3.搜索二维矩阵
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0){
return false;
}
boolean found = false;
if((matrix != null) && (matrix.length >0) && (matrix[0].length>0)){
int row = 0;
int column = matrix[0].length-1;
while((row < matrix.length)&&(column>=0)){
if(matrix[row][column]==target){
found = true;
break;
}else if(matrix[row][column]>target){
-- column;
}else{
++ row;
}
}
}
return found;
}
}
4.替换空格
双指针方式
public class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
int length = str.length();
if(str == null && length <= 0){
return str.toString();
}
int originalLength = 0;
int numberOfBlank = 0;
int i = 0;
while(i<length){
++ originalLength;
if(str.charAt(i) == ' '){
++ numberOfBlank;
}
i++;
}
int newLength = originalLength + numberOfBlank*2;
str.setLength(newLength);
int indexOfOriginal = originalLength-1;
int indexOfNew = newLength-1;
while(indexOfOriginal >=0 && indexOfNew >0){
if(str.charAt(indexOfOriginal) == ' '){
str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--,'0');
str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--,'2');
str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--,'%');
--indexOfOriginal;
}else{
str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--,str.charAt(indexOfOriginal));
--indexOfOriginal;
}
}
return str.toString();
}
}
stringbuffer方法
public class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
if(str.charAt(i) == ' '){
str.replace(i,i+1,"%20");
}
}
return str.toString();
}
}
5.从尾到头打印链表
栈 先出后进
1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.Stack;
3 public class Solution {
4 public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
5 Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
6 while(listNode!=null){
7 stack.push(listNode.val);
8 listNode=listNode.next;
9 }
10
11 ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
12 while(!stack.isEmpty()){
13 list.add(stack.pop());
14 }
15 return list;
16 }
17 }
递归法
1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 public class Solution {
3 ArrayList<Integer> arrayList=new ArrayList<Integer>();
4 public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
5 if(listNode!=null){
6 this.printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next);
7 arrayList.add(listNode.val);
8 }
9 return arrayList;
10 }
11 }
6 重建二叉树
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
TreeNode root=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,0,pre.length-1,in,0,in.length-1);
return root;
}
//前序遍历{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6}
private TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int startPre,int endPre,int [] in,int startIn,int endIn) {
if(startPre>endPre||startIn>endIn)
return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(pre[startPre]);
for(int i=startIn;i<=endIn;i++)
if(in[i]==pre[startPre]){
root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,startPre+1,startPre+i-startIn,in,startIn,i-1);
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,i-startIn+startPre+1,endPre,in,i+1,endIn);
break;
}
return root;
}
}
7 用两个栈实现队列
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.size()<=0){
while(stack1.size()>0){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
8 旋转数组的最小数字
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
if(array == null || array.length <=0){
return 0;
}
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = array.length-1;
int indexMid = index1;
while(array[index1] >= array[index2]){
if(index2 - index1 == 1){
indexMid = index2;
break;
}
indexMid = (index1+index2)/2;
if(array[indexMid] >= array[index1]){
index1 = indexMid;
}else if(array[indexMid] <= array[index2]){
index2 = indexMid;
}
}
return array[indexMid];
}
}
2.4.2 递归和循环
9 斐波那契数列
public class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
int preNum=1;
int prePreNum=0;
int result=0;
if(n==0)
return 0;
if(n==1)
return 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
result=preNum+prePreNum;
prePreNum=preNum;
preNum=result;
}
return result;
}
}
青蛙跳台阶
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if(target<2)
return target;
int f1=1;
int f2=0;
int f=0;
for(int i=1;i<=target;++i)
{
f=f1+f2;
f2=f1;
f1=f;
}
return f;
}
}
变态跳台阶
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
if (target <= 0) {
return -1;
} else if (target == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return 2 * JumpFloorII(target - 1);
}
}
}
矩形覆盖
public class Solution {
public int RectCover(int target) {
if (target <= 2){
return target;
}
int pre1 = 2; // n 最后使用一块,剩下 n-1 块的写法
int pre2 = 1; // n 最后使用两块,剩下 n-2 块的写法
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++){
int cur = pre1 + pre2;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = cur;
}
return pre1; //相对于 n+1 块来说,第 n 种的方法
}
}
2.4.3 位运算
10 二进制中1的个数
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n!=0)
{
n = n&(n-1);
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
11 数值的整数次方
循环
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if (exponent == 0) {
return 1.0;
}
if (base - 0.0 == 0.00001 || base - 0.0 == -0.00001) {
if (exponent < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("除0异常");
}else{
return 0.0;
}
}
int e = exponent > 0 ? exponent: -exponent;
double result = 1;
while (e != 0) {
result = (e & 1) != 0 ? result * base : result;
base *= base;
e = e >> 1;
}
return exponent > 0 ? result : 1/result;
}
}
递归
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
boolean flag = exponent < 0;
if (flag) {
exponent = -exponent;
}
double result = getPower(base, exponent);
return flag ? 1 / result : result;
}
public static double getPower(double base, int exp) {
if (exp == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (exp == 1) {
return base;
}
double ans = getPower(base, exp >> 1);
ans *= ans;
if ((exp & 1) == 1) {
ans *= base;
}
return ans;
}
}
12 打印1到最大的n位数
13 在0(1)时间删除链表结点
14 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
int length = array.length;
if(length == 0){
return;
}
int pBegin=0;
int pEnd = length-1;
while(pBegin < pEnd ){
while(pBegin < pEnd && (array[pBegin] & 0x1) != 0){
pBegin ++;
}
while(pBegin < pEnd && (array[pEnd] & 0x1) == 0){
pEnd--;
}
if(pBegin < pEnd){
int tmp = array[pBegin];
array[pBegin] = array[pEnd];
array[pEnd] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
拓展,牛客网多条件情况:并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length;i++){
for (int j = array.length - 1; j>i;j--)
{
if (array[j] % 2 == 1 && array[j - 1]%2 == 0) //前偶后奇交换
{
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j-1];
array[j-1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
3.4 代码的鲁棒性
15 链表中倒数第k个结点、
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head == null || k==0){
return null;
}
ListNode pAhead = head;
ListNode pBehind = null;
for(int i=0;i<k-1;++i){
if(pAhead.next != null){
pAhead = pAhead.next;
}else{
return null;
}
}
pBehind = head;
while(pAhead.next != null){
pAhead = pAhead.next;
pBehind = pBehind.next;
}
return pBehind;
}
}
相关题目:
求链表中间结点
从链表头结点出发,一个指针走一步,一个指针走两步。
判断词汇表单向链表是否形成了环形结构。同上一个,如果走的快的指针追上了走得慢的指针,就是;如果走到链表末尾(next指向null),就不是。
应用--leetcode题目 141. 环形链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null ){
return false;
}
ListNode ahead = head.next;
ListNode behind = head;
while(ahead != behind){
if(ahead.next == null || ahead.next.next == null){
return false;
}
ahead = ahead.next.next;
behind = behind.next;
}
return true;
}
}
16 反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode reversedHead = null;
ListNode node = head;
ListNode prenode = null;
while(node != null){
ListNode next = node.next;
if(next == null){
reversedHead = node;
}
node.next = prenode;
prenode = node;
node = next;
}
return reversedHead;
}
}
17 合并两个排序的链表
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1 == null){
return l2;
}
if(l2 == null){
return l1;
}
ListNode mergeHead = null;
if(l1.val >= l2.val){
mergeHead = l2;
mergeHead.next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
}else{
mergeHead = l1;
mergeHead.next = mergeTwoLists(l2,l1.next);
}
return mergeHead;
}
}
18 树的子结构
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
boolean result = false;
if(root1 != null && root2 != null){
if(root1.val == root2.val){
result = DoesTree1HasTree2(root1,root2);
}
if(!result){
result = HasSubtree(root1.left,root2);
}
if(!result){
result = HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
}
return result;
}
boolean DoesTree1HasTree2(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2){
if(root2 == null){
return true;
}
if(root1 == null){
return false;
}
if(root1.val!= root2.val){
return false;
}
return DoesTree1HasTree2(root1.left,root2.left)&&
DoesTree1HasTree2(root1.right,root2.right);
}
}
19 二叉树的镜像
递归实现
public class Solution {
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null ||
(root.left == null && root.right == null)){
return;
}
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
if(root.left != null){
Mirror(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
Mirror(root.right);
}
}
}
循环实现

import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(node.left != null||node.right != null){
TreeNode temp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = temp;
}
if(node.left!=null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
}
}
20 顺时针打印矩阵

import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer> ();
if(matrix.length==0) return result;
int row = matrix.length,col = matrix[0].length;
if(col==0) return result;
// 定义四个关键变量,表示左上和右下的打印范围
int left = 0, top = 0, right = col - 1, bottom = row - 1;
while(left <= right && top <= bottom){
// left to right
for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) result.add(matrix[top][i]);
// top to bottom
for (int i = top + 1; i <= bottom; ++i) result.add(matrix[i][right]);
// right to left
if (top != bottom)
for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; --i) result.add(matrix[bottom][i]);
// bottom to top
if (left != right)
for (int i = bottom - 1; i > top; --i) result.add(matrix[i][left]);
left++;top++;right--;bottom--;
}
return result;
}
}

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
int row = matrix.size();
int col = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> res;
// 输入的二维数组非法,返回空的数组
if (row == 0 || col == 0) return res;
// 定义四个关键变量,表示左上和右下的打印范围
int left = 0, top = 0, right = col - 1, bottom = row - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom)
{
// left to right
for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) res.push_back(matrix[top][i]);
// top to bottom
for (int i = top + 1; i <= bottom; ++i) res.push_back(matrix[i][right]);
// right to left
if (top != bottom)
for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; --i) res.push_back(matrix[bottom][i]);
// bottom to top
if (left != right)
for (int i = bottom - 1; i > top; --i) res.push_back(matrix[i][left]);
left++,top++,right--,bottom--;
}
return res;
}
};
21 包含min函数的栈
Stack实现

import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
if(stack2.isEmpty() || node < stack2.peek()){
stack2.push(node);
}else{
stack2.push(stack2.peek());
}
}
public void pop() {
assert(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty());
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack1.peek();
}
public int min() {
return stack2.peek();
}
}
ArrayList实现

import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
list.add(0,node);
}
public void pop() {
list.get(0);
list.remove(0);
}
public int top() {
return list.get(0).intValue();
}
public int min() {
int temp = top();
for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++){
if(temp>list.get(i).intValue()){
temp = list.get(i).intValue();
}
}
return temp;
}
}
22 栈的压入、弹出序列
Stack实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) {
boolean bResult = false;
int nLength = pushA.length;
if(pushA != null && popA != null && nLength>0){
int nextpush =0;
int nextpop = 0;
Stack<Integer> stackData = new Stack<Integer>();
while(nextpop < nLength){
while(stackData.empty() || stackData.peek() != popA[nextpop]){
if(nextpush == nLength){
break;
}
stackData.push(pushA[nextpush]);
nextpush++;
}
if(stackData.peek() != popA[nextpop]){
break;
}
stackData.pop();
nextpop++;
}
if(stackData.empty() && nextpop == nLength){
bResult = true;
}
}
return bResult;
}
}
23 从上往下打印二叉树
按层打印,实际就是广度优先搜索 BFS, 借助一个队列就可以实现.
广度优先搜索 BFS:主要借助一个队列、一个布尔类型数组、邻接矩阵完成(判断一个点是否查看过,用于避免重复到达同一个点,造成死循环等),先将各点以及各点的关系存入邻接矩阵。
再从第一个点开始,将一个点存入队列,然后在邻接表中找到他的相邻点,存入队列,每次pop出队列头部并将其打印出来(文字有些抽象,实际过程很简单),整个过程有点像往水中投入石子水花散开。
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
queue.add(root);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
TreeNode temp = queue.remove(0);
if (temp.left != null){
queue.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
queue.add(temp.right);
}
list.add(temp.val);
}
return list;
}
}
扩展:
广度优先遍历一个有向图,同样可以基于队列实现。树是图的一种特殊退化形式,从上到下按层遍历二叉树,本质上就是广度优先遍历二叉树。
24 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
后序遍历:先遍历子结点,再遍历父结点。在后序遍历得到的序列中,最后一个数字是树的根结点。
public class Solution {
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence == null || sequence.length <= 0){
return false;
}
int root = sequence[sequence.length-1];
int[] sequenceleft = new int[sequence.length];
int[] sequenceright = new int[sequence.length];
//在二叉搜索树中左子树的结点小于结点
int i=0;
for(;i<sequence.length -1;++i){
if(sequence[i] > root){
break;
}
sequenceleft[i] = sequence[i];
}
//早二叉搜索树中右子树的结点大于根结点
int j=i;
int k=0;
for(;j < sequence.length -1;++j){
if(sequence[j] < root){
return false;
}
k++;
sequenceright[k] = sequence[j];
}
//判断左子树是不是二叉搜索树
boolean left = true;
if(i>0){
left = VerifySquenceOfBST(sequenceleft);
}
boolean right = true;
if(i<sequence.length-1){
right = VerifySquenceOfBST(sequenceright);
}
return (left && right);
}
}
前中后序遍历
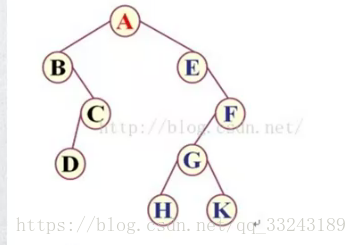
前、中、后指的是根节点的顺序。前序遍历有根节点开始。
前序遍历:ABCDEFGHK
中序遍历:BDCAEHGKF
后序遍历:DCBHKGFEA
中序排列思想:

25 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int target) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> paths=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(root==null)return paths;
find(paths,new ArrayList<Integer>(),root,target);
return paths;
}
public void find(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> paths,ArrayList<Integer> path,TreeNode root,int target){
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
if(target==root.val){
paths.add(path);
}
return;
}
ArrayList<Integer> path2=new ArrayList<>();
path2.addAll(path);
if(root.left!=null)find(paths,path,root.left,target-root.val);
if(root.right!=null)find(paths,path2,root.right,target-root.val);
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int target) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList=
new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(root==null)
return pathList;
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
FindPath(root,target,stack,pathList );
return pathList;
}
private void FindPath(TreeNode root, int target,
Stack<Integer> path,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathList) {
if(root==null)
return;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
if(root.val==target){
ArrayList<Integer> list=
new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i:path){
list.add(new Integer(i));
}
list.add(new Integer(root.val));
pathList.add(list);
}
}
else{
path.push(new Integer(root.val));
FindPath(root.left, target-root.val, path, pathList);
FindPath(root.right, target-root.val, path, pathList);
path.pop();
}
}
}
26 复杂链表的复制
分治法,通常分治法的思路都可以用递归实现
在复杂链表的结点中,除了有指向下一个结点的指针,还有指向任意结点的指针。、
/*
public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
RandomListNode(int label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
{
CloneNodes(pHead);
ConnectSiblingNodes(pHead);
return ReconnectNodes(pHead);
}
void CloneNodes(RandomListNode pHead){
RandomListNode pNode = pHead;
while(pNode != null){
RandomListNode pCloned = new RandomListNode(pNode.label);
pCloned.next = pNode.next;
pCloned.random = null;
pNode.next = pCloned;
pNode = pCloned.next;
}
}
void ConnectSiblingNodes(RandomListNode pHead){
RandomListNode pNode = pHead;
while(pNode!= null){
RandomListNode pCloned = pNode.next;
if(pNode.random != null){
pCloned.random = pNode.random.next;
}
pNode = pCloned.next;
}
}
RandomListNode ReconnectNodes(RandomListNode pHead){
RandomListNode pNode = pHead;
RandomListNode pClonedHead = null;
RandomListNode pClonedNode = null;
if(pNode != null){
pClonedNode = pNode.next;
pClonedHead = pClonedNode;
pNode.next = pClonedNode.next;
pNode = pNode.next;
}
while(pNode != null){
pClonedNode.next = pNode.next;
pClonedNode = pClonedNode.next;
pNode.next = pClonedNode.next;
pNode = pNode.next;
}
return pClonedHead;
}
}
27 二叉搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树:左子结点的值小于父结点的值,右子节点的值大于父结点的值。
直接递归
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null) return pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree = ConvertNode(pRootOfTree);
while(pRootOfTree.left!= null) pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.left;
return pRootOfTree;
}
TreeNode ConvertNode(TreeNode root)
{
if(root == null) return root;
if(root.left != null)
{
TreeNode left = ConvertNode(root.left);
while(left.right!= null) left = left.right;
left.right = root;
root.left = left;
}
if(root.right != null)
{
TreeNode right = ConvertNode(root.right);
while(right.left!= null) right = right.left;
right.left = root;
root.right = right;
}
return root;
}
}
此解法暂时未通过
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
TreeNode pLastNodeInList = null;
ConvertNode(pRootOfTree, pLastNodeInList);
//pLastNodeInList双向链表尾结点
//需要返回头结点
TreeNode pHeadOfList = pLastNodeInList;
while(pHeadOfList != null && pHeadOfList.left != null){
pHeadOfList = pHeadOfList.left;
}
return pHeadOfList;
}
void ConvertNode(TreeNode pNode, TreeNode pLastNodeInList){
if(pNode == null){
return;
}
TreeNode pCurrent = pNode;
if(pCurrent.left != null){
ConvertNode(pCurrent.left, pLastNodeInList);
}
pCurrent.left = pLastNodeInList;
if(pLastNodeInList != null){
pLastNodeInList.right = pCurrent;
}
pLastNodeInList = pCurrent;
if(pCurrent.right != null){
ConvertNode(pCurrent.right,pLastNodeInList);
}
}
}
28 字符串的排列
解法一:递归
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
if(str!=null && str.length()>0){
PermutationHelper(str.toCharArray(),0,list);
Collections.sort(list);
}
return list;
}
private void PermutationHelper(char[] chars,int i,ArrayList<String> list){
if(i == chars.length-1){
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}else{
Set<Character> charSet = new HashSet<Character>();
for(int j=i;j<chars.length;++j){
if(j==i || !charSet.contains(chars[j])){
charSet.add(chars[j]);
swap(chars,i,j);
PermutationHelper(chars,i+1,list);
swap(chars,j,i);
}
}
}
}
private void swap(char[] cs,int i,int j){
char temp = cs[i];
cs[i] = cs[j];
cs[j] = temp;
}
}
解法二:字典序排列算法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
if(str==null || str.length()==0){
return list;
}
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chars);
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
int len = chars.length;
while(true){
int lIndex = len-1;
int rIndex;
while(lIndex>=1 && chars[lIndex-1]>=chars[lIndex]){
lIndex--;
}
if(lIndex == 0)
break;
rIndex = lIndex;
while(rIndex<len && chars[rIndex]>chars[lIndex-1]){
rIndex++;
}
swap(chars,lIndex-1,rIndex-1);
reverse(chars,lIndex);
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
return list;
}
private void reverse(char[] chars,int k){
if(chars==null || chars.length<=k)
return;
int len = chars.length;
for(int i=0;i<(len-k)/2;i++){
int m = k+i;
int n = len-1-i;
if(m<=n){
swap(chars,m,n);
}
}
}
private void swap(char[] cs,int i,int j){
char temp = cs[i];
cs[i] = cs[j];
cs[j] = temp;
}
}
29 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
方法1:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
Arrays.sort(array);
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(array[i]==array[array.length/2]){
count++;
}
}
if(count>array.length/2){
return array[array.length/2];
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
方法2:HashMap
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(!map.containsKey(array[i])){
map.put(array[i],1);
}else{
int count = map.get(array[i]);
map.put(array[i],++count);
}
}
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
Integer key =(Integer)entry.getKey();
Integer val = (Integer)entry.getValue();
if(val>array.length/2){
return key;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
方法3:快排思想--未通过
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
if(array.length<=0)
return 0;
int start = 0;
int length = array.length;
int end = length-1;
int middle = length>>1;
int index = Partition(array,start,end);
while(index!=middle){
if(index>middle){
index = Partition(array,start,index-1);
}
else{
index = Partition(array,index+1,end);
}
}
int result = array[middle];
int times = 0;
for(int i=0;i<length;++i){
if(array[i] == result)
times++;
}
if(times*2<length){
System.out.println(times);
return 0;
}else{
return result;
}
}
public int Partition(int[] array,int start,int end){
int flag = (array[start]+array[end])/2;
while(start<end){
while(array[end]>flag){
end--;
}
swap(array,start,end);
while(array[start]<=flag){
start++;
}
swap(array,start,end);
}
return start;
}
public void swap(int[] array,int num1,int num2){
int temp =array[num1];
array[num1] =array[num2];
array[num2] =temp;
}
}
30 最小的K个数
解法一:冒泡排序
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (k > input.length) {
return al;
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < input.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (input[j] < input[j + 1]) {
int temp = input[j];
input[j] = input[j + 1];
input[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
al.add(input[input.length - i - 1]);
}
return al;
}
}
解法2:利用快速排序中的获取分割(中轴)点位置函数getPartitiion--用例未通过
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(input==null || k>input.length || k<=0) return result;
int start = 0;
int end = input.length-1;
int index = getPartition(input,start,end);
while(index != (k-1))
{
if(index > (k-1))
{
end = index - 1;
index = getPartition(input,start,end);
}
else
{
start = index + 1;
index = getPartition(input,start,end);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<k;++i)
{
result.add(input[i]);
}
return result;
}
public void swap(int fir,int sec)
{
int temp = fir;
fir = sec;
sec = temp;
}
public int getPartition(int [] input,int start,int end)
{
if(input==null || start>end) return -1;
int temp = input[end];
int j = start - 1;
for(int i=start;i<end;++i)
{
if(input[i]<=temp)
{
++j;
if(i!=j) swap(input[i],input[j]);
}
}
swap(input[j+1],input[end]);
return (j+1);
}
}
31 连续子数组的最大和
解法1:分析数组规律
public class Solution {
public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
int len = array.length;
if(array==null || len<0){
return 0;
}
int nCurSum = 0;
int nGreatestSum = 0x80000000;
for(int i=0; i<len;i++){
if(nCurSum <= 0){
nCurSum = array[i];
}else{
nCurSum += array[i];
}
if(nCurSum > nGreatestSum){
nGreatestSum = nCurSum;
}
}
return nGreatestSum;
}
}
解法2:动态规划思想,代码一致
32 从1到n整数中1出现的次数
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int number = 0;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
number += numberOf1(i);
}
return number;
}
public int numberOf1(int n){
int number = 0;
while(n>0){
if(n%10 == 1){
number ++;
}
n = n/10;
}
return number;
}
}
33 把数组排成最小的数
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Solution {
public String PrintMinNumber(int [] numbers) {
int n;
String s="";
ArrayList<Integer> list= new ArrayList<Integer>();
n=numbers.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
list.add(numbers[i]);
}
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>(){
public int compare(Integer str1,Integer str2){
String s1=str1+""+str2;
String s2=str2+""+str1;
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
});
for(int j:list){
s+=j;
}
return s;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public String PrintMinNumber(int [] numbers) {
String str = "";
for (int i=0; i<numbers.length; i++){
for (int j=i+1; j<numbers.length; j++){
int a = Integer.valueOf(numbers[i]+""+numbers[j]);
int b = Integer.valueOf(numbers[j]+""+numbers[i]);
if (a > b){
int t = numbers[i];
numbers[i] = numbers[j];
numbers[j] = t;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
str += String.valueOf(numbers[i]);
}
return str;
}
}
34 丑数
解法一:暴力破解 超时
public class Solution {
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if(index <= 0){
return 0;
}
int number = 0;
int uglyFound = 0;
while(uglyFound < index){
++number;
if(IsUgly(number)){
++uglyFound;
}
}
return number;
}
boolean IsUgly(int number){
while(number % 2 == 0){
number /= 2;
}
while(number % 3 == 0){
number /= 3;
}
while(number % 5 == 0){
number /= 5;
}
return (number==1)?true:false;
}
}
方法二:创建数组保存已找到的丑数,用空间换时间
public class Solution {
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if(index <=0){
return 0;
}
int[] uglyNums = new int[index];
uglyNums[0]=1;
int nextUglyIndex = 1;
int mul2 = 0;
int mul3 = 0;
int mul5 = 0;
while(nextUglyIndex < index){
int min = Min(uglyNums[mul2]*2, uglyNums[mul3]*3, uglyNums[mul5]*5);
uglyNums[nextUglyIndex] = min;
while(uglyNums[mul2]*2 <= uglyNums[nextUglyIndex]){
++mul2;
}
while(uglyNums[mul3]*3 <= uglyNums[nextUglyIndex]){
++mul3;
}
while(uglyNums[mul5]*5 <= uglyNums[nextUglyIndex]){
++mul5;
}
++nextUglyIndex;
}
int ugly = uglyNums[nextUglyIndex - 1];
return ugly;
}
int Min(int num1, int num2, int num3){
int min = (num1 <= num2)?num1:num2;
min = (min <= num3)?min:num3;
return min;
}
}
35 第一个只出现一次的字符
方法1:哈希表 ASCII码
public class Solution {
public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
int[] words = new int[58];
for(int i = 0;i<str.length();i++){
words[((int)str.charAt(i))-65] += 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
if(words[((int)str.charAt(i))-65]==1)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
}
方法2:字符串函数 第一次和最后一次出现的位置相同
public class Solution {
public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (str.indexOf(ch) == str.lastIndexOf(ch))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
}
***相似题目*** 统计多个字符是不是在字符串出现过或者次数
删除第一个字符串中在第二个字符串中出现的字符
删除字符串中所有重复出现的字符
变位词
36 数组中的逆序对
方法1:归并排序 按书上代码没有通过用例
public class Solution {
public int InversePairs(int [] array) {
if(array == null || array.length <0){
return 0;
}
int len = array.length;
int[] copy = new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
copy[i] = array[i];
}
int count = InversePairsCore(array,copy,0,len-1);
return count;
}
int InversePairsCore(int[] array, int[] copy, int start, int end){
if(start == end){
copy[start] = array[start];
return 0;
}
int len = (end - start)/2;
int left = InversePairsCore(copy, array, start, start + len);
int right = InversePairsCore(copy, array, start + len+1,end);
int i =start +len;
int j=end;
int indexCopy = end;
int count = 0;
while(i>= start && j >= start + len+ 1){
if(array[i] > array[j]){
copy[indexCopy--] = array[i--];
count += j-start-len;
}else{
copy[indexCopy--] = array[j--];
}
}
for(;i>=start;--i){
copy[indexCopy--] = array[i];
}
for(;j>= start + len +1;--j){
copy[indexCopy] = array[j];
}
return left+right+count;
}
}
37 两个链表的第一个公共结点
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
int len1 = GetListLen(pHead1);
int len2 = GetListLen(pHead2);
int lendif = len1-len2;
ListNode headLong = pHead1;
ListNode headShort = pHead2;
if(len2>len1){
headLong = pHead1;
headShort = pHead2;
lendif = len2-len1;
}
for(int i=0;i<lendif;++i){
headLong = headLong.next;
}
while(headLong != null && headShort != null && headLong != headShort){
headLong = headLong.next;
headShort = headShort.next;
}
ListNode firstCommNode = headLong;
return firstCommNode;
}
int GetListLen(ListNode pHead){
int len = 0;
ListNode pNode = pHead;
while(pNode != null){
++ len;
pNode = pNode.next;
}
return len;
}
}
38 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
方法1:二分法:
public class Solution {
public int GetNumberOfK(int [] array , int k) {
int number = 0;
int len = array.length;
if(array != null && len >0){
int first = GetFirstK(array, len,k, 0,len-1);
int last = GetLastK(array, len,k,0,len-1);
if(first > -1 && last > -1){
number = last-first+1;
}
}
return number;
}
int GetFirstK(int[] array, int length, int k, int start, int end){
if(start > end){
return -1;
}
int midIndex = (start + end)/2;
int midData = array[midIndex];
if(midData == k){
if((midIndex > 0 && array[midIndex -1] != k) || midIndex==0){
return midIndex;
}else{
end = midIndex -1;
}
}else if(midData > k){
end = midIndex - 1;
}else{
start = midIndex +1;
}
return GetFirstK(array, length, k, start, end);
}
int GetLastK(int[] array, int length, int k, int start, int end){
if(start > end){
return -1;
}
int midIndex = (start + end)/2;
int midData = array[midIndex];
if(midData == k){
if((midIndex <length-1 && array[midIndex + 1] != k) || midIndex==length-1){
return midIndex;
}else{
start = midIndex + 1;
}
}else if(midData < k){
start = midIndex +1;
}else{
end = midIndex - 1;
}
return GetLastK(array, length, k, start, end);
}
}
39 二叉树的深度
public class Solution {
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = TreeDepth(root.left);
int right = TreeDepth(root.right);
return (left>right)?(left+1):(right+1);
}
}
****拓展:平衡二叉树
二叉树中任意结点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1就是平衡二叉树。
解法1:
public class Solution {
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
int left = TreeDepth(root.left);
int right = TreeDepth(root.right);
int diff = left-right;
if(diff > 1 || diff < -1){
return false;
}
return IsBalanced_Solution(root.left) && IsBalanced_Solution(root.right);
}
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = TreeDepth(root.left);
int right = TreeDepth(root.right);
return (left>right)?(left+1):(right+1);
}
}
解法2:每个结点遍历一次 ---未通过所有用例
public class Solution {
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
int depth = 0;
return IsBalanced_Solution(root, depth);
}
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if(root == null){
depth = 0;
return true;
}
int left=depth;
int right=depth;
if(IsBalanced_Solution(root.left, left) && IsBalanced_Solution(root.right, right)){
int diff = left - right;
if(diff <= 1 && diff >= -1){
depth = 1+(left>right ? left:right);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
40 数组中只出现一次的数字
--未通过
//num1,num2分别为长度为1的数组。传出参数
//将num1[0],num2[0]设置为返回结果
public class Solution {
public void FindNumsAppearOnce(int [] array,int num1[] , int num2[]) {
if(array.length < 2){
return;
}
if(array.length == 2){
num1[0] = array[0];
num2[0] = array[1];
return;
}
int resultExclusiveOR = array[0];
for(int i=0; i<array.length; ++i){
resultExclusiveOR ^= array[i];
}
int indexOf1 = FindFirstBitIs1(resultExclusiveOR);
for(int j=0; j<array.length;++j){
if(IsBit1(array[j],indexOf1)){
num1[j] ^= array[j];
}else{
num2[j] ^= array[j];
}
}
}
int FindFirstBitIs1(int num){
int indexBit = 0;
while((num &1)==0 && indexBit < 32){
num = num >>1;
indexBit++ ;
}
return indexBit;
}
boolean IsBit1(int num, int indexBit){
num = num >> indexBit;
return (num&1) == 1;
}
}
41 和为s的两个数字 VS 和为s的连续正数序列
42 反转单词顺序 VS 左旋转字符串
43 n个骰子的点数
44 扑克牌的顺子
45 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
46 求1+2+...+n
47 不用加减乘除做加法
48 不能被继承的类
49 把字符串转换成整数
50 书中两个结点的最低公共祖先
