1.集合遍历时候,有时候需要remove或add操作,这时候遍历方式可能会影响程序运行
例如:
@Test public void test1() { List<Integer> intList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { intList.add(Integer.valueOf(i)); } // 迭代器遍历, 异常 Iterator<Integer> iterator_int = intList.iterator(); while (iterator_int.hasNext()) { Integer integer = iterator_int.next(); //ConcurrentModificationException if (integer.intValue() == 5) { //这里选择集合靠中间的数据操作 //intList.remove(integer); //这里使用集合的remove方法 intList.add(55); } } // foreach遍历, 异常 for (Integer value : intList) { //ConcurrentModificationException if (value.intValue() == 5) { intList.remove(value); //这里使用集合的remove方法 } } //普通for循环 , 正常 for (int i = 0; i < intList.size(); i++) { if (intList.get(i) == 5) { intList.remove(intList.get(i)); } } }
2.为什么上面的迭代器和foreach遍历会有异常?
首先,看迭代器方式遍历,在 iterator_int.next() 方法出报异常.看一下源码:
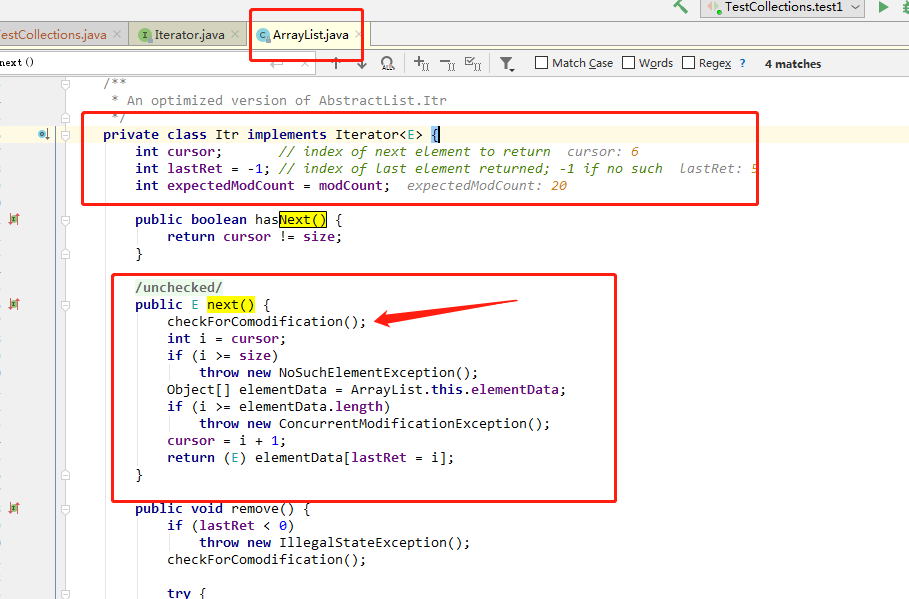
① 在父类AbstractList中定义了一个int型的属性:modCount
protected transient int modCount = 0;
② 在ArrayList的所有涉及结构变化的方法中都增加modCount的值,包括:add()、remove()、addAll()、removeRange()及clear()方法。这些方法每调用一次,modCount的值就加1。
注:add()及addAll()方法的modCount的值是在其中调用的ensureCapacity()方法中增加的。
③AbstractList中的iterator()方法(ArrayList直接继承了这个方法)使用了一个私有内部成员类Itr,生成一个Itr对象(Iterator接口)返回:
public Iterator iterator() { return new Itr(); }
④ Itr实现了Iterator()接口,其中也定义了一个int型的属性:expectedModCount,这个属性在Itr类初始化时被赋予ArrayList对象的modCount属性的值。
int expectedModCount = modCount;
注:内部成员类Itr也是ArrayList类的一个成员,它可以访问所有的AbstractList的属性和方法。理解了这一点,Itr类的实现就容易理解了。
⑤ checkForComodification (检查是否并发修改)
/**
* 在对一个集合对象进行跌代操作的同时,并不限制对集合对象的元素进行操作
* 这些操作包括一些可能引起跌代错误的add()或remove()等危险操作。
* 在AbstractList中,使用了一个简单的机制来规避这些风险。
* 这就是modCount和expectedModCount的作用所在
*/
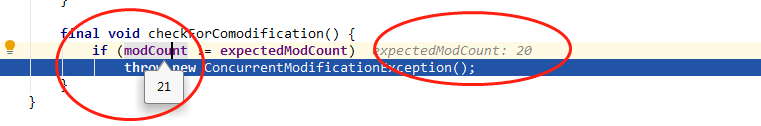
断点可以看到,remove操作后,modeCount=21, 而expectedModCount=20 不相等,抛出异常.
下面是集合类的remove方法:
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }
fastRemove方法:
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++; //remove会加1,所以checkForComodification校验时候会异常
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
3.foreach遍历是对迭代器封装了一下,所以也会报异常.
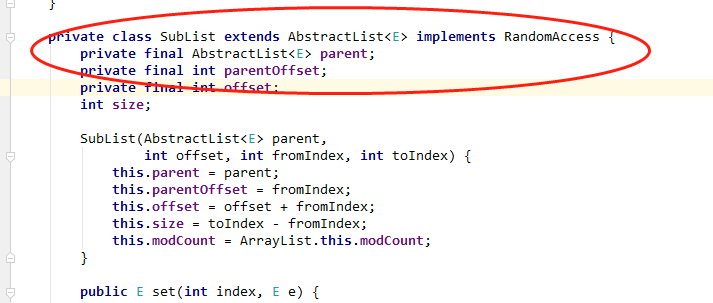
4. 普通for循环不会异常,因为使用的checkForComodification是另一个内部类的方法
SubList :
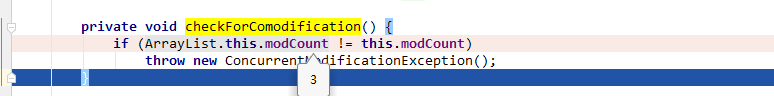
checkForComodification方法:
5.fail-fast机制
有两个线程(线程A,线程B),其中线程A负责遍历list、线程B修改list。
线程A在遍历list过程的某个时候(此时expectedModCount = modCount=N),线程启动,
同时线程B增加一个元素,这是modCount的值发生改变(modCount + 1 = N + 1)。 线程A继续遍历执行next方法时,
通告checkForComodification方法发现expectedModCount = N , 而modCount = N + 1,两者不等,
这时就抛出ConcurrentModificationException 异常,从而产生fail-fast机制。
6.避免fail-fast机制
① 方法1
public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { SubList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
可以看到,该remove方法并不会修改modCount的值,并且不会对后面的遍历造成影响,
因为该方法remove不能指定元素,只能remove当前遍历过的那个元素,所以调用该方法并不会发生fail-fast现象。该方法有局限性。
例:
// intList.remove(integer); //集合类remove iterator_int.remove(); //迭代器的remove()方法
②方法2
使用java并发包(java.util.concurrent)中的类来代替ArrayList 和hashMap。
比如使用 CopyOnWriterArrayList代替ArrayList,CopyOnWriterArrayList在是使用上跟ArrayList几乎一样,CopyOnWriter是写时复制的容器(COW),在读写时是线程安全的。
该容器在对add和remove等操作时,并不是在原数组上进行修改,而是将原数组拷贝一份,在新数组上进行修改,待完成后,才将指向旧数组的引用指向新数组,
所以对于CopyOnWriterArrayList在迭代过程并不会发生fail-fast现象。但 CopyOnWrite容器只能保证数据的最终一致性,不能保证数据的实时一致性。
对于HashMap,可以使用ConcurrentHashMap,ConcurrentHashMap采用了锁机制,是线程安全的。
在迭代方面,ConcurrentHashMap使用了一种不同的迭代方式。在这种迭代方式中,当iterator被创建后集合再发生改变就不再是抛出ConcurrentModificationException,
取而代之的是在改变时new新的数据从而不影响原有的数据 ,iterator完成后再将头指针替换为新的数据 ,这样iterator线程可以使用原来老的数据,而写线程也可以并发的完成改变。
即迭代不会发生fail-fast,但不保证获取的是最新的数据。
---------------------
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zymx14/article/details/78394464
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40254498/article/details/81386920