URL队列被爬行进程赋予一个URL(或者来自于其他爬行进程的主机分离器)。它维护了一个包含大量URL的队列,并且每当有爬虫线程寻找URL的时候,它都会按照某种顺序重新排序。以何种顺序返回队列中的URL,需要有两个方面的考虑。
第一个要考虑的是具有很高更新频率的高质量页面,即页面的优先级。一个页面的优先级权值应该是由它的改变频率和它本身网页质量(使用一些恰当的质量评估方法)共同决定的。这是很必要的,因为在每次抓取的时候,很多更新频率很高的页面都是质量很差的垃圾页面。
第二个要考虑的就是礼貌策略:我们必须避免在很短的时间间隔内重复抓取同一个主机。因此,如果URL队列被设计成简单的优先级队列的话,可能会造成对某一主机的大量的访问请求。就算我们设定对于某台主机,任何时候最多只允许一个线程可以进行爬取,这样的情况仍然会发生。一个好的想法是在对某一主机进行连续的爬取请求之间插入一段时间间隔,这个空隙的数量级应该大于最近大部分对该主机爬取所花费的时间。
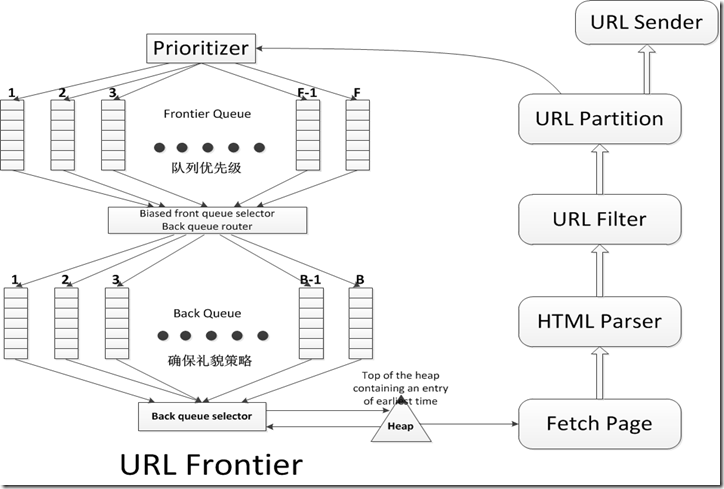
图1 展示了一个基于礼貌和权值策略的URL队列的实现。它的目标是确保(i)每次只有一个连接去访问一台主机 (ii)连续对同一个主机的访问请求之间存在几秒钟的等待时间(有时robots.txt文件会指定这个时间) (iii)具有高优先级的页面将会被优先爬取。
图1 中有两个重要的子模块,前部分的front队列集合F以及后部分的back队列集合B。这两种队列均是FIFO队列。Front队列实现了对权值相关处理,而back队列实现了对礼貌策略的相关处理。在一条URL被添加到队列的过程中,它将会先后穿越front和back队列。首先,权值计算器会给该URL分配一个介于1和F之间的整数权值,该权值是可能基于爬取历史记录而得出的,比如参考该URL所指向的页面内容在最近几次爬取之间改变的频率(关于优先级权值的讨论是一个很大的话题,不展开讨论)。例如,具有很高更新频率的文档将会被赋予一个很高的权值。类似的还有某些明确的特定的应用,比如新闻类的页面可能总是会被赋予很高的权值。在该URL被赋予了权值i之后,它将会被添加到front队列集合中的第i个队列。
每个back队列需要遵循下面的几条不变定律:
(i)当它处于信息采集过程中,必须保证其队列是非空的。
(ii)它只包含来自于同一台主机上的URL。一个辅助表T(图2)被用来维护主机到back队列之间的映射关系。每当back队列为空,要被front队列重新填充的时,T表必须要进行相应的更新。
图1 URL队列
从爬取页面上抽取出来的URL会流向图表中的顶端。爬取线程会从图示的底部抽取出待爬取的URL。一个URL在整个过程会穿过负责处理权值的front队列,以及负责处理爬虫礼貌策略的back队列。
|
主机 |
Back 队列 |
|
standford.edu |
23 |
|
microsoft.com |
47 |
|
acm.org |
12 |
图2 主机到Back队列对应关系的辅助表格样例
此外,我们需要维护一个堆,堆里存放着的条目对应每一个back队列,该条目记录着该队列所对应的主机可以再次被连接的最早时间te。请求获取URL的爬虫线程会抽取出堆顶元素,然后一直等到相应te时间。接下来,它会获取到该堆顶元素所对应的back队列j的队首URL u,进而开始进行URL u的抓取。抓取过程完成后,调用线程会检查队列j是否为空。如果为空,它会挑选一个front队列,然后抽取出其队首URL v。Front 队列的选择方法对于更高优先级的队列来说可能并不公平(通常是一个随机的过程),但这样做是确保高优先级的URL可以更快的流入到back队列中来。接下来,我们会检查v,判断v所对应的主机是否已经存在并且已经存有一些URL。如果是这样的话,v 会被添加到该队列里,然后重新返回到front队列,寻找另一个可以插入到空队列 j 的URL。这个过程会一直持续,直到队列 j 再次变为非空。同时,该线程会向堆中插入一条包含最早开始时间 te的新条目,这个时间是根据队列 j 中最新被提取的URL的相关属性所决定的(比如上次何时进行的连接或是上次爬取花费的时间),之后会继续执行这个过程。
Front队列的数量以及分配权值和挑选队列的策略共同组成了我们希望植入系统的优先级属性。Back队列的数量决定着我们可以维持多少线程处于运行状态同时又遵守着礼貌性特征。Mercator的设计者提出一个比较粗糙的建议:可以使用数量三倍于爬虫线程的back队列。
在大规模下的信息采集过程中,随着URL队列的增长,可能会造成节点的可用内存不足(经过实验,的确是这样,这个问题也是很棘手的问题)。一个解决方法是让大多数URL队列存储在磁盘上,只将每个队列中的一部分保存在内存中,当内存中数据不足时,可以从磁盘中读取更多的数据。
一些关键实现细节(linux,c++):
维护一个最小堆,堆的比较元素为爬取时间te,使用的sys/time.h文件下的timeval变量类型,它在linux环境下,可以精确到微妙,但是不会特别精确。
/*
* minheap.h
*
* Created on: 2012-2-24
* Author: xiaojay
*/
#ifndef MINHEAP_H_
#define MINHEAP_H_
#include <sys/time.h>
struct node {
timeval te;
int backpos;
public:
node() //default constructor
{
backpos = -1;
}
};
class minheap
{
private:
int maxheapsize;
int currentsize;
node * heap;
//adjust the head from upon downto bottom
void siftdown(int currentPos , int m);
//adjust the heap from bottom to upon
void siftup(int start);
public:
//build a min heap
minheap(int maxheapsize);
~minheap();
//insert an element
void insert(timeval te, int backpos);
//remove an element
//position of back queue in urlfrontier.h and node.te returns as reference value
void removemin(int & backpos , timeval & te);
inline int size() {return this->currentsize ;}
};
#endif
#include"minheap.h"
#include<assert.h>
//constructor
minheap::minheap(int maxheapsize)
{
assert(maxheapsize>0);
this->maxheapsize = maxheapsize;
this->currentsize = 0;
heap = new node [maxheapsize];
}
//destructor
minheap::~minheap()
{
delete [] heap;
}
//adjust the heap from top to bottom
void minheap::siftdown(int currentPos , int m)
{
int i=currentPos;
int j=currentPos*2+1;//i's leftChild
timeval temp=heap[i].te;
int temppos = heap[i].backpos;
while(j<=m)
{
if(j<m&&timercmp(&heap[j].te,&heap[j+1].te,>)) j++; // j points to minChild
if(timercmp(&temp,&heap[j].te,<=)) break;
else
{
heap[i].te=heap[j].te;
heap[i].backpos = heap[j].backpos;
i=j;
j=2*i+1;
}
}
heap[i].te=temp;
heap[i].backpos = temppos;
}
//adjust the heap from bottom to top
void minheap::siftup(int start)
{
int i=start,j=(i-1)/2;
timeval temp=heap[i].te;
int temppos = heap[i].backpos;
while(i>0)
{
if(timercmp(&heap[j].te,&temp,>))
{
heap[i].te=heap[j].te;
heap[i].backpos = heap[j].backpos;
i=j;
j=(i-1)/2;
}
else break;
}
heap[i].te=temp;
heap[i].backpos = temppos;
}
//add a node to heap
void minheap::insert(timeval te , int backpos)
{
if(currentsize>=maxheapsize)
{
return ;
}
heap[currentsize].te=te;
heap[currentsize].backpos = backpos;
siftup(currentsize);
currentsize++;
}
//pass value to backpos and te then remove the node
void minheap::removemin(int & backpos , timeval & te)
{
assert(currentsize>=0);
backpos = heap[0].backpos;
te = heap[0].te;
heap[0] = heap[currentsize-1];
currentsize --;
siftdown(0, currentsize-1);
}
urlFrontier 实现:
/*
* urlfrontier.h
*
* Created on: 2012-3-2
* Author: xiaojay
*/
#ifndef URLFRONTIER_H_
#define URLFRONTIER_H_
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include "url.h"
#include "minheap.h"
#include "../config.h"
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
class urlfrontier
{
private:
/*frontQueue maintains urls which have higher priority
cound route to back queue more quickly.
frontQueue[i] contains all urls whose priority is i.*/
queue<url *> * frontQueue;
/*
backQueue[i] contains urls whose have the same hostname
*/
queue<url *> * backQueue;
int maxF,maxB;//the max number of frontQueue and backQueue
map<string,int> hostmap;
minheap * heap;
//route urls from frontQueue to backQueue
bool router();
int size;
public:
//constructor
//parameters: nf->maxF, nb->maxB
urlfrontier (int nf , int nb);
//destructor
~urlfrontier();
//add a url
void pushurl(url * u) ;
//get a url
url * popurl();
void displayState();
int getsize(){return this->size;}
};
#endif /* URLFRONTIER_H_ */
#include "urlfrontier.h"
//constructor
urlfrontier::urlfrontier( int nf , int nb)
{
this->maxF = nf;
this->maxB = nb;
this->size = 0;
frontQueue = new queue<url *>[maxF];
backQueue = new queue<url *>[maxB];
heap = new minheap(nb);
}
//destructor
urlfrontier::~urlfrontier()
{
delete [] frontQueue;
delete [] backQueue;
delete heap;
}
//add url
void urlfrontier::pushurl(url * u)
{
if(!u->isValid()) return ;
int priority = u->getPriority();
if(priority>=maxF|| priority<0) return ;
frontQueue[priority].push(u);
size++;
//router();
}
//route urls from frontQueue to backQueue
bool urlfrontier ::router()
{
int pos = maxF;
int size = 0;
/*MAX_URLS_ONCE limits the max number of urls moved ,
to ignore much expenses*/
int limit = MAX_URLS_ONCE;
while(pos>0&&limit>0)
{
limit--;
pos--;
size = frontQueue[pos].size();
if (size==0) continue;
while(!frontQueue[pos].empty()&&size>0)
{
size--;
url * u = frontQueue[pos].front();
if(hostmap.count(u->getHost()))
{
int backpos = hostmap[u->getHost()];
backQueue[backpos].push(u);
frontQueue[pos].pop();
}
else
{
//find empty pos ;
int posB = 0;
while(posB<maxB&&!backQueue[posB].empty()) posB++;
if(posB==maxB)
{
frontQueue[pos].pop();
frontQueue[pos].push(u);
continue;
}
//update the hostmap
hostmap.insert(map<string,int>::value_type(u->getHost(),posB));
backQueue[posB].push(u);
//update heap
timeval now ;
gettimeofday(&now,NULL);
heap->insert(now,posB);
frontQueue[pos].pop();
}
}
}
return true;
}
//get a url
url * urlfrontier::popurl()
{
if(heap->size()<=0)
{
router();
}
if(heap->size()<=0) return NULL;
int backpos;
timeval te;
heap->removemin(backpos,te);
url * u = backQueue[backpos].front();
u->setTe(te);
if(u==NULL) return NULL;
backQueue[backpos].pop();
if(backQueue[backpos].empty())
{
router();//route urls from frontqueue to backqueue
hostmap.erase(u->getHost());
}
else
{
//the time between two request is 5 seconds
te.tv_sec += 5;
heap->insert(te,backpos);
}
size --;
return u ;
}
参考资料:
(美)Christopher D. Manning, Prabhakar Raghavan, Hinrich Schütze. Introduction to information retrieval: 信息检索导论[M].北京:人民邮电出版社,2010