最近在给自己的服务器框架加上统计信息,其中一项就是统计创建的对象数,以及当前还存在的对象数,那么自然以对象名字作key。但写着写着,忽然纠结是用std::string还是const char *作key,哪个效率高些。由于这服务器框架业务逻辑全在lua脚本,在C++需要统计的对象没几个,其实用哪个没多大区别。我纠结的是,很久之前就知道这两者效率区别不大,但直到现在我都还没搞清楚为啥,于是写些代码来测试。
V1版本的代码如下:

#ifndef __MAP_H__ #define __MAP_H__ //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // MurmurHash2, by Austin Appleby // Note - This code makes a few assumptions about how your machine behaves - // 1. We can read a 4-byte value from any address without crashing // 2. sizeof(int) == 4 // And it has a few limitations - // 1. It will not work incrementally. // 2. It will not produce the same results on little-endian and big-endian // machines. static inline unsigned int MurmurHash2 ( const void * key, int len, unsigned int seed ) { // 'm' and 'r' are mixing constants generated offline. // They're not really 'magic', they just happen to work well. const unsigned int m = 0x5bd1e995; const int r = 24; // Initialize the hash to a 'random' value unsigned int h = seed ^ len; // Mix 4 bytes at a time into the hash const unsigned char * data = (const unsigned char *)key; while(len >= 4) { unsigned int k = *(unsigned int *)data; k *= m; k ^= k >> r; k *= m; h *= m; h ^= k; data += 4; len -= 4; } // Handle the last few bytes of the input array switch(len) { case 3: h ^= data[2] << 16; case 2: h ^= data[1] << 8; case 1: h ^= data[0]; h *= m; }; // Do a few final mixes of the hash to ensure the last few // bytes are well-incorporated. h ^= h >> 13; h *= m; h ^= h >> 15; return h; } /* 自定义类型hash也可以放到std::hash中,暂时不这样做 * https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/hash */ /* the default hash function in libstdc++:MurmurHashUnaligned2 * https://sites.google.com/site/murmurhash/ by Austin Appleby * other hash function(djb2,sdbm) http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~oz/hash.html */ struct hash_c_string { size_t operator()(const char *ctx) const { return MurmurHash2(ctx,strlen(ctx),static_cast<size_t>(0xc70f6907UL)); } }; /* compare function for const char* */ struct cmp_const_char { bool operator()(const char *a, const char *b) const { return std::strcmp(a, b) < 0; } }; /* compare function for const char* */ struct equal_c_string { bool operator()(const char *a, const char *b) const { return 0 == std::strcmp(a, b); } }; /* 需要使用hash map,但又希望能兼容旧版本时使用map_t */ #if __cplusplus < 201103L /* -std=gnu99 */ #include <map> #define map_t std::map #define const_char_map_t(T) std::map<const char *,T,cmp_const_char> #else /* if support C++ 2011 */ #include <unordered_map> #define map_t std::unordered_map // TODO:template<class T> using const_char_map_t = ...,但03版本不支持 #define const_char_map_t(T) std::unordered_map<const char *,T,hash_c_string,equal_c_string> #endif #endif /* __MAP_H__ */

#include <map> #include <ctime> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> /* srand, rand */ #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include "map_v1.h" #if(__cplusplus >= 201103L) # include <unordered_map> #else # include <tr1/unordered_map> namespace std { using std::tr1::unordered_map; } #endif #include <iostream> #define M_TS 1000 #define N_TS 1000 typedef std::pair<unsigned short,unsigned short> pair_key_t; struct pair_hash { unsigned int operator () (const pair_key_t& pk) const { return (0xffff0000 & (pk.first << 16)) | (0x0000ffff & pk.second); } }; struct pair_equal { bool operator () (const pair_key_t& a, const pair_key_t& b) const { return a.first == b.first && a.second == b.second; } }; struct pair_less { bool operator () (const pair_key_t& a, const pair_key_t& b) const { return (a.first < b.first) || (a.first == b.first && a.second < b.second); } }; typedef std::map< pair_key_t,unsigned int,pair_less > std_map_t; typedef std::unordered_map< pair_key_t,unsigned int,pair_hash,pair_equal > unordered_map_t; void run_unordered_map_test() { unordered_map_t _protocol; clock_t start = clock(); for ( unsigned short m = 0;m < M_TS;m ++ ) for ( unsigned short n = 0;n < N_TS;n ++ ) { unsigned int result = (0xffff0000 & (m << 16)) | (0x0000ffff & n); _protocol.insert( std::make_pair(std::make_pair(m,n),result) ); } std::cout << "unordered_map create cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; start = clock(); for ( unsigned short m = 0;m < M_TS;m ++ ) for ( unsigned short n = 0;n < N_TS;n ++ ) { unordered_map_t::iterator itr = _protocol.find( std::make_pair(m,n) ); if ( itr == _protocol.end() ) { std::cout << "unordered_map error" << std::endl; return; } } std::cout << "unordered_map find cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; } void run_std_map_test() { std_map_t _protocol; clock_t start = clock(); for ( unsigned short m = 0;m < M_TS;m ++ ) for ( unsigned short n = 0;n < N_TS;n ++ ) { unsigned int result = (0xffff0000 & (m << 16)) | (0x0000ffff & n); _protocol.insert( std::make_pair(std::make_pair(m,n),result) ); } std::cout << "std_map create cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; start = clock(); for ( unsigned short m = 0;m < M_TS;m ++ ) for ( unsigned short n = 0;n < N_TS;n ++ ) { std_map_t::iterator itr = _protocol.find( std::make_pair(m,n) ); if ( itr == _protocol.end() ) { std::cout << "std_map error" << std::endl; return; } } std::cout << "std_map find cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; } void create_random_key(std::vector<std::string> &vt) { srand (time(NULL)); for (int idx = 0;idx < 10000000;idx ++) { int ikey = rand(); int ikey2 = rand(); char skey[64]; sprintf(skey,"%X%X",ikey,ikey2); vt.push_back(skey); } } void test_unorder_string(const std::vector<std::string> &vt) { std::unordered_map<std::string,int> test_map; clock_t start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size();idx ++) { test_map[ vt[idx].c_str() ] = idx; } std::cout << "unorder_map std::string create cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size()/2;idx ++) { if (test_map.find(vt[idx].c_str()) == test_map.end()) { std::cout << "unorder_map std::string find fail" << std::endl; return; } } std::cout << "unorder_map std::string find cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; } void test_unorder_char(const std::vector<std::string> &vt) { std::unordered_map<const char *,int,hash_c_string,equal_c_string> test_map; clock_t start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size();idx ++) { test_map[ vt[idx].c_str() ] = idx; } std::cout << "unorder_map char create cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size()/2;idx ++) { if (test_map.find(vt[idx].c_str()) == test_map.end()) { std::cout << "unorder_map char find fail" << std::endl; return; } } std::cout << "unorder_map char find cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; } void test_stdmap_char(const std::vector<std::string> &vt) { std::map<const char *,int,cmp_const_char> test_map; clock_t start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size();idx ++) { test_map[ vt[idx].c_str() ] = idx; } std::cout << "std_map char create cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size()/2;idx ++) { if (test_map.find(vt[idx].c_str()) == test_map.end()) { std::cout << "std_map char find fail" << std::endl; return; } } std::cout << "std_map char find cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; } void test_stdmap_string(const std::vector<std::string> &vt) { std::map<std::string,int> test_map; clock_t start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size();idx ++) { test_map[ vt[idx] ] = idx; } std::cout << "std_map string create cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; start = clock(); for (int idx = 0;idx < vt.size()/2;idx ++) { if (test_map.find(vt[idx]) == test_map.end()) { std::cout << "std_map char find fail" << std::endl; return; } } std::cout << "std_map string find cost " << (float(clock()-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; } /* unordered_map create cost 0.08 unordered_map find cost 0.01 std_map create cost 0.28 std_map find cost 0.13 key为10000000时: std_map char create cost 31.73 std_map char find cost 15.69 std_map string create cost 56.44 std_map string find cost 28.48 unorder_map char create cost 11.61 unorder_map char find cost 1.17 unorder_map std::string create cost 11.75 unorder_map std::string find cost 2.13 key为100000时 std_map char create cost 0.09 std_map char find cost 0.04 std_map string create cost 0.15 std_map string find cost 0.08 unorder_map char create cost 0.03 unorder_map char find cost 0.01 unorder_map std::string create cost 0.06 unorder_map std::string find cost 0.02 */ // valgrind --tool=callgrind --instr-atstart=no ./unoder_map int main() { //run_unordered_map_test(); //run_std_map_test(); std::vector<std::string> vt; create_random_key(vt); //test_stdmap_char(vt); //test_stdmap_string(vt); int idx = 0; // wait valgrind:callgrind_control -i on //std::cin >> idx; test_unorder_char(vt); test_unorder_string(vt); //std::cin >> idx; return 0; }
上面的代码直接使用const char *为key,MurmurHash2作为字符串hash算法(这个是stl默认的字符串hash算法),使用strcmp对比字符串。在key长为16,CPU为I5,虚拟机debian7运行情况下,效率区别真的不大:
key为100000时: unorder_map char create cost 0.03 unorder_map char find cost 0.01 unorder_map std::string create cost 0.06 unorder_map std::string find cost 0.02 key为10000000时: unorder_map char create cost 11.61 unorder_map char find cost 1.17 unorder_map std::string create cost 11.75 unorder_map std::string find cost 2.13
看到这个结果我是真的有点不服气了。毕竟std::string是一个复杂的结构,怎么也应该慢比较多才对。于是拿出了valgrind来分析下: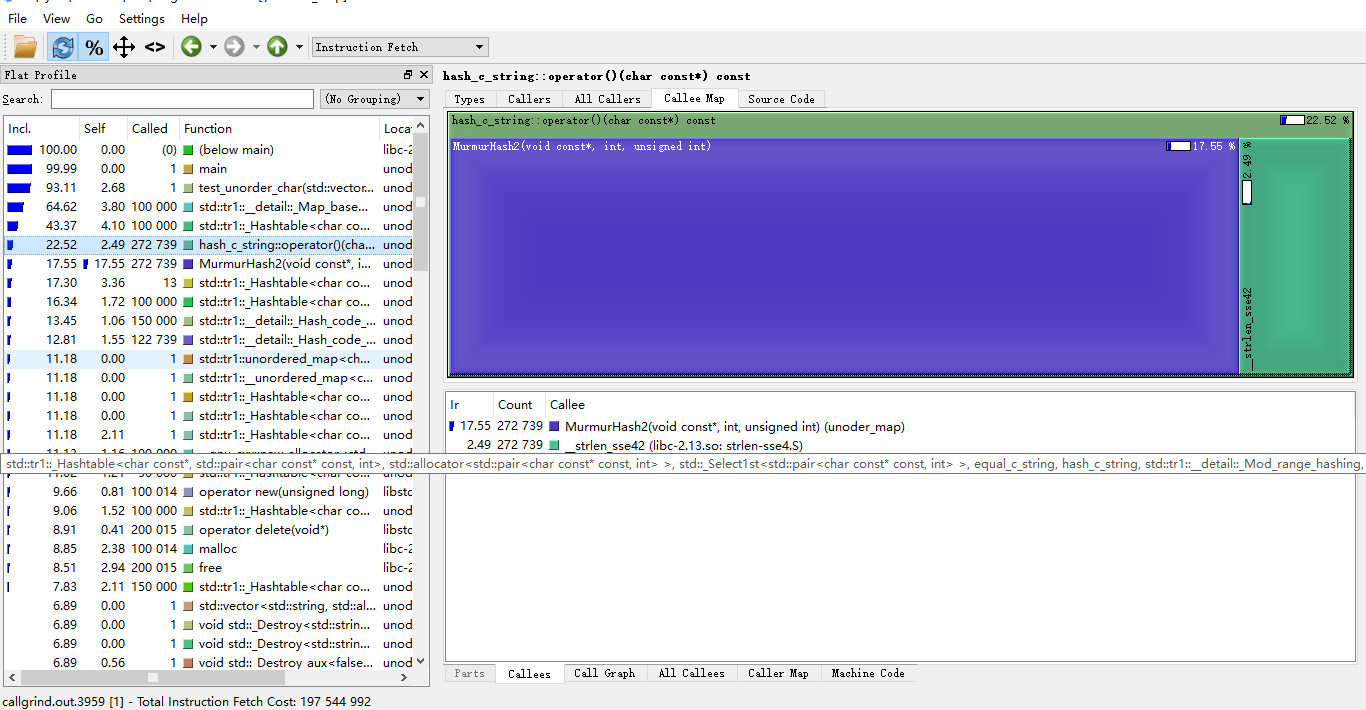
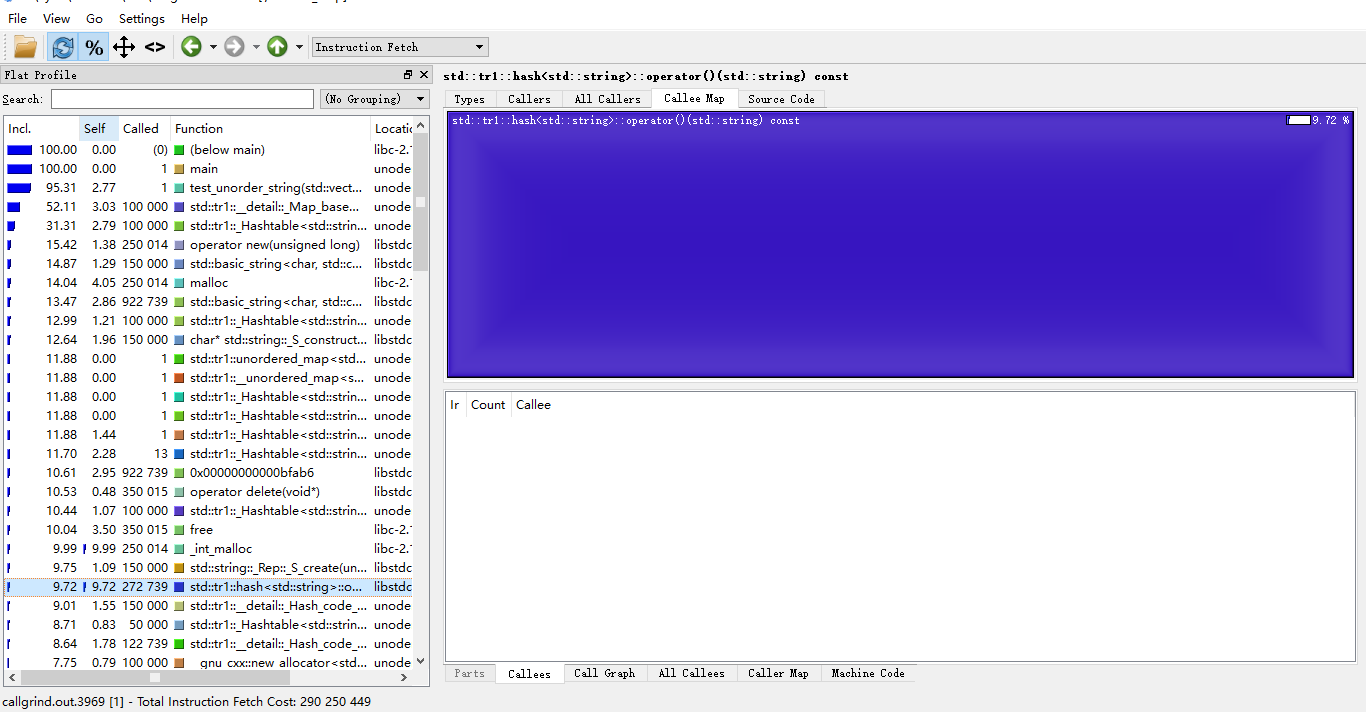
第一张图是用const char*作key的,第二张则是用std::string作key的。可以看到除去std::unordered_map的构造函数,剩下的基本是hash、operator new这两个函数占时间了。在const char*作key的时,hash函数占了22%,new函数占9.66%,而std::string时,new占了15.42,hash才9.72%,因此这两者的效率没差多少。
看到自己的hash函数写得太差,寻思着改一下。hash函数由两部分构成,一部分是用strlen算长度,另一部分是算hash,那么我们可以优化一下,把这两个变量记一下,就不用经常调用了。
struct c_string { size_t _length; unsigned int _hash; const char *_raw_ctx; c_string(const char *ctx) { _raw_ctx = ctx; _length = strlen(ctx); _hash = MurmurHash2(ctx,_length,static_cast<size_t>(0xc70f6907UL)); } };
然后再试了下,结果发现差别基本是一样的。没错,hash的消耗是下来了,可是new的占比又上去了。毕竟struct c_string这个结构和std::string这个结构没差多少啊,自己的hash函数还是没STL的效率高,所以白忙活。
然后自己还是不死心,网上(http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~oz/hash.html)查了下,换了几个hash函数,连strlen都去掉了
// djb2 unsigned long hash(unsigned char *str) { unsigned long hash = 5381; int c; while (c = *str++) hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + c; /* hash * 33 + c */ return hash; } // sdbm static unsigned long sdbm(str) unsigned char *str; { unsigned long hash = 0; int c; while (c = *str++) hash = c + (hash << 6) + (hash << 16) - hash; return hash; }
发现也并没有发生质的变化。hash函数复杂一些,效率慢一些,但冲突就少了。简单了,冲突多了,std::unordered_map那边创建、查询时就慢了。
周末在家,用自己的笔记本继续测了一次,A8 APU,Ubuntu14.04,非虚拟机。意外地发现,差别就比较大了。
// 使用const char*,key为10000000时: unorder_map char create cost 11.7611 unorder_map char find cost 1.55619 unorder_map std::string create cost 13.5376 unorder_map std::string find cost 2.33906 // 使用struct c_string,key为10000000时: unorder_map char create cost 7.35524 unorder_map char find cost 1.60826 unorder_map std::string create cost 14.6082 unorder_map std::string find cost 2.53137
可以看到,以c_string为key时,效率就比较高了。因为我的笔记本APU明显比不上I5,算hash函数就慢多了,但是内存分配没慢多少。
std::string还是const char *作key区别确实不大,影响的因素太多:
1. hash函数的效率和冲突概率。你自己很难写出一个比STL更好的hash函数,STL是有做优化的,比如strlen调用的是__strlen_sse42,是用了SSE指令优化的
2. 用不同的结构,在不同的CPU和内存分配效率,基于不同的操作系统实现,这个都会有不同的表现
3. 你自己是通过什么结构去构造、查询。用std::string时,创建和查询时其实是一个引用。如果你传入的是std::string,可能并不会创建对象。但传入char*就会先构造一对象
4. 用char*还要注意引用的字符串生命周期问题
最终,还是引用网上那几句话:
don't use a char * as a key std::string keys are never your bottleneck the performance difference between a char * and a std::string is a myth.
