-
遇到进程卡死,没有gdb 符号表;只能strace 跟踪处理分析
排查过程:
1、ps -aux 查看卡死进程pid
2、strace -T -tt -e trace=all -p 查看卡死进程系统调用信息
此时卡在read 系统调用上, read 的第一个参数为句柄
3、ls -l /proc/pid/fd
可以看到fd的指向的是哪个socket 或者文件以及innode
4、cat /proc/net/tcp 可以查看inode 信息
5、lsof 查看文件相关信息
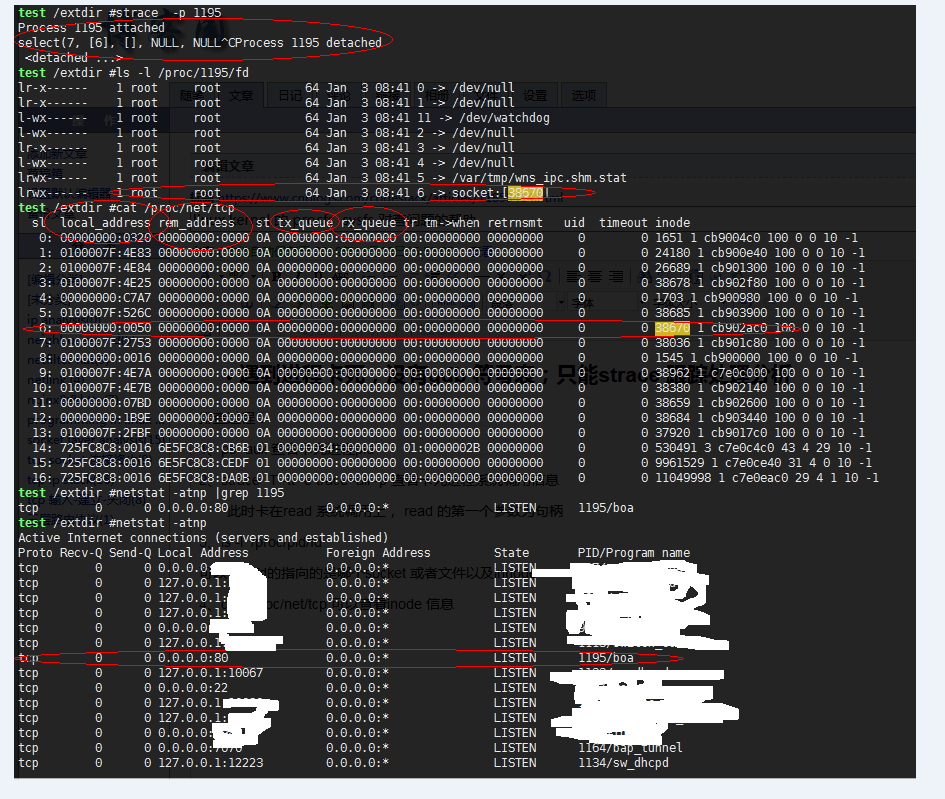
就可以根据fd 找到对应的连接
dynamic debug动态打印 printk_once , 只打印一次。 有些情况下,需要kernel运行时动态打印与否,dynamic debug就派上用场了。 具体用法可以参考: kernel/Documentationdynamic-debug-howto.txt 使用步骤: // 打印 echo 'file nand.c line 4210 +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control // 不打印 echo 'file nand.c line 4210 -p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control // 使用例子 pr_debug(" dynamic debug ");
kprobe:
* specify pre_handler address */ kp.pre_handler=handler_pre; /* specify post_handler address */ kp.post_handler=handler_post; /* specify fault_handler address */ kp.fault_handler=handler_fault; /* specify the address/offset where you want to insert probe. * You can get the address using one of the methods described above. */ kp.addr = (kprobe_opcode_t *) kallsyms_lookup_name("do_fork"); /* check if the kallsyms_lookup_name() returned the correct value. */ if (kp.add == NULL) { printk("kallsyms_lookup_name could not find address for the specified symbol name "); return 1; } /* or specify address directly. * $grep "do_fork" /usr/src/linux/System.map * or * $cat /proc/kallsyms |grep do_fork * or * $nm vmlinuz |grep do_fork */ kp.addr = (kprobe_opcode_t *) 0xc01441d0; /* All set to register with Kprobes */ register_kprobe(&kp); 然后在 init_moudle 中注册的探测器
Kprobes 的好处有很多。不需要重新编译和重新引导内核就可以插入 printk。为了进行调试可以记录 处理器寄存器的日志,甚至进行修改 —— 不会干扰系统。类似地,同样可以无干扰地记录 Linux 内核数据结构的日志,甚至 进行修改