1.3.1邻居系统状态图(老外给的解释)
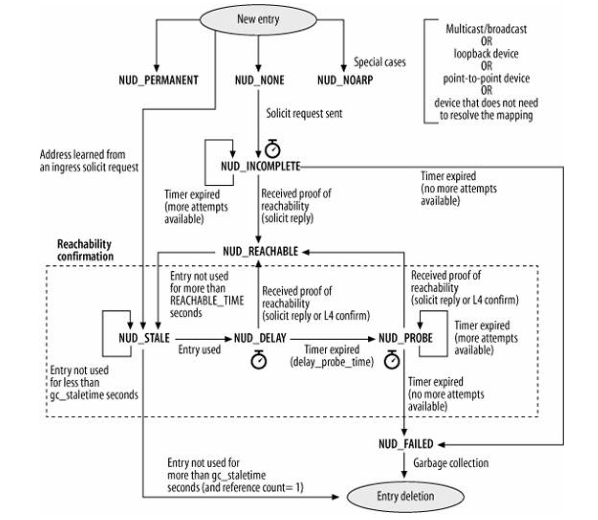
NUD_VALID : An entry is considered to be in the NUD_VALID state if its state is any one of the following, which
represent neighbors believed to have an available address:
NUD_PERMANENT NUD_NOARP NUD_REACHABLE NUD_PROBE NUD_STALE NUD_DELAY
NUD_CONNECTED : This is used for the subset of NUD_VALID states that do not have a confirmation process pending:
NUD_PERMANENT NUD_NOARP NUD_REACHABLE
NUD_IN_TIMER : The neighboring subsystem is running a timer for this entry, which happens when the status is
unclear. The basic states that correspond to this are:
NUD_INCOMPLETE NUD_DELAY NUD_PROBE
1.3.2 邻居表项的查找
邻居项查找是通过neigh_lookup相关函数来进行的;该函数根据输出设备和主键值(IPv4为目的ip地址)在邻居项hash表中查找,
并且在找到邻居项之后,进行引用计数的递增,然后返回该项;
struct neighbour *neigh_lookup(struct neigh_table *tbl, const void *pkey, struct net_device *dev) { struct neighbour *n; int key_len = tbl->key_len; u32 hash_val; struct neigh_hash_table *nht; NEIGH_CACHE_STAT_INC(tbl, lookups); rcu_read_lock_bh(); nht = rcu_dereference_bh(tbl->nht);/* 获取hash */ /* 计算hash值 */ hash_val = tbl->hash(pkey, dev, nht->hash_rnd) >> (32 - nht->hash_shift);/* 计算hash值 */ /* 遍历hash表项 */ for (n = rcu_dereference_bh(nht->hash_buckets[hash_val]); n != NULL; n = rcu_dereference_bh(n->next)) { /* 找到则返回该项 */ if (dev == n->dev && !memcmp(n->primary_key, pkey, key_len)) { if (!atomic_inc_not_zero(&n->refcnt)) n = NULL; NEIGH_CACHE_STAT_INC(tbl, hits); break; } } rcu_read_unlock_bh(); return n; }
1.3.3 邻居状态更新
下面我们分析一下函数neigh_update:
该函数的功能:邻居项的更新,主要是更新二层地址与邻居项的状态,并会 根据邻居项的状态,选择相对应的输出函数
1、判断输入二层地址,判断是否需要覆盖邻居项的二层地址
2、判断邻居项状态的改变是否合法
3、根据不同的邻居项状态设置不同的邻居项输出函数,并设置与该邻居项关联的所有二层缓存头部
该函数被调用的情形有:
1、当接收到邻居项的应答报文后,则会调用该函数更新二层地址和状态为CONNECT
2、当接收到邻居项的请求报文后,则会调用该函数将邻居项的状态设置为STALE
3、处理通过ioctl或者netlink执行的邻居项的添加、删除邻居项时,也会调用该函数
更新邻居项的状态与二层地址
/* Generic update routine. -- lladdr is new lladdr or NULL, if it is not supplied. -- new is new state. -- flags NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE allows to override existing lladdr, if it is different. NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE will suspect existing "connected" lladdr instead of overriding it if it is different. It also allows to retain current state if lladdr is unchanged. NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ADMIN means that the change is administrative. NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE_ISROUTER allows to override existing NTF_ROUTER flag. NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ISROUTER indicates if the neighbour is known as a router. Caller MUST hold reference count on the entry. */ /* 更新指定的邻居项,更新内容为硬件地址和状态,如果新状态有效,并且有缓存包,则发送 */ int neigh_update(struct neighbour *neigh, const u8 *lladdr, u8 new, u32 flags) { u8 old; int err; int notify = 0; struct net_device *dev; int update_isrouter = 0; static unsigned long log_timeout = 0; int i; write_lock_bh(&neigh->lock); dev = neigh->dev; old = neigh->nud_state; err = -EPERM; /* 原状态是NOARP或者PERMANENT,必须要求是用户管理员发生的更新 */ if (!(flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ADMIN) && (old & (NUD_NOARP | NUD_PERMANENT))) goto out; /* 新状态不是有效状态 */ if (!(new & NUD_VALID)) { neigh_del_timer(neigh);/* 删除定时器 */ if (old & NUD_CONNECTED) /* 原状态是已连接状态,更新输出函数 */ neigh_suspect(neigh); neigh->nud_state = new;/* 设置状态 */ err = 0; notify = old & NUD_VALID; NEIGH_PRINTK2("%s,%d old 0x%x, new 0x%x flags 0x%x ", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, old, new, flags); /* 原状态为INCOMPLETE或者PROBE,新状态为失败状态 */ 或者old为admin用户下的等xx状态 则清空缓存队列 if ((((old & (NUD_INCOMPLETE | NUD_PROBE | NUD_REACHABLE | NUD_STALE | NUD_DELAY | NUD_FAILED)) && (flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ADMIN)) || (old & (NUD_INCOMPLETE | NUD_PROBE)))&& (new & NUD_FAILED)) { /* 清空缓存包队列 */ neigh_invalidate(neigh);// neigh_invalidate发送错误报告,并发送通知信息,函数返回 notify = 1; } goto out; } /*
1、对于设备二层地址长度为0的情形,则不需要更新二层地址,直接使用neigh->ha
2、原状态为有效的,且要更改的地址与邻居项存储的地址相同,则无需更改
3、原状态为无效,且要更改的地址也是无效,则是逻辑错误,函数直接 返回
4、原状态有效,且要更改的地址无效时,则先将地址设置为邻居项的地址=
5、其他情况下不更改传进来的二层地址。
即:
原状态有效,且修改的地址与原邻居项地址不同
原状态无效,且修改的地址有效时
*/ /* Compare new lladdr with cached one */ if (!dev->addr_len) { /* First case: device needs no address. */ lladdr = neigh->ha; } else if (lladdr) { /* The second case: if something is already cached and a new address is proposed: - compare new & old - if they are different, check override flag */ if ((old & NUD_VALID) && !memcmp(lladdr, neigh->ha, dev->addr_len)) lladdr = neigh->ha; } else { /* No address is supplied; if we know something, use it, otherwise discard the request. */ err = -EINVAL; if (!(old & NUD_VALID)) goto out; lladdr = neigh->ha; } if (new & NUD_CONNECTED) neigh->confirmed = jiffies; neigh->updated = jiffies; /* If entry was valid and address is not changed, do not change entry state, if new one is STALE. */ err = 0; update_isrouter = flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE_ISROUTER; if (old & NUD_VALID) { /* 原状态有效 */ /* 地址不同 && 无UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE标记 */ if (lladdr != neigh->ha && !(flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE)) { update_isrouter = 0; if ((flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE) && (old & NUD_CONNECTED)) { /* 有UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE状态 && 原状态是连接状态 */ lladdr = neigh->ha; /* 更新硬件地址为邻居项地址 */ new = NUD_STALE; } else goto out; } else { /* 地址相同或者有UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE标记 */ if (lladdr == neigh->ha && new == NUD_STALE && ((flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE) || (old & NUD_CONNECTED)) ) new = old; } } if (new != old) { if (new & NUD_REACHABLE) { notify = 1; } neigh_del_timer(neigh); /* 删除定时器 */ if (new & NUD_IN_TIMER) /* 新状态需要定时器,则添加 */ neigh_add_timer(neigh, (jiffies + ((new & NUD_REACHABLE) ? neigh->parms->reachable_time : 0))); neigh->nud_state = new; /* 设置新状态 */ } /*
如果邻居项的二层地址不同,则更新邻居项里的二层地址,并
调用neigh_update_hhs,更新与该邻居项相关联的所有二层头部缓存。
如果新状态不是CONNECT状态,则将confirm时间设置为比当前时间早2*base_reachable_time.根据邻居项的不同更新邻居项的输出函数:
当为NUD_CONNECTED,则调用neigh_connect将邻居项的输出函数设置为快速输出函数
当为非NUD_CONNECTED,则调用neigh_suspect将邻居项的输出函数设置为通用输出函数
*/ if (lladdr != neigh->ha) { /* 新旧状态不同或新旧地址不同 */ write_seqlock(&neigh->ha_lock); memcpy(&neigh->ha, lladdr, dev->addr_len); /* 拷贝新地址 */ write_sequnlock(&neigh->ha_lock); neigh_update_hhs(neigh); if (!(new & NUD_CONNECTED)) /* 新状态不是连接状态,更新确认时间 */ neigh->confirmed = jiffies - (neigh->parms->base_reachable_time << 1); notify = 1; } if (new == old) goto out; if (new & NUD_CONNECTED) /* 新状态为CONNECTED,更新输出函数为connected_out */ neigh_connect(neigh); else neigh_suspect(neigh); /* 否则,输出函数为output */ if (!(old & NUD_VALID)) { /* 原状态无效,新状态有效 */ struct sk_buff *skb; /* Again: avoid dead loop if something went wrong */ while (neigh->nud_state & NUD_VALID && /* 新状态有效,缓存队列不为空 */ (skb = __skb_dequeue(&neigh->arp_queue)) != NULL) { struct dst_entry *dst = skb_dst(skb); struct neighbour *n2, *n1 = neigh; write_unlock_bh(&neigh->lock); rcu_read_lock(); /* Why not just use 'neigh' as-is? The problem is that * things such as shaper, eql, and sch_teql can end up * using alternative, different, neigh objects to output * the packet in the output path. So what we need to do * here is re-lookup the top-level neigh in the path so * we can reinject the packet there. */ n2 = NULL; if (dst) { /* 有路由缓存,则根据路由缓存获取邻居项,有则替换 */ n2 = dst_neigh_lookup_skb(dst, skb); if (n2) n1 = n2; } n1->output(n1, skb); /* 输出数据包 */ if (n2) /* 是否引用的邻居项 */ neigh_release(n2); rcu_read_unlock(); write_lock_bh(&neigh->lock); } skb_queue_purge(&neigh->arp_queue); /* 清空数据包缓存队列 */ neigh->arp_queue_len_bytes = 0; } out: if (update_isrouter) { neigh->flags = (flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ISROUTER) ? (neigh->flags | NTF_ROUTER) : (neigh->flags & ~NTF_ROUTER); } write_unlock_bh(&neigh->lock); if (notify) /* 通知其他关心的模块 */ neigh_update_notify(neigh); return err; }