quic的优点
- Low-latency connection establishment
- Multiplexing without head-of-line blocking
- Authenticated and encrypted header and payload
- Rich signaling for congestion control and loss recovery
- Stream and connection flow control
- Connection migration and resilience to NAT rebindin
- Version negotiation
QUIC packet type:Long Header Format or short header
Long Header Format:
0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ |1| Type (7) | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | | + Connection ID (64) + | | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Packet Number (32) | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Version (32) | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Payload (*) ... +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Long headers are used for packets that are sent prior to the completion of version negotiation and establishment of 1-RTT keys.
Once both conditions are met, a sender switches to sending packets using the short header
- Header Form: The most significant bit (0x80) of octet 0 (the firstoctet) is set to 1 for long headers.
- Long Packet Type: The remaining seven bits of octet 0 contain the packet type. This field can indicate one of 128 packet types
- packet types are defined:
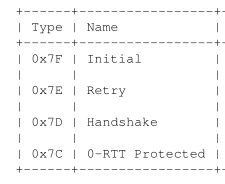
- Version: Octets 9 to 12 contain the selected protocol version. This field indicates which version of QUIC is in use and determines how
the rest of the protocol fields are interpreted
Short Header Format:

The short header can be used after the version and 1-RTT keys are negotiated.
- Packet Numbers:
The packet number is an integer in the range 0 to 2^62-1. The value is used in determining the cryptographic nonce for packet encryption.
Each endpoint maintains a separate packet number for sending and receiving. The packet number for sending MUST increase by at least
one after sending any packet, unless otherwise specified (see Section 5.7.1). A QUIC endpoint MUST NOT reuse a packet number within the same
connection (that is, under the same cryptographic keys). If the packet number for sending reaches 2^62 - 1, the sender MUST close the
connection without sending a CONNECTION_CLOSE frame or any further packets; a server MAY send a Stateless Reset (Section 7.9.4) in
response to further packets that it receives.