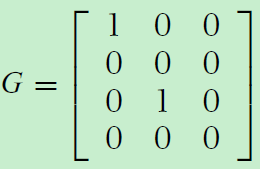from the book principles and practices of interconnection networks
the chapter router architecture
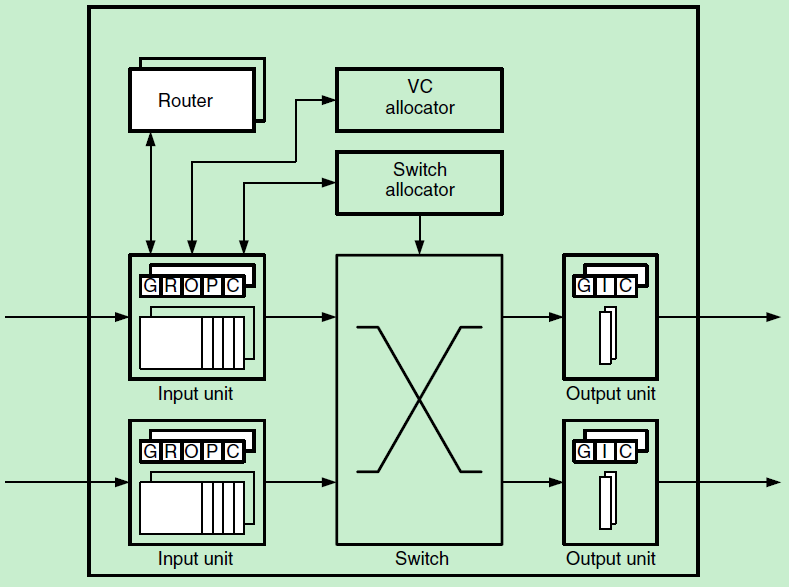
These blocks of the router can be partitioned broadly into two groups based on functionality: the datapath and control plane.
The datapath of the router handles the storage and movement of a packet’s payload and consists of a set of input buffers, a switch, and a set of output buffers.
The remaining blocks implement the control plane of the router and are responsible for coordinating the movement of packets through the resources of the datapath.
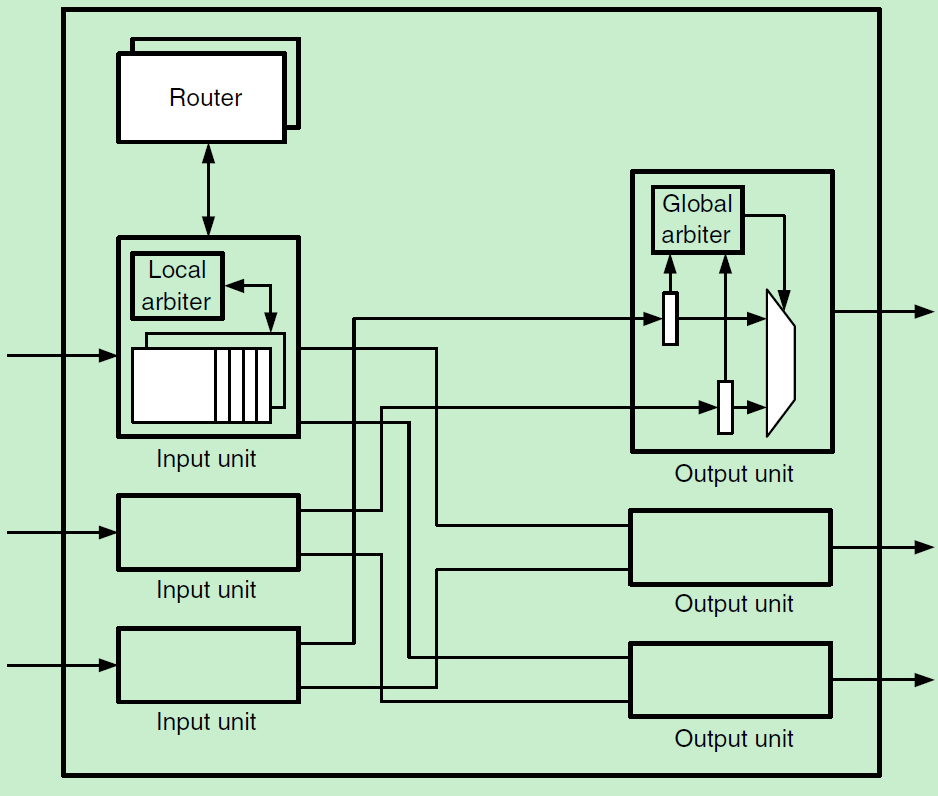
The 21364’s crossbar is implemented as a mux for each output port, as shown.
To meet its aggressive timing requirements, the switch allocator is divided into two distinct units: a local arbiter and a global arbiter.
The local arbiters in each input unit choose a packet among all waiting packets that are ready.
A packet is considered ready when its output port is available and its downstream router has a free packet buffer.
Local arbitration takes one pipeline cycle (SA1) and, during the following cycle, the header information for each packet selected by a local arbiter is read and transported to the correct output (RE).
This header information is enough to begin the global arbitration cycle (SA2).
Since the local arbitration decisions are not coordinated, its quite possible that multiple packets have been selected for a single output.
The global arbiters resolve this conflict by choosing one packet for each output.
background:
While the augmenting path method always finds the maximum matching, it is difficult to parallelize or pipeline and is too slow for applications in which latency is important.
Therefore, the heuristic allocators based on a basic separable alloctor are proposed.
Most heuristic allocators are based on a basic separable allocator.
In a separable allocator, we perform allocation as two sets of arbitration: one across the inputs and one across the outputs.
In an input first separable allocator, an arbitration is first performed to select a single request at each input port.
Then, the outputs of these input arbiters are input to a set of output arbiters to select a single request for each output port.
The result is a legal matching, since there is at most one grant asserted for each input and for each output.
consequence:
It is possible for an input request to win the input arbitration, locking out the only request for a different output, and then lose the output arbitration.
This leaves an input and an output, which could have been trivially connected, both idle.

A 4 × 3 input-first separable allocator. A separable allocator performs allocation using two ranks of arbiters.
With an input-first allocator, the first rank picks one request from each input.
The second rank picks one of these selected input requests for each output.
An input-first separable allocator takes a request matrix and performs arbitration across the rows first and then down the columns.

Assume each arbiter selects the first asserted input.
Thus, the intermediate request matrix X after the input arbiters is
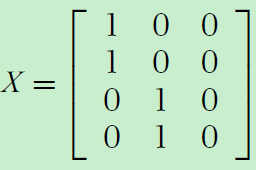
Note that X has eliminated input conflicts and thus has at most one non-zero entry in each row.
The output arbiters then eliminate output conflicts, giving a final grant matrix G with at most one non-zero in each column as well: