1.从classpath读取文件可以避免不同环境下文件路径不一致的问题。
Windows和Linux关于路径的表示不一致
- Windows:C:confdefault.properties
- Linux:/User/admin/conf/default.properties
//先获取getClass(),再通过getResourceAsStream可以获取任意的资源文件
try(InputStream input = getClass().getResourceAsStream("/default.properties")){
if(input != null){
//如果资源文件在classpath未找到,会返回null
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] data1 = {
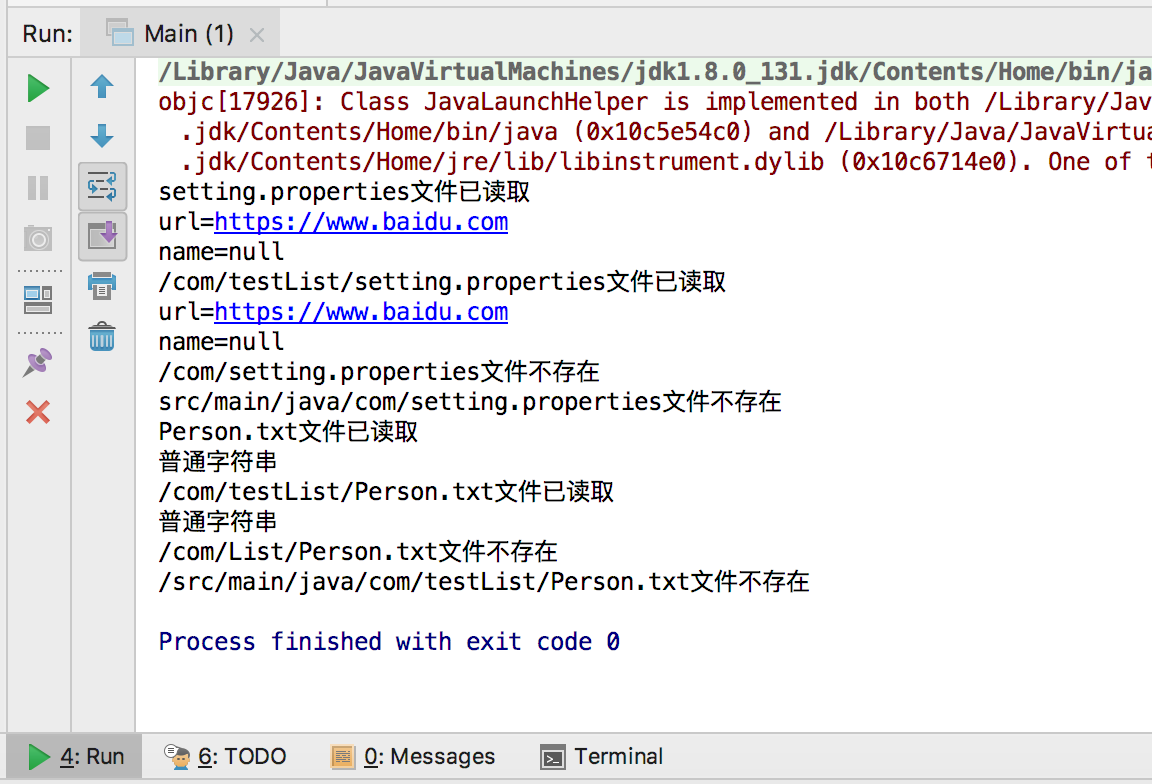
"setting.properties",//正确路径
"/com/testList/setting.properties",//正确路径
"/com/setting.properties",//错误路径
"src/main/java/com/setting.properties",//错误路径
};
for(String data:data1){
getProperty(data);
}
String[] data2 = {
"Person.txt",//正确路径
"/com/testList/Person.txt",//正确路径
"/com/List/Person.txt",//错误路径
"/src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt",//错误路径
};
for(String data:data2){
getText(data);
}
}
static void getProperty(String data) throws IOException{
try(InputStream input = Main.class.getResourceAsStream(data)) {
if(input != null){
System.out.println(data+"文件已读取");
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(input);
System.out.println("url="+props.getProperty("url"));
System.out.println("name="+props.getProperty("name"));
}else{
System.out.println(data+"文件不存在");
}
}
}
static void getText(String data) throws IOException{
try(InputStream input = Main.class.getResourceAsStream(data)){
if(input != null){
System.out.println(data+"文件已读取");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(input));//BufferedReader有readline()方法可以读取第一行文本
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
}else{
System.out.println(data+"文件不存在");
}
}
}
}
2.总结
- 把资源存储在classpath中可以避免文件路径依赖
- Class对象的getResourceAsStream()可以从classpath读取资源
- 需要检查返回的InputStream是否为null