java的基本输入流是java.io.InputStream,该抽象类定义了输入流的基本输入操作方法,实现自该抽象类的子类都有定义自己的数据源,例如ByteArrayInputStream的构造函数指定了ByteArrayInputStream输入流的数据源必须是一个字符数组。这就可以有多种不同的数据源,包括:字符数组、String对象、文件、“管道”、一个由其他种类的流组成的序列...
1 public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[]) {} 2 3 public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length) {}
InputStream子类的继承结构如下,这里列举部分子类,还有很多未能列举:
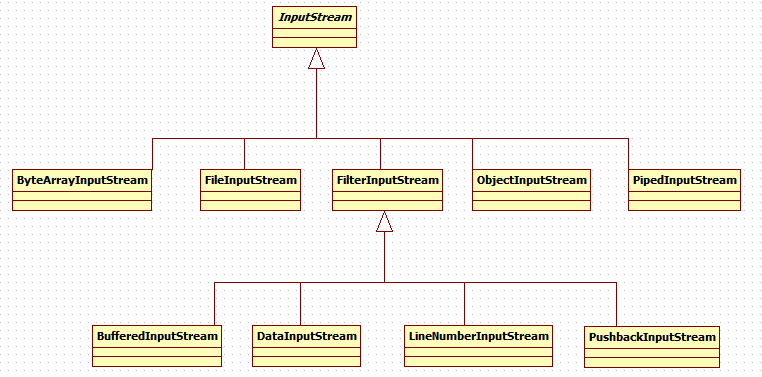
下面对这些不同的输入流稍加分析
1、ByteArrayInputStream,它包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区包含从流中读取的字节。内部计数器跟踪 read 方法要提供的下一个字节。 下面是它的源码:

1 public class ByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream { 2 protected byte buf[]; 3 protected int pos; 4 protected int mark = 0; 5 protected int count; 6 public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[]) { 7 this.buf = buf; 8 this.pos = 0; 9 this.count = buf.length; 10 } 11 public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length) { 12 this.buf = buf; 13 this.pos = offset; 14 this.count = Math.min(offset + length, buf.length); 15 this.mark = offset; 16 } 17 public synchronized int read() { 18 return (pos < count) ? (buf[pos++] & 0xff) : -1; 19 } 20 public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) { 21 if (b == null) { 22 throw new NullPointerException(); 23 } else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) { 24 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); 25 } 26 27 if (pos >= count) { 28 return -1; 29 } 30 31 int avail = count - pos; 32 if (len > avail) { 33 len = avail; 34 } 35 if (len <= 0) { 36 return 0; 37 } 38 System.arraycopy(buf, pos, b, off, len); 39 pos += len; 40 return len; 41 } 42 public synchronized long skip(long n) { 43 long k = count - pos; 44 if (n < k) { 45 k = n < 0 ? 0 : n; 46 } 47 pos += k; 48 return k; 49 } 50 public synchronized int available() { 51 return count - pos; 52 } 53 public boolean markSupported() { 54 return true; 55 } 56 public void mark(int readAheadLimit) { 57 mark = pos; 58 } 59 public synchronized void reset() { 60 pos = mark; 61 } 62 public void close() throws IOException { 63 } 64 }
从源码可以看出,该输入流是一个同步安全的输入流,下面是它的测试代码:

1 static void byteArrayTest(){ 2 String alph="abcddefghijklmnopqrsttuvwxyz"; 3 byte[] cha=alph.getBytes(); 4 ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(cha); 5 if (!bais.markSupported()) { 6 System.out.println("make not supported!"); 7 return ; 8 } 9 int i=0; 10 while(bais.available()>0){ 11 System.out.print((char)bais.read()+" "); 12 i++; 13 } 14 System.out.println(" "+i); 15 }
由于该输入流的数据源是一个字节数组,所以要把字符串转换成字符数组。
2、FileInputStream,文件输入流,用于从一个文件中读取字节,它主要用于读取原始字节流,如图片等,如果读取字符流,需要用FileReader.下面是它的源码:

1 public class FileInputStream extends InputStream 2 { 3 private final FileDescriptor fd; 4 private final String path; 5 private FileChannel channel = null; 6 private final Object closeLock = new Object(); 7 private volatile boolean closed = false; 8 public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException { 9 this(name != null ? new File(name) : null); 10 } 11 public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException { 12 String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null); 13 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); 14 if (security != null) { 15 security.checkRead(name); 16 } 17 if (name == null) { 18 throw new NullPointerException(); 19 } 20 if (file.isInvalid()) { 21 throw new FileNotFoundException("Invalid file path"); 22 } 23 fd = new FileDescriptor(); 24 fd.attach(this); 25 path = name; 26 open(name); 27 } 28 public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) { 29 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); 30 if (fdObj == null) { 31 throw new NullPointerException(); 32 } 33 if (security != null) { 34 security.checkRead(fdObj); 35 } 36 fd = fdObj; 37 path = null; 38 fd.attach(this); 39 } 40 private native void open0(String name) throws FileNotFoundException; 41 private void open(String name) throws FileNotFoundException { 42 open0(name); 43 } 44 public int read() throws IOException { 45 return read0(); 46 } 47 private native int read0() throws IOException; 48 private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException; 49 public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException { 50 return readBytes(b, 0, b.length); 51 } 52 public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException { 53 return readBytes(b, off, len); 54 } 55 public native long skip(long n) throws IOException; 56 public native int available() throws IOException; 57 public void close() throws IOException { 58 synchronized (closeLock) { 59 if (closed) { 60 return; 61 } 62 closed = true; 63 } 64 if (channel != null) { 65 channel.close(); 66 } 67 68 fd.closeAll(new Closeable() { 69 public void close() throws IOException { 70 close0(); 71 } 72 }); 73 } 74 public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException { 75 if (fd != null) { 76 return fd; 77 } 78 throw new IOException(); 79 } 80 public FileChannel getChannel() { 81 synchronized (this) { 82 if (channel == null) { 83 channel = FileChannelImpl.open(fd, path, true, false, this); 84 } 85 return channel; 86 } 87 } 88 private static native void initIDs(); 89 private native void close0() throws IOException; 90 static { 91 initIDs(); 92 } 93 protected void finalize() throws IOException { 94 if ((fd != null) && (fd != FileDescriptor.in)) { 95 close(); 96 } 97 } 98 }
该输入流的数据源是一个文件,从源代码中可以看出,它使用了一个native方法,该方法的底层实现是C代码。下面是文件输入流的一个例子:

1 static void fileInputTest(){//读取一个图片的字节信息 2 try{ 3 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("a.PNG"); 4 try{ 5 byte[] bf=new byte[1024]; 6 while(fis.read(bf)>0){ 7 for(byte by:bf){ 8 System.out.print(by+" "); 9 } 10 System.out.println(); 11 } 12 }catch(IOException e){ 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 }catch(Exception e){ 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 }
这里读取一张照片,然后将读取出的字节输出来。
3、FilterInputStream,它是用来提供装饰器接口,用以控制特定的输入流,在装饰模式中,装饰器能够动态地给一个对象添加额外的职责,FilterInputStream的构造函数是Protected类型的,这说明,它只想让它的子类以及那些和它在同一个包下的类访问它,我们是不能够直接创建它的对象的,这里用该类的一个子类BufferedInputStream为例进行分析,以下是BufferedInputStream的源代码:

1 public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream { 2 private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192; 3 private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 4 protected volatile byte buf[]; 5 private static final 6 AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<BufferedInputStream, byte[]> bufUpdater = 7 AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater 8 (BufferedInputStream.class, byte[].class, "buf"); 9 protected int count; 10 protected int pos; 11 protected int markpos = -1; 12 protected int marklimit; 13 private InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException { 14 InputStream input = in; 15 if (input == null) 16 throw new IOException("Stream closed"); 17 return input; 18 } 19 private byte[] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException { 20 byte[] buffer = buf; 21 if (buffer == null) 22 throw new IOException("Stream closed"); 23 return buffer; 24 } 25 public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) { 26 this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE); 27 } 28 public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) { 29 super(in); 30 if (size <= 0) { 31 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0"); 32 } 33 buf = new byte[size]; 34 } 35 private void fill() throws IOException { 36 byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen(); 37 if (markpos < 0) 38 pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */ 39 else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */ 40 if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */ 41 int sz = pos - markpos; 42 System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz); 43 pos = sz; 44 markpos = 0; 45 } else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) { 46 markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */ 47 pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */ 48 } else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) { 49 throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large"); 50 } else { /* grow buffer */ 51 int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ? 52 pos * 2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE; 53 if (nsz > marklimit) 54 nsz = marklimit; 55 byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz]; 56 System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos); 57 if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) { 58 throw new IOException("Stream closed"); 59 } 60 buffer = nbuf; 61 } 62 count = pos; 63 int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos); 64 if (n > 0) 65 count = n + pos; 66 } 67 public synchronized int read() throws IOException { 68 if (pos >= count) { 69 fill(); 70 if (pos >= count) 71 return -1; 72 } 73 return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff; 74 } 75 private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException { 76 int avail = count - pos; 77 if (avail <= 0) { 78 /* If the requested length is at least as large as the buffer, and 79 if there is no mark/reset activity, do not bother to copy the 80 bytes into the local buffer. In this way buffered streams will 81 cascade harmlessly. */ 82 if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0) { 83 return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len); 84 } 85 fill(); 86 avail = count - pos; 87 if (avail <= 0) return -1; 88 } 89 int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len; 90 System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt); 91 pos += cnt; 92 return cnt; 93 } 94 public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) 95 throws IOException 96 { 97 getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream 98 if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) { 99 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); 100 } else if (len == 0) { 101 return 0; 102 } 103 104 int n = 0; 105 for (;;) { 106 int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n); 107 if (nread <= 0) 108 return (n == 0) ? nread : n; 109 n += nread; 110 if (n >= len) 111 return n; 112 // if not closed but no bytes available, return 113 InputStream input = in; 114 if (input != null && input.available() <= 0) 115 return n; 116 } 117 } 118 public synchronized long skip(long n) throws IOException { 119 getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream 120 if (n <= 0) { 121 return 0; 122 } 123 long avail = count - pos; 124 125 if (avail <= 0) { 126 // If no mark position set then don't keep in buffer 127 if (markpos <0) 128 return getInIfOpen().skip(n); 129 130 // Fill in buffer to save bytes for reset 131 fill(); 132 avail = count - pos; 133 if (avail <= 0) 134 return 0; 135 } 136 137 long skipped = (avail < n) ? avail : n; 138 pos += skipped; 139 return skipped; 140 } 141 public synchronized int available() throws IOException { 142 int n = count - pos; 143 int avail = getInIfOpen().available(); 144 return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail) 145 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE 146 : n + avail; 147 } 148 public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) { 149 marklimit = readlimit; 150 markpos = pos; 151 } 152 public synchronized void reset() throws IOException { 153 getBufIfOpen(); // Cause exception if closed 154 if (markpos < 0) 155 throw new IOException("Resetting to invalid mark"); 156 pos = markpos; 157 } 158 public boolean markSupported() { 159 return true; 160 } 161 public void close() throws IOException { 162 byte[] buffer; 163 while ( (buffer = buf) != null) { 164 if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) { 165 InputStream input = in; 166 in = null; 167 if (input != null) 168 input.close(); 169 return; 170 } 171 } 172 } 173 }
注意,这里BufferedInputStream的构造函数的参数是InputStream的对象,这说明BufferedInputStream的数据来源是一个由InputStream类型的流组成的序列,可以是FileInputStream,这样在读文件的时候,就具备了缓冲能力,这就是“装饰”模式带来的效果,在创建 BufferedInputStream 时,会创建一个内部缓冲区数组。在读取或跳过流中的字节时,可根据需要从包含的输入流再次填充该内部缓冲区,一次填充多个字节。mark 操作记录输入流中的某个点,reset 操作使得在从包含的输入流中获取新字节之前,再次读取自最后一次 mark 操作后读取的所有字节。 用法如下面代码所示:

1 static void bufferedInputTest(){ 2 try{//BufferedInputStream 测试 3 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("a.PNG"); 4 BufferedInputStream buf=new BufferedInputStream(fis); 5 try{ 6 byte[] bf=new byte[1024]; 7 while(buf.read(bf)>0){ 8 for(byte by:bf){ 9 System.out.print(by+" "); 10 } 11 System.out.println(); 12 } 13 }catch(IOException e){ 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 }catch(Exception e){ 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 }
现仅给出以上三个示例,其它类的使用方法可参考java api文档。向着明天,加油!
