一、栈
1.定义:
是一种先进后出的数据结构,只能从一端进行插入和删除的特殊线性表;
压栈:数据进入栈;
弹栈:数据出栈;
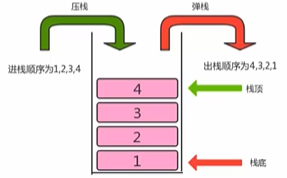
2.基本实现
1)链表,顺序表实现弹栈压栈。
2)括号匹配问题
思路:遍历字符串,如果得到的字符串是左括号,则压栈,如果是右括则从栈中弹出,如果栈中为空,则不匹配,如果不为空继续执行,当字符串遍历完的时候,看栈中是否为空,如果为空则匹配。
3)逆波兰表达式
基本思路:

/** * 使用链表实现栈 * @param <T> */ public class Stack<T> { //头结点 private Node head; //栈的元素个数 private int N; public class Node{ //元素值 T item; //结点 Node next; public Node(T item, Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; } } //初始化栈 public Stack() { this.head = new Node(null, null); this.N =0; } //压栈 public void push(T t){ //找到首结点 Node oldNode = head.next; //创建新结点 Node newNode = new Node(t, oldNode); //头结点指向新结点 head.next=newNode; //新结点指向原来的第一个结点 // newNode.next=oldNode; N++; } //弹栈 public T pop(){ //找到首结点 Node oldFirst = head.next; if(oldFirst==null){ return null; } //头结点指向首结点的下一个结点 head.next=oldFirst.next; return oldFirst.item; } /** * 括号匹配问题 */ public boolean isMatch(String str){ for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { //遍历得到每一个字符并转为字符串 String s = str.charAt(i)+""; //如果为左括号,则压栈 if(s.equals("(")){ push((T) s); }else if(s.equals(")")){ //如果为右括号,弹栈,如果为空则没有匹配的,输出false,有则继续执行 T p = pop(); if(p==null){ return false; } } } //字符串遍历完之后,看栈中是否为空,若为空则匹配,否则不匹配 if (this.n==0){ return true; }else{ return false; } } }
/* 使用线性表完成栈 */ public class Stack<T> { T [] temp; int N; int top;//栈的指针 public Stack(int n) { this.temp = (T[]) new Object[n]; this.N = 0; this.top=-1; } //压栈 public void push(T t){ if (this.top>temp.length-1){ return; } this.top++; temp[this.top]=t; N++; } //弹栈 public T pop(){ if(this.top==-1){ return null; }else{ T el=temp[this.top]; this.top--; return el; } } /** * 逆波兰表达式 */ public int caculate(String a[]){ //从左往右一次遍历逆波兰表达式 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { String s = a[i]; //判断是否为操作符 Integer op1 ; Integer op2 ; Integer result = 0; switch (s){ case "+": //如果为运算符,从栈中弹出两个元素,进行相应的操作 op1= (Integer) pop(); op2=(Integer)pop(); result= op2+op1; push(result); break; case "-": op1= (Integer) pop(); op2=(Integer)pop(); result= op2-op1; push(result); break; case "*": op1= (Integer) pop(); op2=(Integer)pop(); result= op2*op1; push(result); break; case "/": op1= (Integer) pop(); op2=(Integer)pop(); result= op2/op1; push( result); break; default: //为操作数则压入栈中; push( Integer.parseInt(s)); break; } } //弹出元素,即为运算结果 T result=pop(); return (Integer) result; }