深度优先遍历是纵向遍历,一直到底,二叉树的前序遍历、中序遍历,后序遍历都是深度优先遍历。
广度优先遍历是横向遍历,层次遍历,遍历完一层再遍历下一层,直到遍历所有元素。
以矩阵为例,分析深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历的路径:
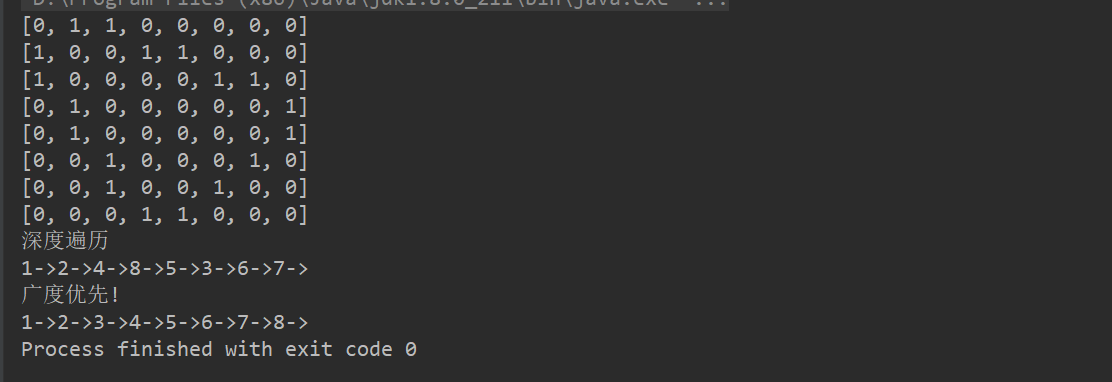
插入矩阵:
//测试一把图是否创建ok int n = 8; //结点的个数 String Vertexs[] = {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"}; //创建图对象 Graph graph = new Graph(n); //循环的添加顶点 for (String vertex : Vertexs) { graph.insertVertex(vertex); } //更新边的关系 graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1); graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1); graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1); graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1); graph.insertEdge(3, 7, 1); graph.insertEdge(4, 7, 1); graph.insertEdge(2, 5, 1); graph.insertEdge(2, 6, 1); graph.insertEdge(5, 6, 1);
矩阵:
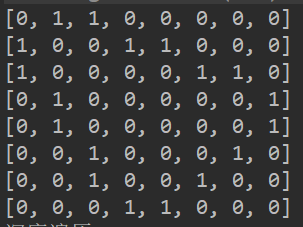
深度优先遍历路径:1->2->4->8->5->3->6->7->

广度优先遍历路径:1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->

代码实现:
1 package wy.datastructures.graph; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 import java.util.LinkedList; 6 import java.util.List; 7 8 public class Graph { 9 10 private int[][] edges; 11 private List<String> vertexList; 12 private int numOfEdges; 13 private boolean[] isVisited; 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 //测试一把图是否创建ok 17 int n = 8; //结点的个数 18 String Vertexs[] = {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"}; 19 20 //创建图对象 21 Graph graph = new Graph(n); 22 //循环的添加顶点 23 for (String vertex : Vertexs) { 24 graph.insertVertex(vertex); 25 } 26 27 //更新边的关系 28 graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1); 29 graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1); 30 graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1); 31 graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1); 32 graph.insertEdge(3, 7, 1); 33 graph.insertEdge(4, 7, 1); 34 graph.insertEdge(2, 5, 1); 35 graph.insertEdge(2, 6, 1); 36 graph.insertEdge(5, 6, 1); 37 38 39 //显示一把邻结矩阵 40 graph.showGraph(); 41 42 //测试一把,我们的dfs遍历是否ok 43 System.out.println("深度遍历"); 44 graph.dfs(); // A->B->C->D->E [1->2->4->8->5->3->6->7] 45 System.out.println(); 46 System.out.println("广度优先!"); 47 graph.bfs(); // A->B->C->D-E [1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8] 48 } 49 50 public void dfs(int index) { 51 isVisited[index] = true; 52 System.out.print(getVertex(index) + "->"); 53 for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) { 54 if (edges[index][i] == 1 && !isVisited[i]) { 55 dfs(i); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 public void dfs() { 61 isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()]; 62 dfs(0); 63 } 64 65 public void bfs() { 66 isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()]; 67 LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 68 for (int x = 0; x < getNumOfVertex(); x++) { 69 if (!isVisited[x]) { 70 isVisited[x] = true; 71 System.out.print(getVertex(x) + "->"); 72 queue.addLast(x); 73 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 74 int index = queue.removeFirst(); 75 for (int y = 0; y < getNumOfVertex(); y++) { 76 if (edges[index][y] == 1 && !isVisited[y]) { 77 isVisited[y] = true; 78 queue.addLast(y); 79 System.out.print(getVertex(y) + "->"); 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 public Graph(int n) { 88 edges = new int[n][n]; 89 vertexList = new ArrayList<>(n); 90 numOfEdges = 0; 91 isVisited = new boolean[n]; 92 } 93 94 public int getNumOfEdges() { 95 return numOfEdges; 96 } 97 98 public int getNumOfVertex() { 99 return vertexList.size(); 100 } 101 102 public String getVertex(int index) { 103 return vertexList.get(index); 104 } 105 106 public int getIndexOfVertex(String vertex) { 107 return vertexList.indexOf(vertex); 108 } 109 110 public int getEdge(int v1, int v2) { 111 return edges[v1][v2]; 112 } 113 114 public void insertVertex(String vertex) { 115 vertexList.add(vertex); 116 } 117 118 public void insertEdge(int v1, int v2, int weight) { 119 edges[v1][v2] = weight; 120 edges[v2][v1] = weight; 121 numOfEdges++; 122 } 123 124 public void showGraph() { 125 for (int[] link : edges) { 126 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(link)); 127 } 128 } 129 130 }
输出结果: