以前在对egg进行换壳tcp时,看到加载了各种配置,到触发生命周期方法。然而改完过了几个月就忘记了,还是记录一下吧,以免下次忘记的时候翻翻。
egg在load了plugin、config、extend后,最后会有一个loadCustomAgent(loadCustomApp)方法,很关键的一个方法,主要是用来启动app.js里的configWillLoad、configDidLoad、willReady等一系列生命周期方法。
以Agent为例,在初始化Agent实例的时候,会实例化一个Lifecycle实例,Lifecycle又实例化两个Ready实例: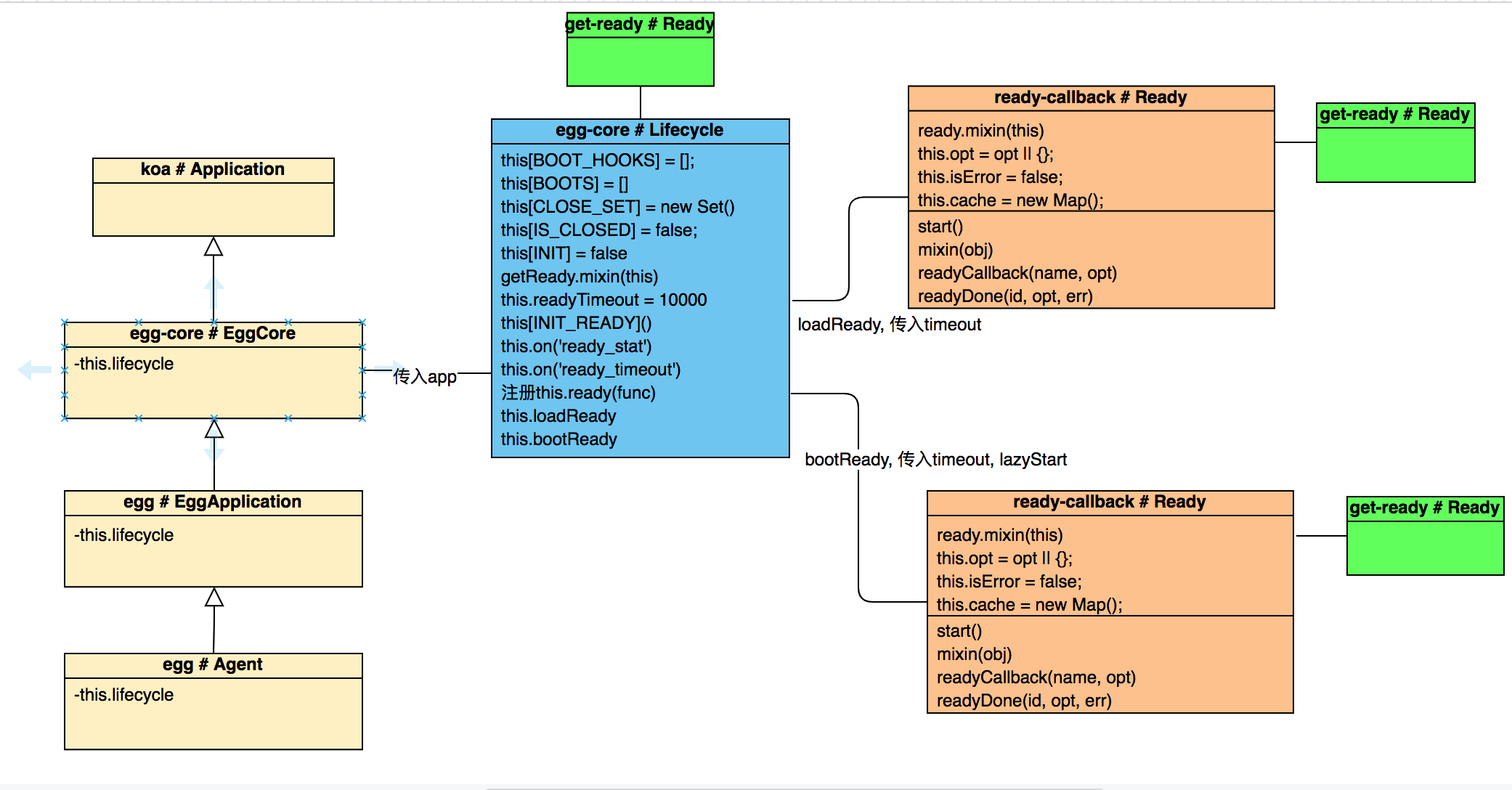
get-ready就像一个搅局者,混进了各个类里面,为类注入ready方法。还有ready-callback实属是对get-ready的封装(这肯定是阿里的人写的。一看npm,果然!)
前期准备做好后,开始:
// egg-core/lib/loader/mixin/custom.js
loadCustomAgent() {
this[LOAD_BOOT_HOOK]('agent');
this.lifecycle.triggerConfigWillLoad();
},
this[LOAD_BOOT_HOOK]在各个加载路径下找到agent.js,并把导出对象加在lifecycle的 this[BOOT_HOOKS] = []里,伪代码:
const agentObj = require('xxx/agent.js');
lifecycle.boot_hooks.push(agentObj);
// 假设agent.js如以下内容
'use strict';
class AppBootHook {
constructor(app) {
this.app = app;
}
configWillLoad() {}
async didLoad() {}
async willReady() {}
async didReady() {}
async serverDidReady() {}
}
module.exports = AppBootHook;
push进来之后,再调用lifecycle.init(),新建一个个agent实例,保存在lifecycle.boots数组:
// egg-core/lib/lifecycle.js
init() {
assert(this[INIT] === false, 'lifecycle have been init');
this[INIT] = true;
this[BOOTS] = this[BOOT_HOOKS].map(t => new t(this.app));
}
最后,终于触发 this.lifecycle.triggerConfigWillLoad(),同步调用configWillLoad、configDidLoad方法:
// egg-core/lib/lifecycle.js
triggerConfigWillLoad() {
for (const boot of this[BOOTS]) {
if (boot.configWillLoad) {
boot.configWillLoad();
}
}
this.triggerConfigDidLoad();
}
关键来了,上一步触发了configDidLoad,接下来触发didLoad方法,代码是这样的:
// egg-core/lib/lifecycle.js
triggerDidLoad() {
debug('register didLoad');
for (const boot of this[BOOTS]) {
const didLoad = boot.didLoad && boot.didLoad.bind(boot);
if (didLoad) {
this[REGISTER_READY_CALLBACK]({
scope: didLoad,
ready: this.loadReady,
timingKeyPrefix: 'Did Load',
scopeFullName: boot.fullPath + ':didLoad',
});
}
}
}
boot.fullPath是该agent.js的全路径;
再到REGISTER_READY_CALLBACK方法:
// egg-core/lib/lifecycle.js
[REGISTER_READY_CALLBACK]({ scope, ready, timingKeyPrefix, scopeFullName }) {
const done = ready.readyCallback(scopeFullName);
process.nextTick(() => {
utils.callFn(scope).then(() => {
done();
}, err => {
done(err);
});
});
}
调用了loadReady.readyCallBack方法,传入一个全路径标识符,去ready-callback找吧:
// ready-callback/lib/ready.js
readyCallback(name, opt) {
opt = Object.assign({}, defaults, this.opt, opt);
const cacheKey = uuid.v1();
opt.name = name || cacheKey;
const timer = setTimeout(() => this.emit('ready_timeout', opt.name), opt.timeout);
const cb = once(err => {
if (err != null && !(err instanceof Error)) {
err = new Error(err);
}
clearTimeout(timer);
// won't continue to fire after it's error
if (this.isError === true) return;
// fire callback after all register
setImmediate(() => this.readyDone(cacheKey, opt, err));
});
debug('[%s] Register task id `%s` with %j', cacheKey, opt.name, opt);
cb.id = opt.name;
this.cache.set(cacheKey, cb);
return cb;
}
只传入了一个路径标识,没有传函数执行体,所以这个函数肯定是用来控制流程的。来了个once模块,传入回调,搭配wrappy模块,作用是保证只执行一次传入的回调。
返回后,注册process.nextTick microtask:
// egg-core/lib/lifecycle.js
[REGISTER_READY_CALLBACK]({ scope, ready, timingKeyPrefix, scopeFullName }) {
const done = ready.readyCallback(scopeFullName);
process.nextTick(() => {
utils.callFn(scope).then(() => {
done();
}, err => {
done(err);
});
});
}
此时,同步代码执行完毕,事件循环转到下一阶段,开始执行process.nextTick的任务,里面的任务就是didLoad方法,didLoad是异步方法,执行完成didLoad方法,再执行done,done就是上面的传入once的方法体:
// ready-callback/lib/ready.js
const cb = once(err => {
if (err != null && !(err instanceof Error)) {
err = new Error(err);
}
clearTimeout(timer);
// won't continue to fire after it's error
if (this.isError === true) return;
// fire callback after all register
setImmediate(() => this.readyDone(cacheKey, opt, err));
});
再次异步调用readyDone方法:
// ready-callback/lib/ready.js
readyDone(id, opt, err) {
this.cache.delete(id);
this.emit('ready_stat', {
id: opt.name,
remain: getRemain(this.cache),
});
if (this.cache.size === 0) {
this.ready(true);
}
return this;
}
如果发现此时,已经没有didLoad方法了,即this.cache.size === 0,就触发ready方法,而在lifecycle里,实例化loadReady时,早就注册了ready方法:
// egg-core/lib/lifecycle.js
this.loadReady.ready(err => {
debug('didLoad done');
if (err) {
this.ready(err);
} else {
this.triggerWillReady();
}
});
此时,ready方法触发,执行域是在ilfecycle,调用triggerWillReady方法,继续往下走生命周期方法,这样就串起来了。
总结来说,egg同阶段的生命周期方法都是异步调用(通过process.nextTick调用),只有等最后那个异步方法调用完成,才触发下一个阶段。
其实可以做的更简单直观点,相当于各个模块之间dependency,执行有个先后顺序。