在使用集合的过程中,我们经常会有遍历集合元素,删除指定的元素的需求,而对于这种需求我们往往使用会犯些小错误,导致程序抛异常或者与预期结果不对,本人很早之前就遇到过这个坑,当时没注意总结,结果前段时间又遇到了这个问题,因此,总结下遍历集合的同时如何删除集合中指定的元素;
1.错误场景复原
public class ListRemoveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
或者如下代码
public class ListRemoveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
for (User user : users) {
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
以上两种用法都会跑出如下异常:
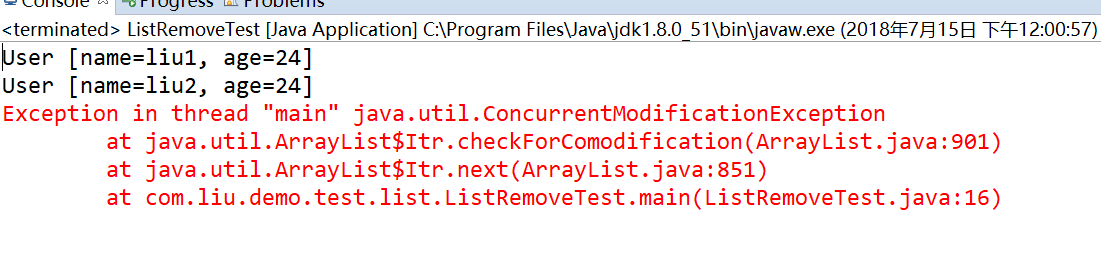
2.原因分析
上面两种错误,我想很多人都遇到过,这是我们很容易犯的错误,但是为啥会出现上述异常呢,我们又该如何正确遍历集合的同时,删除指定的元素呢!
2.1 原因解析
首先,对于foreach循环遍历,本质上还是迭代器的模式,上面的for语句等价于如下代码:
for (Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
因此,上述错误的本质,就要看迭代器iterator的源码啦
在ArrayList中,它的修改操作(add/remove)都会对modCount这个字段+1,modCount可以看作一个版本号,每次集合中的元素被修改后,都会+1(即使溢出)。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
接下来再看看AbsrtactList中iteraor方法
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
它返回一个内部类,这个类实现了iterator接口,代码如下:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor = 0;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
E next = get(cursor);
lastRet = cursor++;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor)
cursor--;
lastRet = -1;
// 修改expectedModCount 的值
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
在内部类Itr中,有一个字段expectedModCount ,初始化时等于modCount,即当我们调用list.iterator()返回迭代器时,该字段被初始化为等于modCount。在类Itr中next/remove方法都有调用checkForComodification()方法,在该方法中检测modCount == expectedModCount,如果不相等则抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
前面说过,在集合的修改操作(add/remove)中,都对modCount进行了+1。
在迭代过程中,执行list.remove(val),使得modCount+1,当下一次循环时,执行 it.next(),checkForComodification方法发现modCount != expectedModCount,则抛出异常。
2.2 预期结果不对,但是不抛异常
注意:还有一种更坑的场景,当删除集合的倒数第二个元素时,程序不会抛出任何异常,只是结果与预期的不相符,如果在应用过程中不认真观察,很难发现该错误!
错误实例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu3")) {
users.remove(user);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
}
运行结果如下:
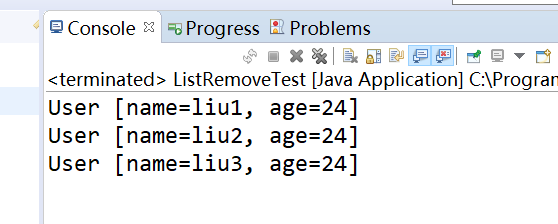
遍历过程删除了倒数第二个元素,那么最后一个元素就永远遍历不到了,这个主要原因就是Iterator源码中hasNext方法中,判断当前元素下标和集合大小是否相等
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
当删除倒数第二个元素后,当前元素下标和集合的大小相等了,跳出了循环,就会遍历最后一个集合元素了;
3.正确用法
要想在集合遍历的过程中删除指定元素,就务必使用迭代器自身的remove方法;
再来看看内部类Itr的remove()方法,在删除元素后,有这么一句expectedModCount
= modCount,同步修改expectedModCount
的值。所以,如果需要在使用迭代器迭代时,删除元素,可以使用迭代器提供的remove方法。
其他集合(Map/Set)使用迭代器迭代也是一样。
所以 Iterator 在工作的时候是不允许被迭代的对象被改变的。
但你可以使用 Iterator 本身的方法 remove() 来删除对象, Iterator.remove() 方法会在删除当前迭代对象的同时维护索引的一致
具体正确用法代码如下:
public class ListRemoveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("liu1",24));
users.add(new User("liu2",24));
users.add(new User("liu3",24));
users.add(new User("liu4",24));
Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
User user = iterator.next();
if(user.getName().equals("liu2")) {
iterator.remove();
}
System.out.println(user);
}
System.out.println(users);
}
}
运行结果如下:

与预期结果一致;