前言
在上一篇文章中,我们查看了Tomcat启动时调用的Bootstrap.java类的main方法,这篇我们就把main方法中涉及的启动相关的方法逐一查看!
第一部分 init 方法
/**
* Initialize daemon.
*/
public void init() throws Exception {
// Set Catalina path
//1
setCatalinaHome();
//2
setCatalinaBase();
//3
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
//4
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method = startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
//5
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
setCatalinaHome
/**
* Set the <code>catalina.home</code> System property to the current
* working directory if it has not been set.
*/
private void setCatalinaHome() {
if (System.getProperty(Globals.CATALINA_HOME_PROP) != null)
return;
File bootstrapJar = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir"), "bootstrap.jar");
if (bootstrapJar.exists()) {
try {
System.setProperty(Globals.CATALINA_HOME_PROP, (new File(System.getProperty("user.dir"), "..")).getCanonicalPath());
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore
System.setProperty(Globals.CATALINA_HOME_PROP, System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
} else {
System.setProperty(Globals.CATALINA_HOME_PROP, System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
}
代码很简单,简单到只需要读方法注释就好,大致就是设置变量catalina.home的值,存在就不设置,不存在设置为当前工作目录。
setCatalinaBase
这个方法源码也很简单,类似于setCatalinaHome方法,设置变量catalina.base,略过。
initClassLoaders
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if (commonLoader == null) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
第一步通过一个私有方法createClassLoader创建了一个类型为ClassLoader的成员变量commonLoader,我们跟进下createClassLoader一探究竟,他是如何创建的。
下面代码只保留了主要代码
String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");
if ((value == null) || (value.equals("")))
return parent;
value = replace(value);
List<Repository> repositories = new ArrayList<Repository>();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(value, ",");
while (tokenizer.hasMoreElements()) {
...
}
return ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader(repositories, parent);
先调用了CatalinaProperties的静态方法getProperty,传递的参数是common.loader,我们继续深入查看CatalinaProperties这个类,方法getProperty代码如下
return properties.getProperty(name);
那么就可以直接去看变量properties是如何初始化的,我们找到了这个类有个静态代码块,跟进去看一下
static {
loadProperties();
}
//删除loadProperties 多余代码
/**
* Load properties.
*/
private static void loadProperties() {
InputStream is = null;
...
if (is == null) {
try {
File home = new File(getCatalinaBase());
File conf = new File(home, "conf");
File propsFile = new File(conf, "catalina.properties");
is = new FileInputStream(propsFile);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
}
}
...
if (is != null) {
try {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
error = t;
}
}
...
// Register the properties as system properties
Enumeration<?> enumeration = properties.propertyNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
String value = properties.getProperty(name);
if (value != null) {
System.setProperty(name, value);
}
}
}
可以看出properties这个变量内部的参数KV的值主要来源于CATALINA_BASEconfcatalina.properties。那么去catalina.properties这个配置文件中搜索common.loader可以看到如下内容
common.loader=${catalina.base}/lib,${catalina.base}/lib/*.jar,${catalina.home}/lib,${catalina.home}/lib/*.jar
这里看到common.loader指向了4个目录或者文件,猜想是根据这4个目录(repository)来创建了一个叫做commonLoader的classloader,我们直接跳到createClassLoader方法最后一看,debug到这行看看他相关参数。
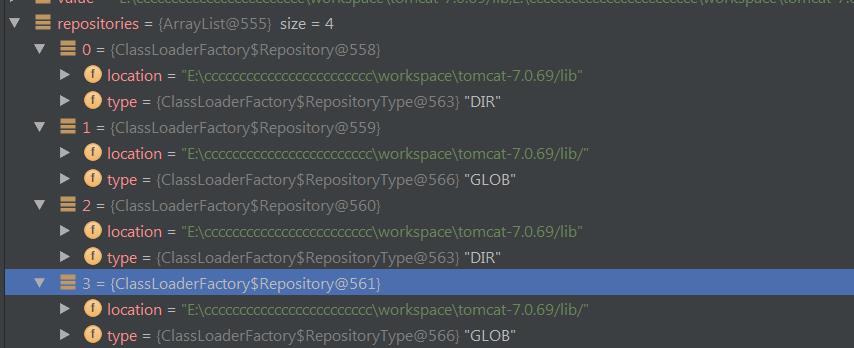
果然他是根据4个repository创建了一个classloader,当然4个路径被统一处理成了一个。到此为止我们可以得出一个结论就是commonLoader是用来加载CATALINA_HOMElib下的内容的类加载器。
类似的在initClassLoaders方法中,成员变量catalinaLoader和sharedLoader的创建过程跟commonLoader类似。
initClassLoaders小总结:
- Tomcat在init的过程中,会创建3个classloader,分别叫做commonLoader,catalinaLoader,sharedLoader。(其实还是创建了别的classloader的,要不可以思考一下,我们使用的Bootstrap类是谁加载的?)
- commonLoader是核心类加载器,用来加载
CATALINA_HOMElib目录下的类文件。- commonLoader是其他两个类加载器的父类加载器。
- 三个类加载器的类型全部是
URLClassLoader
更多classloader的说明可以参考http://www.cnblogs.com/coldridgeValley/p/5260403.html
好了initClassLoaders方法我们已经看完了,现在继续往下看。
//4
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method = startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
//5
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
这段代码熟悉反射的人看起来非常容易,使用catalinaLoader加载了Catalina类,并且调用了setParentClassLoader的方法,将Catalina类的父类加载器设置为sharedLoader,最后将Catalina类的变量实例赋值给catalinaDeamon变量。
到这里init方法就结束了,由于load和start方法需要涉及的内容很多,就放在下面文章中讲解了。
init方法总结:
init方法总计做了6件主要的事情
- 设置了系统变量
CATALINA_HOME。 - 设置了系统变量
CATALINA_BASE。 - 创建了3个类加载器
commonloader,catalinaLoader,sharedLoader。 - 将当前启动线程的类加载器设置为
catalinaLoader。 - 创建类
Catalina的实例,并且调用setParentClassLoader方法,将Catalina类的父类加载器设置为catalinaLoader。 - 将第五条创建的
Catalina类实例赋值给catalinaDaemon变量。
下篇文章我们将继续查看main方法中剩余的load和start方法!