题目链接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5652
A long time ago there are no himalayas between India and China, the both cultures are frequently exchanged and are kept in sync at that time, but eventually himalayas rise up. With that at first the communation started to reduce and eventually died.
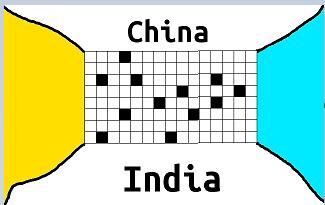
Let's assume from my crude drawing that the only way to reaching from India to China or viceversa is through that grid, blue portion is the ocean and people haven't yet invented the ship. and the yellow portion is desert and has ghosts roaming around so people can't travel that way. and the black portions are the location which have mountains and white portions are plateau which are suitable for travelling. moutains are very big to get to the top, height of these mountains is infinite. So if there is mountain between two white portions you can't travel by climbing the mountain.
And at each step people can go to 4 adjacent positions.
Our archeologists have taken sample of each mountain and estimated at which point they rise up at that place. So given the times at which each mountains rised up you have to tell at which time the communication between India and China got completely cut off.

Let's assume from my crude drawing that the only way to reaching from India to China or viceversa is through that grid, blue portion is the ocean and people haven't yet invented the ship. and the yellow portion is desert and has ghosts roaming around so people can't travel that way. and the black portions are the location which have mountains and white portions are plateau which are suitable for travelling. moutains are very big to get to the top, height of these mountains is infinite. So if there is mountain between two white portions you can't travel by climbing the mountain.
And at each step people can go to 4 adjacent positions.
Our archeologists have taken sample of each mountain and estimated at which point they rise up at that place. So given the times at which each mountains rised up you have to tell at which time the communication between India and China got completely cut off.
Input
There are multi test cases. the first line is a sinle integer T which represents the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains two space seperated integers N,M. next N lines consists of strings composed of 0,1 characters. 1 denoting that there's already a mountain at that place, 0 denoting the plateau. on N+2 line there will be an integer Q denoting the number of mountains that rised up in the order of times. Next Q lines contain 2 space seperated integers X,Y denoting that at ith year a mountain rised up at location X,Y.
T≤1
For each test case, the first line contains two space seperated integers N,M. next N lines consists of strings composed of 0,1 characters. 1 denoting that there's already a mountain at that place, 0 denoting the plateau. on N+2 line there will be an integer Q denoting the number of mountains that rised up in the order of times. Next Q lines contain 2 space seperated integers X,Y denoting that at ith year a mountain rised up at location X,Y.
T≤1
Output
Single line at which year the communication got cut off.
print -1 if these two countries still connected in the end.
Hint:
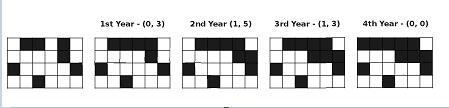
From the picture above, we can see that China and India have no communication since 4th year.
print -1 if these two countries still connected in the end.
Hint:

From the picture above, we can see that China and India have no communication since 4th year.
Sample Input
1
4 6
011010
000010
100001
001000
7
0 3
1 5
1 3
0 0
1 2
2 4
2 1
Sample Output
4
容我bb两句:这个题的提议很容易理解,做这道题时首先想到bfs了,但还是wa了。
后来看了卿学姐的博客顿时清醒,卿学姐博客链接http://www.cnblogs.com/qscqesze/p/5324497.html
下面是弱菜的代码
# include <iostream> # include <cmath> # include <algorithm> # include <cstdio> # include <cstring> # include <string> # include <cstdlib> # include <vector> # include <bitset> # include <map> # include <queue> # include <ctime> # include <stack> # include <set> # include <list> # include <deque> # include <functional> # include <sstream> # include <fstream> # include <complex> # include <numeric> using namespace std; char maps[520][520]; char s[520][520]; int n,m; int xi[]= {0,0,1,-1}; int yi[]= {1,-1,0,0}; int yes; const int INF=11111111; typedef pair<int,int>P; int sx=0,sy=0; int d[520][520]; P vis[250090]; bool bfs(int q) { for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) strcpy(maps[i],s[i]); for(int i=1; i<=q; i++) maps[vis[i].first+1][vis[i].second]='1'; // for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%s ",maps[i]); queue<P>que; for(int i=0; i<=n+1; i++) for(int j=0; j<m; j++) d[i][j]=INF; que.push(P(sx,sy)); d[sx][sy]=0; while(que.size()) { P p=que.front(); que.pop(); if(p.first==n+1) { return true; } for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { int nx=p.first+xi[i]; int ny=p.second+yi[i]; if(nx>=0&&nx<=n+1&&ny>=0&&ny<m&&maps[nx][ny]!='1'&&d[nx][ny]==INF) { que.push(P(nx,ny)); d[nx][ny]=d[p.first][p.second]+1; } } } return false; } int main() { int t; //freopen("data.in.txt","r",stdin); scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) scanf("%s",s[i]); int len; scanf("%d",&len); for(int i=1; i<=len; i++) scanf("%d %d",&vis[i].first,&vis[i].second); if(bfs(len)) cout<<-1<<endl; else { int l=0,r=len,ans=0; int mid=(l+r)/2; while(l<=r) { mid=(l+r)/2; if(!bfs(mid)) { r=mid-1; ans=mid; } else l=mid+1; } cout<<ans<<endl; } } return 0; }