java web技术三大组件之servlet
在ava web应用之中核心组件有三个:servlet 、Filter、Listener。本篇文章主要介绍servlet相关的基础知识
servlet的定义
从代码的角度看,搜索的Servlet都是实现了servlet接口的实现类,如果的单纯的实现servlet接口,实现servlet接口会比较麻烦,有好多功能需要自己写,所以我们一般继承HttpServlet类。
下面是Servlet的结构图
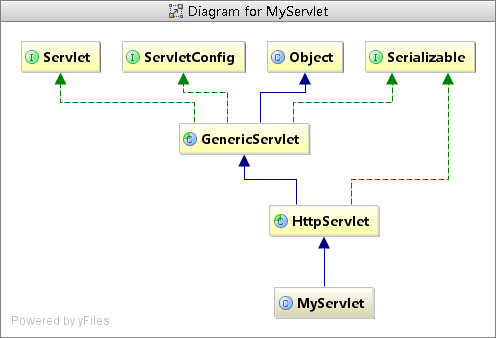
继承HttpServlet后的MyServlet类就会有许多扩展的方法供我们使用,如下图
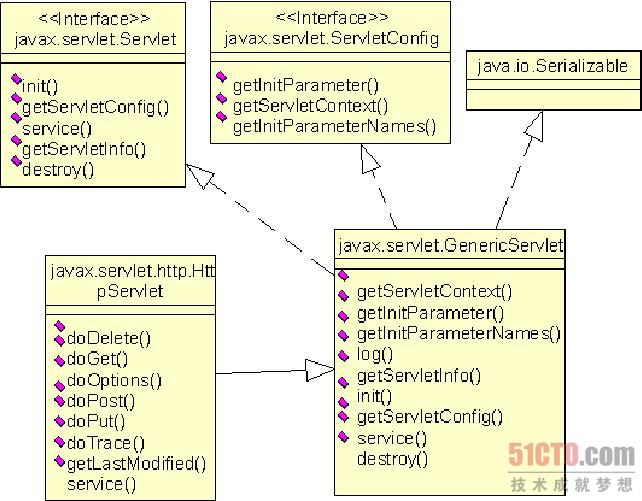
下面的代码就是一个实现例子
package com.web.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public MyServlet() { super(); System.out.println("MyServlet() 构造器运行"); } @Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { super.init(config); System.out.println("servlet 开始初始化"); } @Override public void destroy() { super.destroy(); System.out.println("servelt开始销毁"); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("请求执行了"); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
Servlet定义好之后,可以通过web.xml进行注册,也可以通过ServletContainerInitializer接口的实现类进行注册(SPI机制实现),
https://www.cnblogs.com/cplinux/p/12312496.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/cplinux/p/12323316.html
Servlet 的生命周期
从之前的内容我们知道,我们编写的MyServlet其实是一个实现了Servlet接口的类,那么这个类要运行就必须加载进虚拟机中,
(1)Servlet默认的加载时机是在第一次访问时,
(2)但是有的Servlet比较特殊,需要在Tomcat启动时就加载并且实例化,比如DispatcherServlet。这个可以通过web.xml文件中的<load-on-startup>进行配置。
(3)Servlet实例化之后,会调用执行init方法,并且这个方法只执行一次
(4) init方法执行之后,就是执行service方法,或者doGet/doPost方法,这些方法时用来相应用户请求的
(5) 当服务器关闭时,destroy() 方法只会被调用一次,在 Servlet 生命周期结束时被调用。 destroy() 方法可以让您的 Servlet 关闭数据库连接、停止后台线程、把 Cookie 列表或点击计数器写入到磁盘,并执行其他类似的清理活动。
package javax.servlet; import java.io.IOException; public interface Servlet { /** * Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the * servlet is being placed into service. * * <p>The servlet container calls the <code>init</code> * method exactly once after instantiating the servlet. * The <code>init</code> method must complete successfully * before the servlet can receive any requests. * * <p>The servlet container cannot place the servlet into service * if the <code>init</code> method * <ol> * <li>Throws a <code>ServletException</code> * <li>Does not return within a time period defined by the Web server * </ol> * * * @param config a <code>ServletConfig</code> object * containing the servlet's * configuration and initialization parameters * * @exception ServletException if an exception has occurred that * interferes with the servlet's normal * operation * * @see UnavailableException * @see #getServletConfig * */ public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException; /** * * Returns a {@link ServletConfig} object, which contains * initialization and startup parameters for this servlet. * The <code>ServletConfig</code> object returned is the one * passed to the <code>init</code> method. * * <p>Implementations of this interface are responsible for storing the * <code>ServletConfig</code> object so that this * method can return it. The {@link GenericServlet} * class, which implements this interface, already does this. * * @return the <code>ServletConfig</code> object * that initializes this servlet * * @see #init * */ public ServletConfig getServletConfig(); /** * Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to * a request. * * <p>This method is only called after the servlet's <code>init()</code> * method has completed successfully. * * <p> The status code of the response always should be set for a servlet * that throws or sends an error. * * * <p>Servlets typically run inside multithreaded servlet containers * that can handle multiple requests concurrently. Developers must * be aware to synchronize access to any shared resources such as files, * network connections, and as well as the servlet's class and instance * variables. * More information on multithreaded programming in Java is available in * <a href="http://java.sun.com/Series/Tutorial/java/threads/multithreaded.html"> * the Java tutorial on multi-threaded programming</a>. * * * @param req the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains * the client's request * * @param res the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that contains * the servlet's response * * @exception ServletException if an exception occurs that interferes * with the servlet's normal operation * * @exception IOException if an input or output exception occurs * */ public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException; /** * Returns information about the servlet, such * as author, version, and copyright. * * <p>The string that this method returns should * be plain text and not markup of any kind (such as HTML, XML, * etc.). * * @return a <code>String</code> containing servlet information * */ public String getServletInfo(); /** * * Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the * servlet is being taken out of service. This method is * only called once all threads within the servlet's * <code>service</code> method have exited or after a timeout * period has passed. After the servlet container calls this * method, it will not call the <code>service</code> method again * on this servlet. * * <p>This method gives the servlet an opportunity * to clean up any resources that are being held (for example, memory, * file handles, threads) and make sure that any persistent state is * synchronized with the servlet's current state in memory. * */ public void destroy(); }
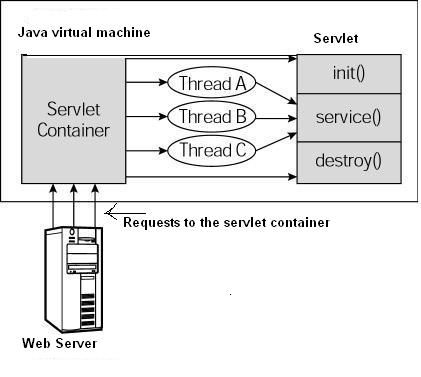
Servlet的实例对象是单例的,在整个tomcat运行期间,一个Servlet只有一个实例,但是每个Http请求确有一个线程,如果一个Servlet被多次请求,那么就会产生多个线程。