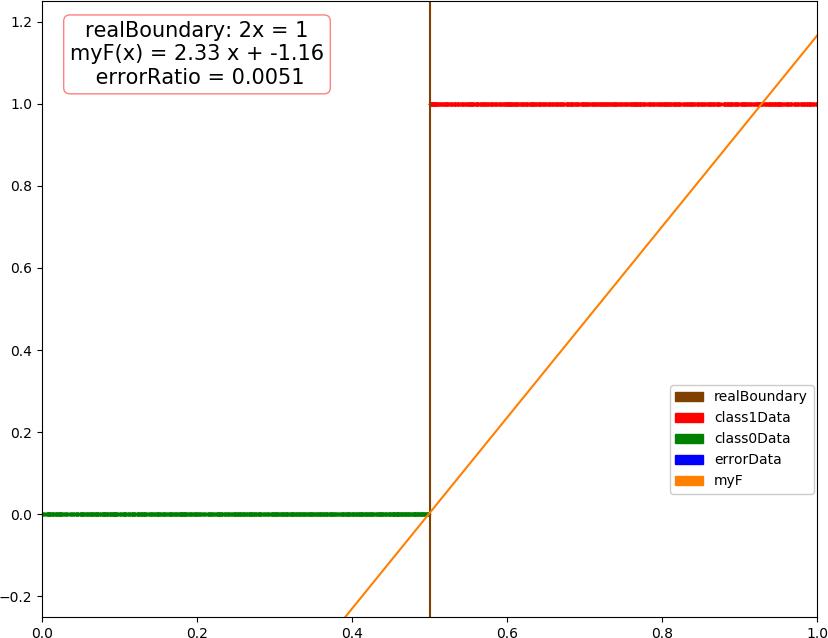
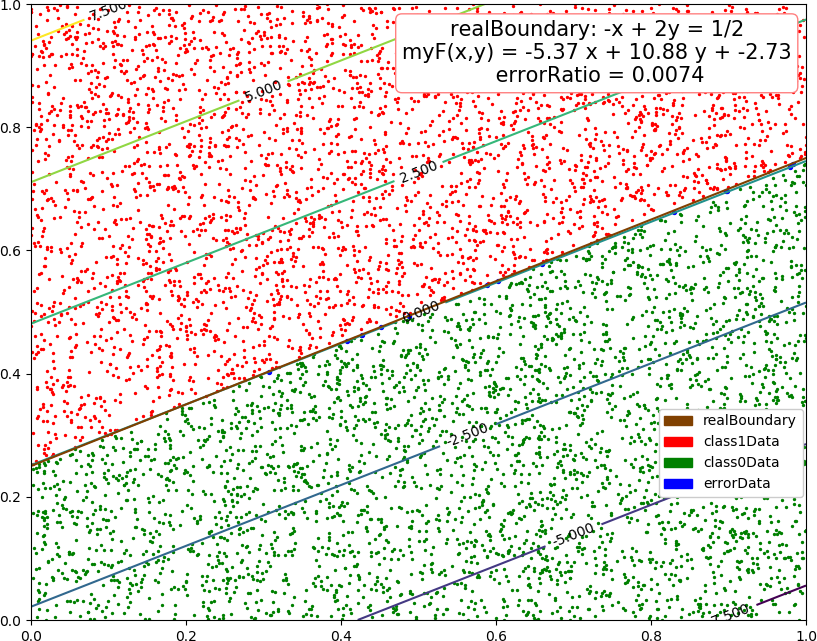
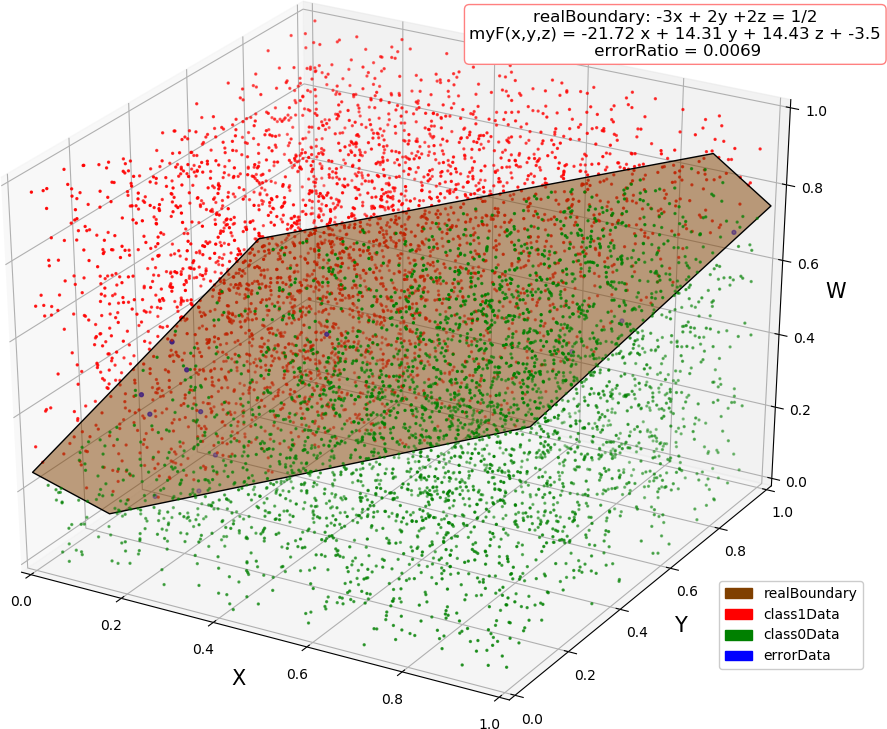
▶ 感知机来找到线性可分数据集的分割,很像单层神经网络
● 原始形式感知机,代码
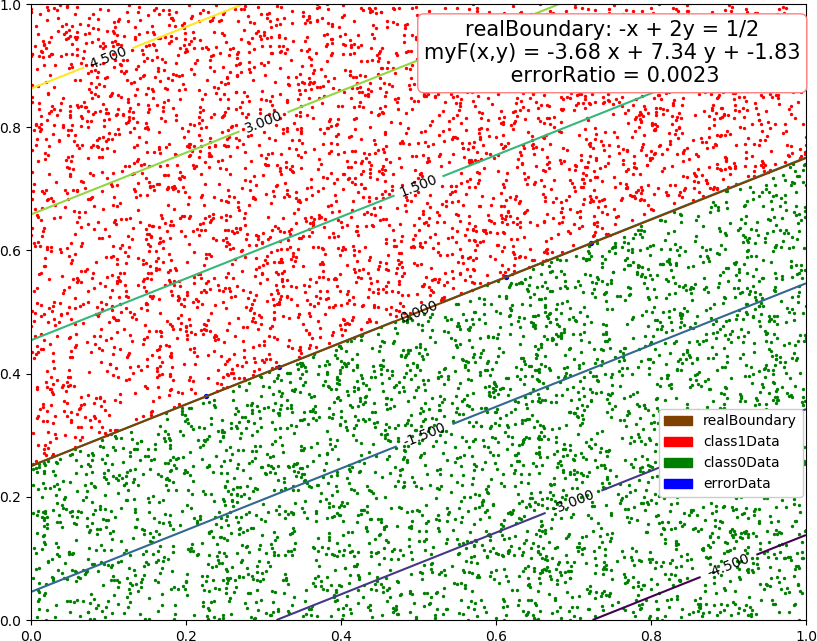
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 4 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection 5 from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle 6 import warnings 7 8 warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") 9 dataSize = 10000 10 trainRatio = 0.3 11 maxTurn = 300 12 ita = 0.3 13 epsilon = 0.01 14 colors = [[0.5,0.25,0],[1,0,0],[0,0.5,0],[0,0,1],[1,0.5,0]] # 棕红绿蓝橙 15 trans = 0.5 16 17 def dataSplit(x, y, part): # 将数据集按给定索引分为两段 18 return x[:part], y[:part],x[part:],y[part:] 19 20 def function(x,para): # 回归函数 21 return np.sum(x * para[0]) + para[1] 22 23 def judge(x, para): # 分类函数,由乘加部分和阈值部分组成 24 return np.sign(function(x, para)) 25 26 def createData(dim, count = dataSize): # 创建数据集 27 np.random.seed(103) 28 X = np.random.rand(count,dim) 29 Y = 2 * ((3 - 2 * dim)*X[:,0] + 2 * np.sum(X[:,1:], 1) > 0.5).astype(int) - 1 # 只考虑 {-1,1} 的二分类 30 #print(output) 31 class1Count = 0 32 for i in range(count): 33 class1Count += (Y[i] + 1)>>1 34 print("dim = %d, dataSize = %d, class 1 count -> %4f"%(dim, count, class1Count / count)) 35 return X, Y 36 37 def perceptron(dataX, dataY): # 感知机 38 count, dim = np.shape(dataX) 39 w = np.random.rand(dim) # 随机初值 40 b = np.random.rand() 41 42 turn = 0 43 while turn < maxTurn: 44 error = 0.0 45 for i in range(count): 46 if dataY[i] * (np.sum(w * dataX[i]) + b) <= 0: # 找到分类错误的点 47 w += ita * dataX[i] * dataY[i] # 修正 w 和 b 48 b += ita *dataY[i] 49 error += np.sum(w * dataX[i] + b - dataY[i]) ** 2 50 error /= count 51 turn += 1 52 print("turn = ", turn, ", error = ", error) 53 if error < epsilon: 54 break 55 return (w, b) 56 57 def test(dim): 58 allX, allY = createData(dim) 59 trainX, trainY, testX, testY = dataSplit(allX, allY, int(dataSize * trainRatio)) 60 61 para = perceptron(trainX, trainY) 62 63 myResult = [ judge(x, para) for x in testX] # 测试结果 64 errorRatio = np.sum((np.array(myResult) - testY)**2) / (dataSize * (1 - trainRatio)) 65 print("dim = %d, errorRatio = %4f "%(dim, errorRatio)) 66 67 if dim >= 4: # 4维以上不画图,只输出测试错误率 68 return 69 errorPX = [] # 测试数据集分为错误类,1 类和 0 类 70 errorPY = [] 71 class1 = [] 72 class0 = [] 73 for i in range(len(testX)): 74 if myResult[i] != testY[i]: 75 errorPX.append(testX[i]) 76 errorPY.append(testY[i]) 77 elif myResult[i] == 1: 78 class1.append(testX[i]) 79 else: 80 class0.append(testX[i]) 81 errorPX = np.array(errorPX) 82 errorPY = np.array(errorPY) 83 class1 = np.array(class1) 84 class0 = np.array(class0) 85 86 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 87 88 if dim == 1: 89 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 90 plt.ylim(-0.25,1.25) 91 plt.plot([0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, 1.25], color = colors[0],label = "realBoundary") 92 plt.plot([0, 1], [ function(i, para) for i in [0,1] ],color = colors[4], label = "myF") 93 plt.scatter(class1, np.ones(len(class1)), color = colors[1], s = 2,label = "class1Data") 94 plt.scatter(class0, np.zeros(len(class0)), color = colors[2], s = 2,label = "class0Data") 95 if len(errorPX) != 0: 96 plt.scatter(errorPX, errorPY,color = colors[3], s = 16,label = "errorData") 97 plt.text(0.2, 1.12, "realBoundary: 2x = 1 myF(x) = " + str(round(para[0][0],2)) + " x + " + str(round(para[1],2)) + " errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 98 size=15, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 99 R = [Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = colors[k]) for k in range(5)] 100 plt.legend(R, ["realBoundary", "class1Data", "class0Data", "errorData", "myF"], loc=[0.81, 0.2], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 101 102 if dim == 2: 103 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 104 plt.ylim(0.0,1.0) 105 plt.plot([0,1], [0.25,0.75], color = colors[0],label = "realBoundary") 106 xx = np.arange(0, 1 + 0.1, 0.1) 107 X,Y = np.meshgrid(xx, xx) 108 contour = plt.contour(X, Y, [ [ function((X[i,j],Y[i,j]), para) for j in range(11)] for i in range(11) ]) 109 plt.clabel(contour, fontsize = 10,colors='k') 110 plt.scatter(class1[:,0], class1[:,1], color = colors[1], s = 2,label = "class1Data") 111 plt.scatter(class0[:,0], class0[:,1], color = colors[2], s = 2,label = "class0Data") 112 if len(errorPX) != 0: 113 plt.scatter(errorPX[:,0], errorPX[:,1], color = colors[3], s = 8,label = "errorData") 114 plt.text(0.73, 0.92, "realBoundary: -x + 2y = 1/2 myF(x,y) = " + str(round(para[0][0],2)) + " x + " + str(round(para[0][1],2)) + " y + " + str(round(para[1],2)) + " errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 115 size = 15, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 116 R = [Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = colors[k]) for k in range(4)] 117 plt.legend(R, ["realBoundary", "class1Data", "class0Data", "errorData"], loc=[0.81, 0.2], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 118 119 if dim == 3: 120 ax = Axes3D(fig) 121 ax.set_xlim3d(0.0, 1.0) 122 ax.set_ylim3d(0.0, 1.0) 123 ax.set_zlim3d(0.0, 1.0) 124 ax.set_xlabel('X', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 125 ax.set_ylabel('Y', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 126 ax.set_zlabel('W', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 127 v = [(0, 0, 0.25), (0, 0.25, 0), (0.5, 1, 0), (1, 1, 0.75), (1, 0.75, 1), (0.5, 0, 1)] 128 f = [[0,1,2,3,4,5]] 129 poly3d = [[v[i] for i in j] for j in f] 130 ax.add_collection3d(Poly3DCollection(poly3d, edgecolor = 'k', facecolors = colors[0]+[trans], linewidths=1)) 131 ax.scatter(class1[:,0], class1[:,1],class1[:,2], color = colors[1], s = 2, label = "class1") 132 ax.scatter(class0[:,0], class0[:,1],class0[:,2], color = colors[2], s = 2, label = "class0") 133 if len(errorPX) != 0: 134 ax.scatter(errorPX[:,0], errorPX[:,1],errorPX[:,2], color = colors[3], s = 8, label = "errorData") 135 ax.text3D(0.8, 0.98, 1.15, "realBoundary: -3x + 2y +2z = 1/2 myF(x,y,z) = " + str(round(para[0][0],2)) + " x + " + 136 str(round(para[0][1],2)) + " y + " + str(round(para[0][2],2)) + " z + " + str(round(para[1],2)) + " errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 137 size = 12, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1, 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1, 1, 1))) 138 R = [Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = colors[k]) for k in range(4)] 139 plt.legend(R, ["realBoundary", "class1Data", "class0Data", "errorData"], loc=[0.83, 0.1], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 140 141 fig.savefig("R:\dim" + str(dim) + ".png") 142 plt.close() 143 144 if __name__ == '__main__': 145 test(1) 146 test(2) 147 test(3) 148 test(4)
● 输出结果
dim = 1, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.509000 turn = 1 , error = 0.017389410798594473 turn = 2 , error = 0.0 dim = 1, errorRatio = 0.004571 dim = 2, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.496000 turn = 1 , error = 0.21416356258715985 ... turn = 11 , error = 0.10398373598573663 turn = 12 , error = 0.045706020341763055 turn = 13 , error = 0.0 dim = 2, errorRatio = 0.002286 dim = 3, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.498200 turn = 1 , error = 0.45650719829126757 ... turn = 12 , error = 0.14528529033345788 turn = 13 , error = 0.1376817605623497 turn = 14 , error = 0.0 dim = 3, errorRatio = 0.000571 dim = 4, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.496900 turn = 1 , error = 0.7717105869223287 ... turn = 298 , error = 0.7316455346511096 turn = 299 , error = 0.6088039354340593 turn = 300 , error = 0.48205216369651693 dim = 4, errorRatio = 0.005143
● 画图
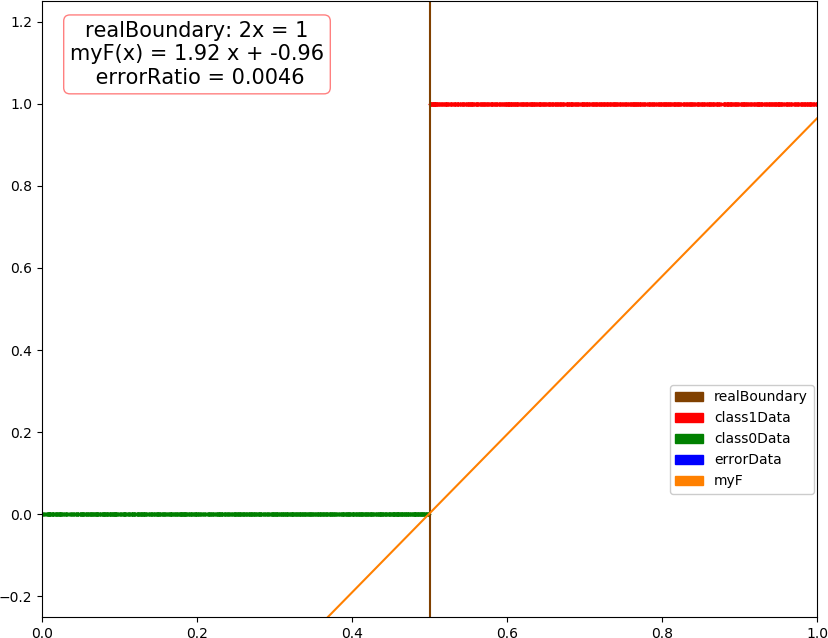

● 对偶形式感知机,代码,只改变函数 perceptron,不用 Gram 矩阵,太占空间
1 def perceptron(dataX, dataY): 2 count, dim = np.shape(dataX) 3 w = np.random.rand(dim) # 随机初值 4 b = np.random.rand() 5 alpha = np.zeros(count) 6 xy = dataX * dataY.reshape(count,1) 7 8 turn = 0 9 while turn < maxTurn: 10 error = 0.0 11 for i in range(count): 12 t = np.sum(np.matmul(alpha,xy) * dataX[i]) + b # 当前预测值 13 if dataY[i] * t <= 0: # 选取分类错误的点进行修正 14 alpha[i] += ita 15 b += ita * dataY[i] 16 17 w = np.matmul(alpha,xy) # 一轮结束,计算 w 和误差 18 error = np.sum( (np.sign(np.sum(w * dataX, 1) + b) - dataY) ** 2 ) / count 19 turn += 1 20 print("turn = ", turn, ", error = ", error) 21 if error < epsilon: 22 break 23 return (w, b)
● 输出结果,似乎更快,但是精度有所下降
dim = 1, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.509000 turn = 1 , error = 0.0 dim = 1, errorRatio = 0.005143 dim = 2, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.496000 turn = 1 , error = 0.008 dim = 2, errorRatio = 0.007429 dim = 3, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.498200 turn = 1 , error = 0.07333333333333333 turn = 2 , error = 0.3293333333333333 turn = 3 , error = 0.018666666666666668 turn = 4 , error = 0.012 turn = 5 , error = 0.172 turn = 6 , error = 0.10666666666666667 turn = 7 , error = 0.05333333333333334 turn = 8 , error = 0.0026666666666666666 dim = 3, errorRatio = 0.006857 dim = 4, dataSize = 10000, class 1 count -> 0.496900 turn = 1 , error = 0.088 ... turn = 45 , error = 0.021333333333333333 turn = 46 , error = 0.009333333333333334 dim = 4, errorRatio = 0.010857
● 画图