1. 解析的基本的概念
解析:从事先规定好的格式中提取数据
解析前提:提前约定好格式,数据提供方按照格式提供数据、数据获取方则按照格式获取数据
iOS开发常见的解析:XML解析、JOSN解析
2. XML数据结构
1> 概述
XML:Extensible markup language(可扩展标记语言),主流数据格式之一,可以用来存储和传输数据。
2> XML数据格式的功能
-
数据交换
-
内容管理
-
用作配置文件
3> XML数据格式的语法
-
声明
-
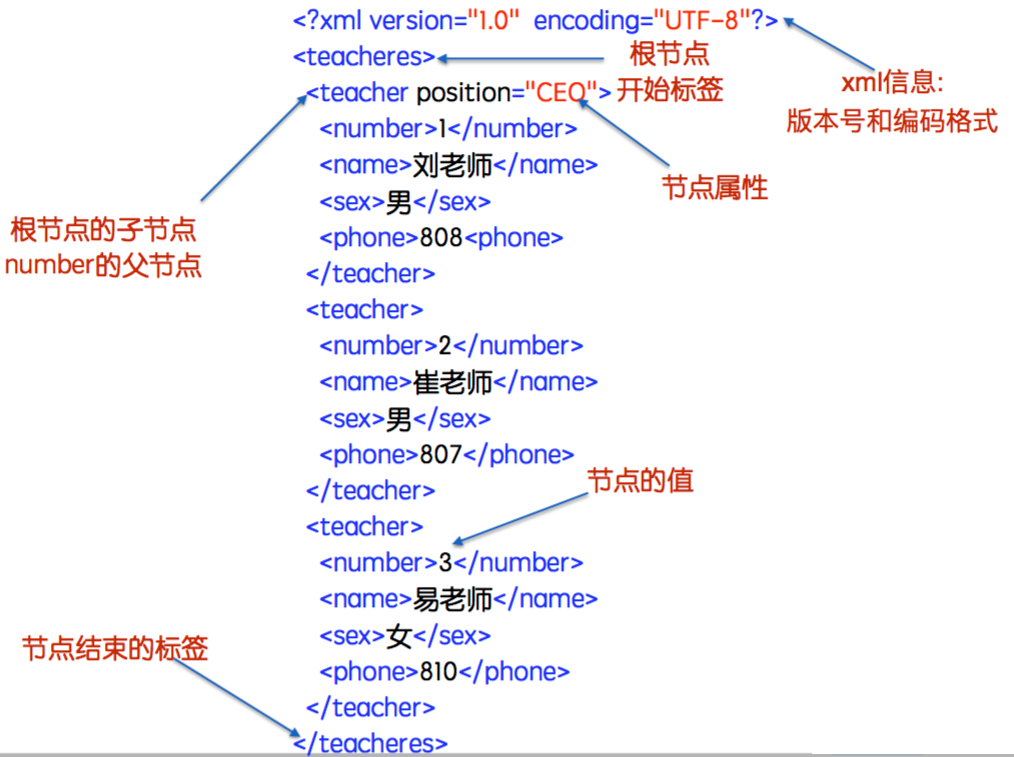
节点使用一对标签表示:起始和结束标签。
-
根节点是起始节点,只有一个,节点可以嵌套。
-
节点可以有值,存储在一对儿标签中。
4> XML实例
3. 使用SAX工具解析XML
1> 概述
Simple API for XML。基于事件驱动的解析方式,逐行解析数据。(采用协议回调机制)
2> NSXMLParser类概述
-
NSXMLParser是iOS自带的XML解析类,采用SAX方式解析数据
-
解析过程由NSXMLParserDelegate协议方法回调
-
解析过程:开始标签 --> 取值 --> 结束标签 --> 取值
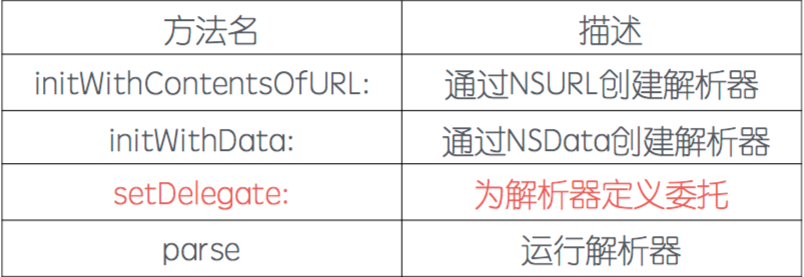
3> 初始化NSXMLParser
使用NSXMLParser要先创建它,设置各种属性,主要用到一下几个方法:
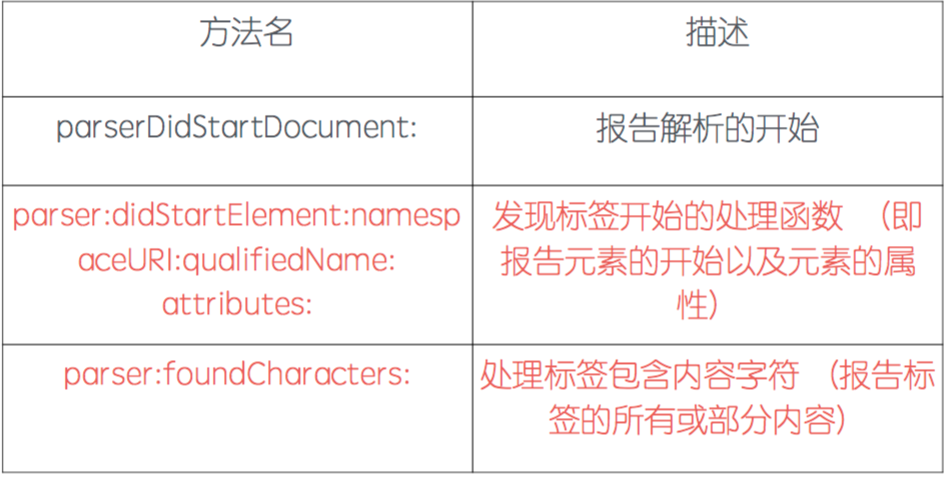
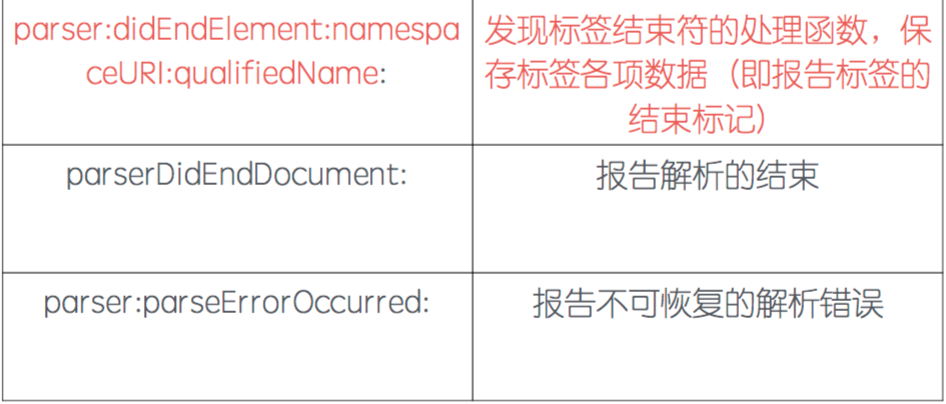
4> NSXMLParserDelegate代理方法
5> 代码
1 #pragma mark - SAX解析xml文件 2 - (IBAction)saxParserActionXMLDocument:(UIButton *)sender 3 { 4 // 1. 获取文件路径(获取xcode中的文件路径) 5 NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"StudentInfo_XML" ofType:@"txt"]; 6 7 // 2. 获取NSData类型的数据 8 NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path]; 9 10 NSLog(@"data = %@", data); 11 12 // 3. 设置SAX解析,并关联相关的xml文件 13 NSXMLParser *parser = [[NSXMLParser alloc] initWithData:data]; 14 15 // 4. 设置代理 16 parser.delegate = self; 17 18 // 5. 开始解析 19 [parser parse]; 20 } 21 22 23 #pragma mark NSXMLParserDelegate的协议方法 24 25 #pragma mark 1. 文档解析 26 - (void)parserDidStartDocument:(NSXMLParser *)parser 27 { 28 29 } 30 31 #pragma mark 2. 开始标签解析 32 - (void)parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser didStartElement:(NSString *)elementName namespaceURI:(NSString *)namespaceURI qualifiedName:(NSString *)qName attributes:(NSDictionary<NSString *,NSString *> *)attributeDict 33 { 34 // 根据需求的标签获取相关的数据 35 if ([elementName isEqualToString:@"student"]) { 36 Student *stu = [Student new]; 37 38 // 在这里不需要赋值 39 40 // 将数据对象添加到数组中 41 [self.dataArray addObject:stu]; 42 } 43 44 // 将当前的标签值传给声明的标签属性 45 self.currentElement = elementName; 46 47 } 48 49 #pragma mark 3. 解析标签中的内容然后赋值给对象 50 - (void)parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser foundCharacters:(NSString *)string 51 { 52 // 从数组中取出相关的Student对象,每次取数组中最后的一个元素,保证值为最新的对象内容 53 Student *stu = [self.dataArray lastObject]; 54 55 // KVC 56 [stu setValue:string forKey:self.currentElement]; 57 58 } 59 60 #pragma mark 4. 结束标签 61 - (void)parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser didEndElement:(NSString *)elementName namespaceURI:(NSString *)namespaceURI qualifiedName:(NSString *)qName 62 { 63 self.currentElement = nil; 64 } 65 66 #pragma mark 5. 结束文档解析 67 - (void)parserDidEndDocument:(NSXMLParser *)parser 68 { 69 for (Student *stu in self.dataArray) { 70 NSLog(@"name = %@, gender = %@, age = %ld", stu.name, stu.gender, stu.age); 71 } 72 } 73 74 #pragma mark 6. 错误处理 75 - (void)parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser parseErrorOccurred:(NSError *)parseError 76 { 77 NSLog(@"error = %@", parseError); 78 } 79 80 - (void)viewDidLoad { 81 [super viewDidLoad]; 82 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 83 } 84 85 - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { 86 [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; 87 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 88 }
4. 使用DOM工具解析XML
1> 概述
DOM:Document Object Model(文档对象模型)。DOM方式解析XML时,读入整个XML文档并构建一个驻留内存的树结构(节点树),通过遍历树结构可以检索任意XML节 点,读取它的属性和值。而且通常情况下,可以借助XPath,直接查询XML节点。
2> GDataXMLNode概述
-
采用DOM方式解析数据
-
iOS中包含一个C语言的动态链接库libxml2.dylib(xcode7以后改为libxml2.tbd),解析速度比NSXMLParser快。
-
GDataXMLNode是Google提供的开源XML解析类,对libxml2.tbd进行了Objective-C的封装,能对较小或中等的xml文档进行读写操作且支持XPath语法。
3> GDataXMLNode使用方法
-
获取GDataXMLNode.h/m文件,将GDataXMLNode.h/m文件添加到工程中。
编译后会出现一个错误
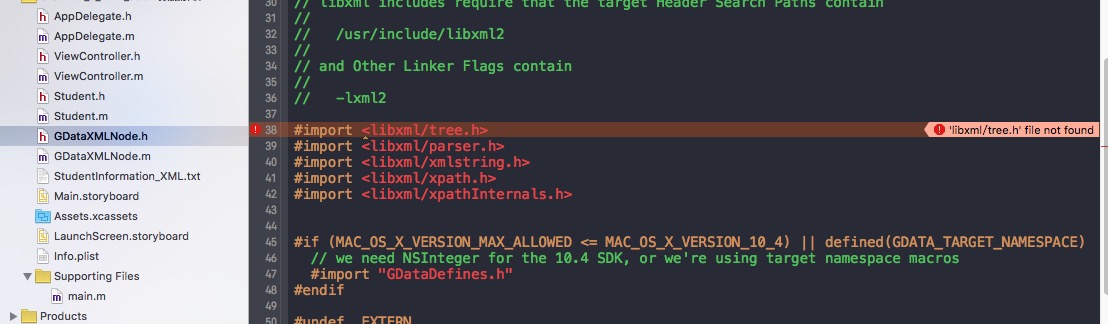
这是因为没有进行配置,朋友们不需要紧张,往下看配置。
-
向工程中增加“libxml2.tbd”动态库。
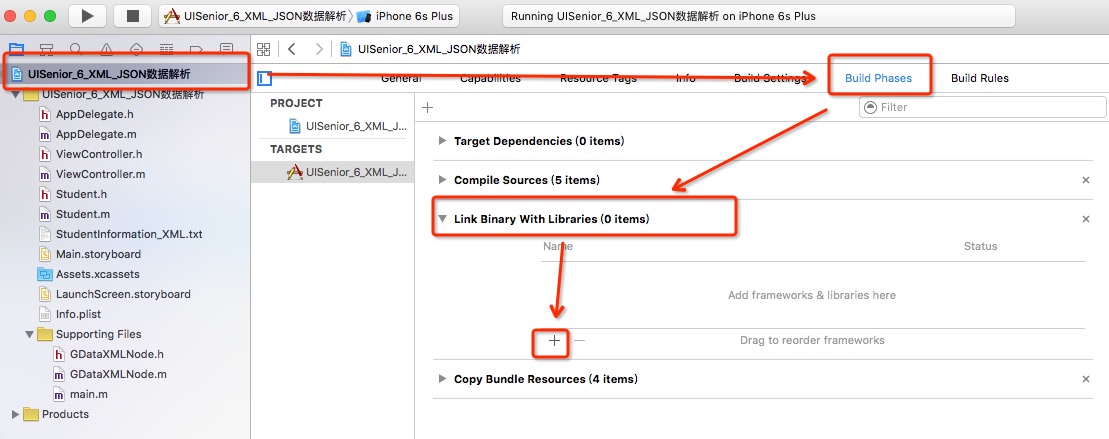
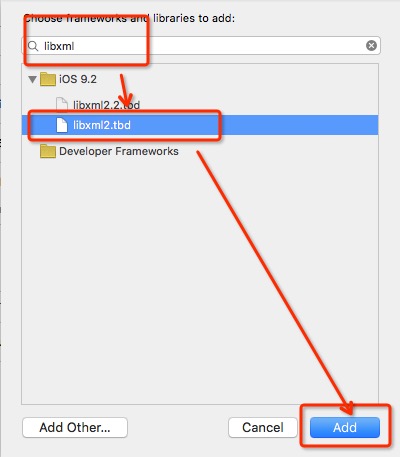
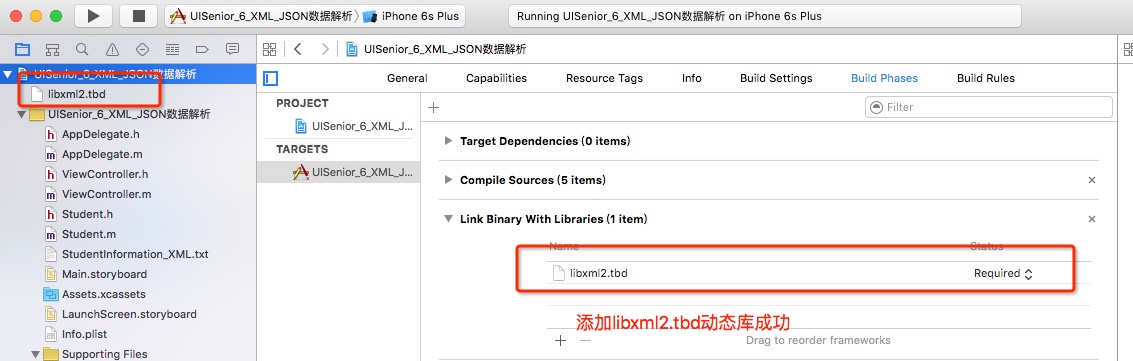
- 在工程的“Build Settings”页中找到“Header Search Path”项,添加/usr/include/libxml2”。
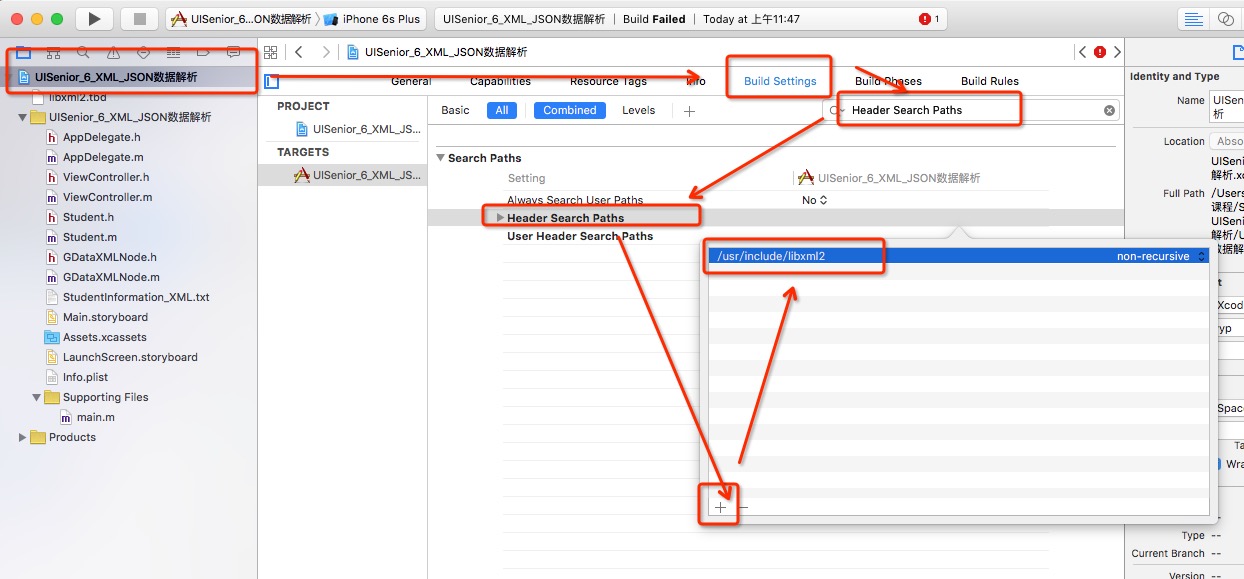
- 在工程的“Build Settings”页中找到“Other Linker Flags”项,添加“-lxml2”。

- 进行完配置后,编译后仍会出错

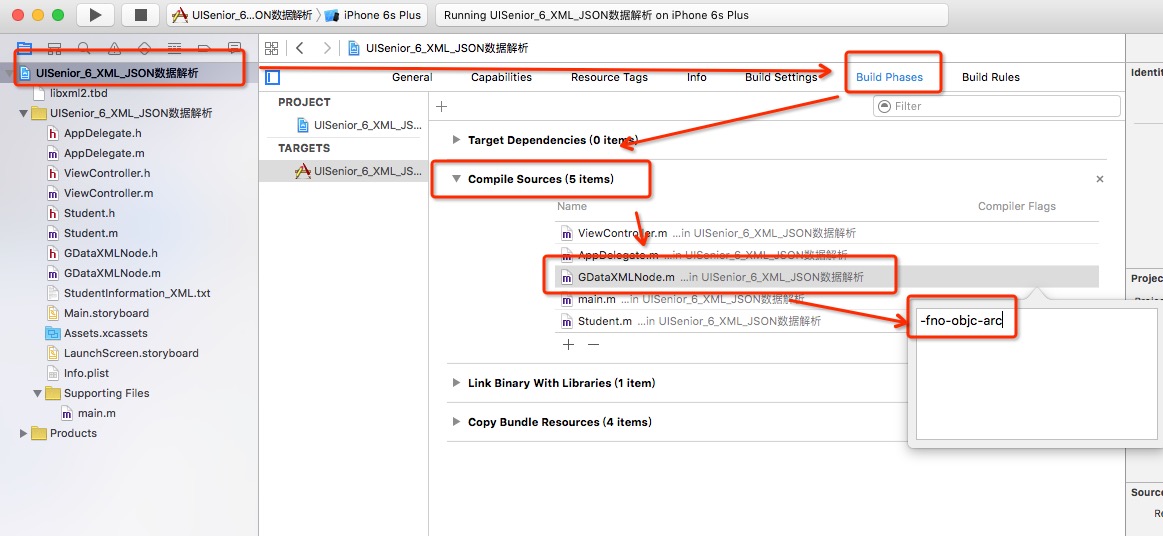
这个错误是因为 非ARC文件在ARC的环境运行时 的常见错误,解决办法:在 Build Phases 的 Compile Sources 中找到非ARC文件对应的 .m 文件, 将 Compiler Flags 的值设为 -fno-objc-arc
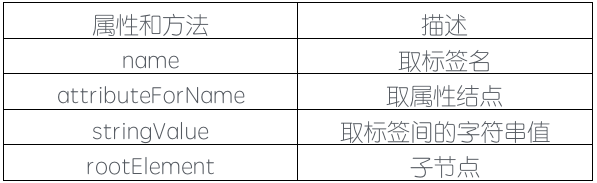
4> GDataXMLElement类的方法
5> 代码
1 #pragma mark - DOM解析xml文件 2 - (IBAction)domParserActionXMLDocument:(UIButton *)sender 3 { 4 // 第一步:引入动态库 5 6 // 1. 获取文件的路径 7 NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"StudentInfo_XML" ofType:@"txt"]; 8 9 // 2. 根据路径获取数据 10 NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path]; 11 12 // 3. 设置DOM解析(创建解析文档) 13 // 第一个参数为数据 14 // 第二个参数为选择项,是一个int型的值,一般为 0 15 GDataXMLDocument *document = [[GDataXMLDocument alloc] initWithData:data options:0 error:nil]; 16 17 // 4. 获取根节点 18 GDataXMLElement *rootElement = document.rootElement; 19 20 // 5. 遍历获取相对应的子节点 21 for (GDataXMLElement *studentElement in rootElement.children) { 22 23 Student *stu = [Student new]; 24 // 遍历子节点的子节点 25 for (GDataXMLElement *propertyElement in studentElement.children) { 26 // NSLog(@"%@", propertyElement); 27 28 // 根据标签给student赋值 29 // propertyElement.name 标签的名字 30 // propertyElement.stringValue 标签的值 31 32 // kvc 33 [stu setValue:propertyElement.stringValue forKey:propertyElement.name]; 34 } 35 36 [self.dataArray addObject:stu]; 37 } 38 39 for (Student *stu in self.dataArray) { 40 41 NSLog(@"name = %@, gender = %@, age = %ld", stu.name, stu.gender, stu.age); 42 } 43 }
5. JOSN数据结构
1> 概述
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,易于阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成。这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。
2> JSON数据结构的语法
- JSON文件有两种结构:
对象:“名称/值”对的集合。不同的语言中,它被理解为对象,记录,结构,字典,哈希表,有键列表,或者关联数组。以“{”开始,以“}”结束,是“名称/值”对的集合。名称和值中间用“:”隔开。多个“名称/值”对之间用“,”隔开。
数组: 值的有序列表。在大部分语言中,它被理解为数组。以“[”开始,以“]”结束,中间是数据。数据以“,”分隔。
- JSON中的数据类型:字符串、数值、BOOL、对象、数组。
3> JSON示例

4> JSON数据结构的功能
-
数据交换
-
内容管理
-
配置文件
6. 使用Foundation进行JSON解析
1> NSJSONSerialization
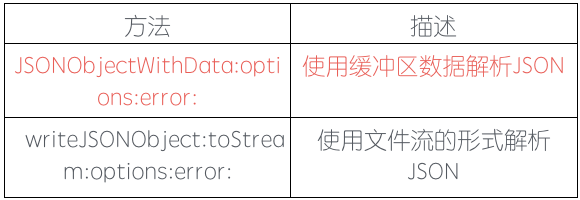
NSJSONSerialization 里面包含了两个方法来通过不同数据形式解析JSON数据。
1 - (IBAction)foundationParserActionJSONDocument:(UIButton *)sender 2 { 3 // 1. 获取文件的路径 4 NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"StudentInfo_json" ofType:@"txt"]; 5 6 // 2. 根据路径获取数据 7 NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path]; 8 9 // 3. 解析 10 // 第一个参数:数据 11 // 第二个参数:选择项,是一个int型的值,一般为 0 12 // 第三个参数:错误处理 13 NSArray *resultArray = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:NSJSONReadingAllowFragments error:nil]; 14 15 // 4. 遍历数组,使用KVC赋值 16 for (NSDictionary *dict in resultArray) { 17 18 Student *stu = [Student new]; 19 20 [stu setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:dict]; 21 22 [self.dataArray addObject:stu]; 23 } 24 25 for (Student *stu in self.dataArray) { 26 27 NSLog(@"name = %@, gender = %@, age = %ld, hobby = %@", stu.name, stu.gender, stu.age, stu.hobby); 28 } 29 }
7. 使用第三方JSONKit解析JSON数据
1> 获取JSONKit.h/m文件,将JSONKit.h/m文件添加到工程中。
源码下载地址:https://github.com/AlonerOwl/JSON-
导入后也需要进行一次 非ARC文件在ARC的环境运行时 所需要的配置,具体见 4. 3>...
2> 代码
1 #pragma mark - 使用JSONKit解析JSON数据 2 - (IBAction)jsonKitParserActionJSONDocument:(id)sender 3 { 4 // 1. 获取文件的路径 5 NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"StudentInfo_json" ofType:@"txt"]; 6 7 // 2. 根据路径获取数据 8 NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path]; 9 10 // 3. 解析 11 NSArray *resultArray = [data objectFromJSONData]; 12 13 // 4. 遍历数组,使用KVC赋值 14 for (NSDictionary *dict in resultArray) { 15 16 Student *stu = [Student new]; 17 18 [stu setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:dict]; 19 20 [self.dataArray addObject:stu]; 21 } 22 23 for (Student *stu in self.dataArray) { 24 25 NSLog(@"name = %@, gender = %@, age = %ld, hobby = %@", stu.name, stu.gender, stu.age, stu.hobby); 26 } 27 28 }
8. XML与JSON两种数据结构的优缺点
1> XML优缺点
优点:
格式统一,符合标准。
容易与其他系统进行远程交互, 数据共享比较方便。
缺点:
XML文件格式文件庞大,格式复杂, 传输占用带宽。
服务器端和客户端都需要花费大量代码来解析XML,不论服务器端还是客户端都使代码变的异常复杂和不容易维护。
客户端不同浏览器之间解析XML的方式不一致,需要重复编写很多代码。
服务器端和客户端解析XML花费资源和时间。
2> JSON优缺点
优点:
数据格式比较简单,易于读写,格式都是压缩的,占用带宽小。
易于解析这种语言。
支持多种语言,包括ActionScript,C,C#,ColdFusion,Java,JavaScript,Perl,PHP,Python,Ruby等语言服务器端语言,便于服务器端的解析。
因为JSON格式能够直接为服务器端代码使用,大大简化了服务器端和客户端的代码开发量,但是完成的任务不变,且易于维护。
缺点:
没有XML格式这么推广的深入人心和使用广泛,没有XML那么通用性。
JSON格式目前在Web Service中推广还属于初级阶段 。