第0章
0-0 编译并运行Hello, world! 程序。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello, world!" << endl; return 0; }
0-1 下面的表达式是做什么的?
3+4
计算3+4,结果为7
0-2 编写一个程序,使它在运行时输出:
This (*) is a quote , and this () is a backlash.
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "This (*) is a quote , and this (\) is a backlash" << endl; return 0; }
0-3 字符串直接量" "代表一个水平制表符;不同的C++实现以不同的形式显示制表符。在你的实现中实验一下,看它是怎样处理制表符的。
处理为4个空格
0-4 编写一个程序,运行时以Hello, world!程序作为这个程序输出。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "#include <iostream> " << "using namespace std; " << "int main() " << "{ " << " cout << "Hello, world!" << endl; " << " return 0; " << "}"; " << "return 0; "; return 0; }
0-5 下面的程序是一个有效的程序吗?说出理由。
#include <iostream> int main() std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl;
这是一个无效程序,因为函数的函数体必须用花括号括起来,就算函数的函数体只有一条语句,也必须用花括号括住它。
0-6 下面的程序是一个有效的程序吗?说出理由。
#include <iostream> int main() {{{{{{ std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl; }}}}}}
这是一个有效程序,一般来说,函数必须包含至少一条的return语句,而且函数的最后一定要有return语句,但main比较特殊,它可以没有返回语句,若果这样,编译器就会假设它返回0。
0-7 那下面的这个程序呢?
#include <iostream> int main() { /*这是一个注释,因为我们使用了/*和*/来作为它的定界符, 所以它占据了几行的范围*/ std::cout << "Does this work?" << std::endl; return 0; }
无效程序,注释有误,注释在前一个结束符*/就结束了,所以后面的内容都未能注释。
0-8 ······这个呢?
#include <iostream> int main() { //这是一个注释,它占据了几行的范围 //在这里,我们使用了//而不是/* //和*/来为注释定界 std::cout << "Does this work?" << std::endl; return 0; }
有效程序,单行注释使用后,后面的多行注释符号不在起作用。
0-9 最短的有效程序是什么?
int main() {}
0-10 重写Hello, workd! 程序,让程序中每一个允许出现空白符的地方都换行。
#include<iostream> #include<conio.h> int main() { std::cout << "hello, world!" << std::endl; return 0; }
第1章
1-0 编译、允许并测试本章中的程序。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> int main() { std::cout <<"Pleause enter your first name: "; std::string name; std::cin >> name; std::cout << "Hello, " << name << "!" << std::endl; return 0; }
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> int main() { std::cout << "Please enter your first name: "; std::string name; std::cin >> name; const std::string greeting = "Hello," + name + "!"; const std::string spaces(greeting.size(),' '); const std::string second = "*" + spaces + "*"; const std::string first(second.size(),'*'); std::cout << std::endl; std::cout <<first << std::endl; std::cout <<second << std::endl; std::cout << "*" << greeting << "*" << std::endl; std::cout << second << std::endl; std::cout << first << std::endl; return 0; }
1-1 以下的定义有效吗?理由是什么?
const std::string hello = "Hello"; const std::string message = hello + ", world" + "!";
a) 定义有效,可以将一个字符串直接量直接赋给一个字符串变量
b) 定义有效,可以用 + 将一个字符串和一个字符串直接量连接起来
1-2 以下的定义有效吗?理由是什么?
const std::string exclam = "!"; const std::string message = "Hello" + ", world" + exclam;
a) 定义有效
b) 定义无效,”Hello” 和 “world”都是字符串直接量,用+操作符是不合法的,因为其中一个必须std::string对象才是合法的。
1-3 以下的定义有效吗?如果有效的话,它是做什么的?如果无效,为什么呢?
#include<iostream> #include<string> int main() { {const std::string s = "a string"; std::cout << s << std::endl;} {const std::string s = "another string"; std::cout << s << std::endl;} return 0; }
有效,s分别为每对花括号内的局部变量。程序输出了两个字符串
1-4 下面的这个程序又怎样呢?如果我们把倒数第三行的 }} 改成 };} 的话,会出现什么情况呢?
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> int main() { {const std::string s = "a string"; std::cout << s << std::endl; {const std::string s = "another string"; //std::cout << s << std::endl;}} std::cout << s << std::endl;} ;} return 0; }
有效。内部作用域嵌套在外部作用域,内部作用域的s隐藏了外部作用域的s,所以程序是有效的,改变之后仍然有效。
1-5 下面这个程序呢?如果有效,它是做什么的?如果无效,说出理由,然后把它改写成有效的程序。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> int main() { {std::string s = "a string"; {std::string x = s+ ", really"; std::cout << s << std::endl;} std::cout << x << std::endl; // x is out of its scope here } return 0; }
无效,x是在内部作用域定义的,出了内部作用域后,x便是不可用的。去掉内部的花括号,程序就变为有效程序。
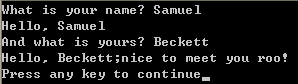
1-6 在下面的程序向你发出输入请求的时候,如果你输入了两个名字(例如,Samuel Beckett),它会怎么样处理呢?在运行程序之前先预测一下结果,然后上机测一下。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> int main() { std::cout << "What is your name? "; std::string name; std::cin >> name; std::cout << "Hello, " << name << std::endl << "And what is yours? "; std::cin >> name; std::cout << "Hello, " << name << ";nice to meet you roo!" << std::endl; return 0; }
第2章
2-0 编译并运行我们在本章中介绍的程序。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; int main() { cout <<"please enter your first name:"; string name; cin >> name; const string greeting ="hello," + name +"!"; const int pad = 1; const int rows = pad*2 + 3; const string::size_type cols = greeting.size() + pad*2 + 2; cout << endl; for (int r = 0; r !=rows; r++) { string::size_type c = 0; while (c != cols) { if (r == pad+1 && c == pad+1) { cout << greeting; c += greeting.size(); }else { if (r == 0 || r == rows-1 || c == 0 || c == cols-1) cout<< "*"; else cout<< " "; ++c; } } cout << endl; } return 0; }
2-1 改写框架程序,输出跟框架没有间隔的问候语。
2-0中 const int pad = 1; 改为 const int pad = 0;
2-2 在我们的框架程序中,我们使用了一定数目的空格来把问候语和顶部以及底部边界分隔开来。现在,重新编写这个程序,在重写的程序中使用数量跟源程序不同的空格来把各边界和问候语分隔开。
把pad的值变成由用户输入即可:
const int pad = 1; 替换成 cout <<"please enter the pad:"; int pad; cin >> pad;
2-3 重写框架程序,让用户自己提供在框架和问候语之间的空格个数。
同上
2-4 在框架程序中的空白行是用来把边界和问候语分隔开的,程序每次一个字符地输出了大部分的空白行。改写这个程序,让它在单独的一条输出表达式中输出所有的空白行。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; int main() { cout <<"please enter your first name:"; string name; cin >> name; const string greeting ="hello," + name +"!"; const int pad = 1; const int rows = pad*2 + 3; const string::size_type cols = greeting.size() + pad*2 + 2; const string spaces = string(greeting.size() + pad * 2, ' '); cout << endl; for (int r = 0; r !=rows; r++) { string::size_type c = 0; while (c != cols) { if (r == pad+1 && c == pad+1) { cout << greeting; c += greeting.size(); }else { if (r == 0 || r == rows-1 || c == 0 || c == cols-1) { cout<< "*"; ++c; } else if (r == pad + 1) { cout<< " "; ++c; }else { cout<< spaces; c +=spaces.size(); } } } cout << endl; } return 0; }
2-5 编写一个程序,让它输出一系列的“*”字符,程序输出的这些字符将构成一个正方形,一个长方形和一个三角形。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; int main() { // this constant is the height of each figure const int height = 5; // these variables are used to track the row and // column count while drawing each figure int row; int col; // draw square row = 0; col = 0; // draw top line while (col < height) { cout <<'*'; ++col; } cout << endl; ++row; // draw middle lines while (row < height - 1) { col = 0; while (col < height) { ++col; if (col == 1) cout <<'*'; else { if (col == height) cout<<'*'; else cout<<' '; } } cout <<endl; ++row; } // draw bottom line col = 0; while (col < height) { cout <<'*'; ++col; } // new line after figure cout << endl; // blank line between figures cout << endl; // draw rectangle row = 0; col = 0; // draw top line while (col < height * 2) { cout <<'*'; ++col; } cout << endl; ++row; // draw middle lines while (row < height - 1) { col = 0; while (col <= height * 2) { ++col; if (col == 1) cout<<'*'; else { if (col == height * 2) cout<<'*'; else cout<<' '; } } cout <<endl; ++row; } // draw bottom line col = 0; while (col < height * 2) { cout <<'*'; ++col; } // new line after figure cout << endl; // blank line between figures cout << endl; // draw triangle row = 0; // draw rows above base while (row < height - 1) { col = 0; while (col < height + row) { ++col; if (col == height - row) cout<<'*'; else { if (col == height + row) cout<<'*'; else cout<<' '; } } cout <<endl; ++row; } // draw the base col = 0; while (col < height * 2 - 1) { cout <<'*'; ++col; } // new line after figure cout << endl; return 0; }
2-6 下面的代码是做什么的?
int i=0; while(i<10) { i+=1; std::cout << i << std::endl; }
代码运行输出1—10的数字,且每个数字占一行。
2-7 编写一个程序来一次输出从10~-5的整数
int i=10; while(i>-5) { std::cout << i << std::endl; i-=1; }
2-8 编写一个程序来计算区间[1,10)中的所有数值的乘积。
int result = 1; for (int i = 1; i< 10; i++) { result *= i; } cout << result<< endl;
2-9 编写一个程序,让用户输入两个数值并告知用户在这两个数值中哪一个较大。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; int main() { int m, n; cout <<"please enter two numbers:"; cin >> m; cin >> n; if (m == n) { cout << m<<" equals " << n; }else if (m > n) { cout << m<<" > " << n; }else { cout << m<<" < " << n; } return 0; }
2-10 在下面的程序中,对std::的每一次使用进行解释。
int main() { int k =0; while (k!=n){ using std::cout; cout << "*"; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }
第1个std::是一个using声明,只适用于最里面的{}内
第2个std::必须明确指出,表示cout的名称空间
第3个std::也要明确指出,表示输出一个新行
第3章
3-0 编译、运行并测试本章中的程序

// test3.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. // #include "stdafx.h" #include<ios> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<iomanip> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::setprecision; using std::string; using std::streamsize; int main() { //请求输入并读入学生的姓名 cout << "please enter your first name: "; string name; cin >> name; cout << "Hello, " << name << "!" << endl; //请求输入并读入期中和期末成绩 cout << "please enter your midterm and final exam grades: "; double midterm, final; cin >> midterm >> final; cout <<"enter all your homework grades, followed by end-of-file: "; //到目前为止,读到的家庭作业成绩的个数及总和 int count =0; double sum =0; //把家庭作业成绩读到变量x中 double x; //不变式 //到目前为止,我们已经读到了count个家庭作业成绩,而且sum等于头count个成绩的总和 while (cin >> x) { ++count; sum += x; } //输出结果 streamsize prec = cout.precision(); cout << "Your final grade is " << setprecision(3) << 0.2 * midterm + 0.4 * final + 0.4 * sum / count << setprecision(prec) << endl; return 0; }
此处不加using namespace std;会报错error C2653: 'vector<double,class std::allocator<double> >' : is not a class
#include "stdafx.h" #include<iomanip> #include<ios> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int main() { //请求输入并读入学生的姓名 cout << "please enter your first name: "; string name; cin >> name; cout << "Hello, " << name << "!" << endl; //请求输入并读入期中和期末成绩 cout << "please enter your midterm and final exam grades: "; double midterm, final; cin >> midterm >> final; cout <<"enter all your homework grades, followed by end-of-file: "; vector<double> homework; double x; //不变式 home包含了所有的家庭作业成绩 while (cin >> x) { homework.push_back(x); } //检查homework是否为空 typedef vector<double>::size_type vec_sz; vec_sz size =homework.size(); if (size == 0) { cout << endl<< "you must enter your grades." "please try again." << endl; return 1; } //对成绩进行排序 sort(homework.begin(), homework.end()); //计算家庭作业成绩的中值 vec_sz mid = size/2; double median; median = (size % 2 ==0) ? (homework[mid] + homework[mid-1]/2) : homework[mid]; //计算并输出总成绩 streamsize prec = cout.precision(); cout << "Your final grade is " << setprecision(3) << 0.2 * midterm + 0.4 * final + 0.4 * median << setprecision(prec) << endl; return 0; }
3-1 假设我们希望找出一个数值集合的中值;同时假定到目前为止,我们已经读进一些数值了,而且不清楚还要再读进多少个值。证明:我们不能丢掉已经读到的任何值。提示:一个可行的证明策略是,先假定我们可以丢掉一个值,然后找出我们的集合中未读的(也就是未知的)那部分数值,要求这些数值将会使中值恰好就是我们丢掉的那个值。
中值是一个可将数值集合划分为相等的上下两部分的数值。对于有限的数集,通过把所有的值高低排序后找出正中间的一个作为中位数。中间点取决于所有的数值。
由此可知,如果任何一个我们已经读到的值被丢弃,则会改变原先中间点的位置,这样就得不出准确的中值。
3-2 把一个整数集合分为个数相等的四部分,而且第一部分含有的整数值比其他各部分的都大,第二部分的值比第一部分的小比其他两部分的大,剩下的两部分则以此类推。按照上面的要求,编写一个程序来计算并且打印这四部分。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> integers; cout << "Integers: "; int x; while (cin >> x) integers.push_back(x); if (integers.size() == 0) { cout << endl<<"No integers!" <<endl; return 1; } sort(integers.rbegin(), integers.rend()); typedef vector<int>::size_type vec_sz; cout << "1st quartile" << endl; for (vec_sz i = 0; i < integers.size() / 4; ++i) cout <<integers[i] << endl; cout << "2nd quartile" << endl; for (vec_sz j = integers.size() / 4; j <integers.size() / 2; ++j) cout <<integers[j] << endl; cout << "3rd quartile" << endl; //注意这里确定第3部分范围的时候的技巧 for (vec_sz k = integers.size() / 2; k <integers.size() * 3 / 4; ++k) cout <<integers[k] << endl; cout << "4th quartile" << endl; for (vec_sz l = integers.size() * 3 / 4; l <integers.size(); ++l) cout <<integers[i] << endl; return 0; }
3-3 编写一个程序来计算在它的输入中的每个不同的单次所出现的次数。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { vector<string> words; vector<int> counts; typedef vector<string>::size_type vec_sz; cout << "enter the words: "; string str; while (cin >> str) { bool found = false; for (vec_sz i = 0; i < words.size(); ++i) { if (str == words[i]) { ++counts[i]; found = true; } } //新字符串才加入向量 if (!found) { words.push_back(str); counts.push_back(1); } } for (vec_sz i = 0; i < words.size(); ++i) { cout <<words[i] <<" appears "<< counts[i] <<" times"<< endl; } return 0; }
3-4 编写一个程序来报告它的输入中最长的以及最短的字符串的长度。
#include "stdafx.h" #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { typedef string::size_type str_sz; string longest; str_sz longest_size =0; string shortest; str_sz shortest_size= 0; cout << "enter words: "; string s; while (cin >> s) { if (longest_size == 0 || s.size() > longest_size) { longest = s; longest_size = s.size(); } if (shortest_size == 0 || s.size() < shortest_size) { shortest = s; shortest_size = s.size(); } } cout <<" 最长的:"<< longest << " (" << longest_size << ")" << endl; cout <<" 最短的:"<< shortest << " (" << shortest_size<< ")" << endl; return 0; }
3-5 编写一个程序来跟踪n个学生的成绩。要求程序能够保持两个向量的同步:第一个应保存学生的姓名;第二个保存总成绩,而这个总成绩能根据读到的输入来计算。读者应假定家庭作业成绩的个数是固定的。
#include "stdafx.h" #include "iostream" #include "string" #include "vector" using namespace std; int main() { int n; //学生总数n string name; vector<string> vNames; vector<double> vGrade; //请求输入并读入学生的姓名 cout << "Please enter number of students: "; cin >> n; for(int i=1; i <= n; i++) { cout << "Please enter name of student " << i << ": "; cin >> name; vNames.push_back(name); //把输入的name加入向量 cout << "Hello, " << name << "!" << endl; int num = 3; cout << "Please enter "<< num << " grades: "; //提示输入3个成绩 double grade; double gradeCount = 0; while(num-->0) { cin >> grade; gradeCount += grade; } //计算的总成绩,加入向量 vGrade.push_back (gradeCount); } for(vector<string>::size_type j=0; j < vNames.size(); j++) { cout << "name: " << vNames[j] << " ,total grade: " << vGrade[j] << endl; } return 0; }
第4章
4-0
#include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; //1 4.1.1 median函数 double median (vector<double>vec) //查找中值 { typedef vector<double>::size_type vec_sz; vec_sz size =vec.size(); if (size == 0) throw domain_error ("median of an empty vector"); sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); vec_sz mid = size/2; return size % 2 == 0 ? (vec[mid] + vec[mid-1])/2 :vec[mid]; } //2 4.1 grade函数 double grade(double midterm, double final, double homework) { return 0.2 * midterm + 0.4 * final +0.4 * homework; } //3 4.1.2 grade函数 double grade(double midterm, double final, const vector<double>& hw) { if (hw.size() == 0) throw domain_error ("student has done no homework"); return grade(midterm, final, median(hw)); } //4 4.1.3 read_hw函数 istream read_hw(istream& in, vector<double>& hw) { if(in){ hw.clear(); //清除原先的内容 double x; //读家庭作业成绩 while (in >>x) hw.push_back(x); in.clear(); //清除流以使输入动作对下一个学生有效 } return in; } int main() { //请求并读入学生姓名 cout << "Please enter your first name: "; string name; cin >> name; cout << "Hello, " << name << "!" << endl; //请求并读入期中和期末考试的成绩 cout << "Please enter your midterm and final exam grades: "; double midterm, final; cin >> midterm >> final; //请求用户输入家庭作业成绩 cout << "Enter all your homework grades, folloowed by end-of-file: "; vector<double> homework; //读入家庭作业成绩 read_hw(cin, homework); //如果可以的话,计算成总成绩 try { double final_grade = grade(midterm, final, homework); //streamsize prec = cout.setprecision(); streamsize prec = cout.precision(); cout << "Your final grade is " << setprecision(3) << final_grade << setprecision(prec) << endl; }catch (domain_error) { cout <<endl << "You must enter your grades. " << "Please try again." <<endl; return 1; } return 0; }
2

#include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; //1 4.1.1 median函数 double median (vector<double>vec) //查找中值 { typedef vector<double>::size_type vec_sz; vec_sz size = vec.size(); if (size == 0) throw domain_error ("median of an empty vector"); sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); vec_sz mid = size/2; return size % 2 == 0 ? (vec[mid] + vec[mid-1])/2 :vec[mid]; } //2 4.1 grade函数 double grade(double midterm, double final, double homework) { return 0.2 * midterm + 0.4 * final +0.4 * homework; } //3 4.1.2 grade函数 double grade(double midterm, double final, const vector<double>& hw) { if (hw.size() == 0) throw domain_error ("student has done no homework"); return grade(midterm, final, median(hw)); } //4 4.1.3 read_hw函数 istream read_hw(istream& in, vector<double>& hw) { if(in){ hw.clear(); //清除原先的内容 double x; //读家庭作业成绩 while (in >>x) hw.push_back(x); in.clear(); //清除流以使输入动作对下一个学生有效 } return in; } struct Student_info{ string name; double midterm, final; vector<double> homework; }; double grade(const Student_info& s) { return grade(s.midterm, s.final, s.homework); } istream& read(istream& is, Student_info& s) { //读入并存储学生的姓名以及期中、期末考试成绩 is >> s.name >> s.midterm >> s.final; read_hw(is, s.homework); //读入并存储学生的所有家庭作业成绩 return is; } bool compare(const Student_info& x, const Student_info& y) { return x.name < y.name; } int main() { vector<Student_info> students; Student_info record; string::size_type maxlen = 0; //读并存储所有的记录,然后找出最长的姓名的长度 while(read(cin, record)){ //maxlen = max(maxlen, record.name.size()); maxlen=_MAX(maxlen, record.name.size()); //vc6用_MAX替代max函数 students.push_back(record); } //按字母顺序排列记录 sort(students.begin(), students.end(), compare); for(vector<Student_info>::size_type i = 0; i != students.size(); ++i){ //输出姓名,填充姓名以达到maxlen +1的长度 cout << setw(maxlen+1) << students[i].name; //计算并输出成绩 try{ double final_grade = grade(students[i]); streamsize prec = cout.precision(); cout << setprecision(3) << final_grade << setprecision(prec); }catch(domain_error e){ cout << e.what(); } cout << endl; } return 0; }
3

#ifndef GUARD_median_h #define GUARD_median_h #include<vector> double median(std::vector<double>); #endif

#include<algorithm> #include<stdexcept> #include<vector> //using std::domain_error; //using std::sort; //using std::vector; using namespace std; double median (vector<double>vec) { typedef vector<double>::size_type vec_sz; vec_sz size =vec.size(); if (size == 0) domain_error ("median of an empty vector"); sort (vec.begin(),vec.end()); vec_sz mid = size/2; return size % 2 == 0 ? (vec[mid] + vec[mid-1]) :vec[mid]; }

#ifndef GUARD_Student_info #define GUARD_Student_info #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> struct Student_info { std::string name; double midterm, final; std::vector<double> homework; }; bool compare(const Student_info&,const Student_info&); std::istream& read(std::istream&, Student_info&); std::istream& read_hw(std::istream&, std::vector<double>&); #endif

#include"Student_info.h" using std::istream; using std::vector; bool compare (const Student_info& x,const Student_info& y){ return x.name < y.name; } istream& read (istream& is, Student_info& s) { is >> s.name>> s.midterm >> s.final; read_hw (is,s.homework); return is; } istream& read_hw (istream& in, vector<double>& hw) { if (in) { hw.clear(); double x; while (in >> x) hw.push_back(x); in.clear(); } return in; }

#ifndef GUARD_grade_h #define GUARD_grade_h #include<vector> #include"Student_info.h" double grade(double,double,double); double grade(double,double,const std::vector<double>&); double grade(const Student_info&); #endif

#include<stdexcept> #include<vector> #include"grade.h" #include"median.h" #include"Student_info.h" using std::domain_error; using std::vector; double grade (double midterm,double final,double homework) { return 0.2 * midterm + 0.4 * final + 0.4 * homework; } double grade (double midterm,double final,const vector<double>& hw) { if (hw.size() == 0) { throw domain_error("studenthas done no homework"); } return grade (midterm, final, median(hw)); } double grade (const Student_info& s) { return grade (s.midterm, s.final, s.homework); }

#include<algorithm> #include<iomanip> #include<ios> #include<iostream> #include<stdexcept> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<conio.h> #include"grade.h" #include"Student_info.h" using namespace std; int main() { vector<Student_info> students; Student_info record; string::size_type maxlen = 0; while (read(cin, record)) { maxlen =_MAX(maxlen, record.name.size()); students.push_back(record); } sort(students.begin(),students.end(), compare); for (vector<Student_info>::size_type i = 0; i!= students.size(); ++i) { cout <<students[i].name << string(maxlen+1-students[i].name.size(),' '); try { double final_grade = grade(students[i]); streamsize prec= cout.precision(); cout <<setprecision(3) << final_grade << setprecision(prec); } catch (domain_error e) { cout <<e.what(); } cout <<endl; } getch(); return 0; }
4-1 我们注意到,在4.2.3中,在调用max的时候,必须让参数的类型严格匹配。下面的代码正确吗?如果有问题的话,那你将怎样改正他呢?
int maxlen; Student_info s; max(s.name.size(), maxlen);
将maxlen定义为int类型是不正确的,因为max函数两个参数必须是同样的类型,而第一个参数的类型是string::size_type,第二个参数的类型是int,不相同,因此是不正确的。
正确的做法是将maxlen的类型定义为string::size_type类型。
4-2 编写一个程序来计算从1-100的整数(int)值的平方。程序的输出分为两列:第一列是整数值,第二列是整数值的平方。使用控制器来控制输出,让数值按列排列起来。
#include<algorithm> #include<iomanip> #include<ios> #include<iostream> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { for(int i=1;i<=100;i++) { cout<< setw(3) << i << setw(5) << i*i <<endl; } return 0; }
4-3 如果我们重写了上题中的程序,让它计算从1到999的整数的平方。但是,我们忘记了更改setw的参数的值。这样做会有什么问题呢?重写这个程序,让它具有更好的适应性。重写后的程序应实现这样的目标:当i增长时我们不需要修正setw的参数。
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<math.h> using namespace std; int get_width(int n) { return log10(n*1.0) + 1; //注意log10()的参数 } int main() { cout << "enter the range min to max: "; int min, max; cin >> min >> max; for(int i=min;i<=max;i++) { cout << setw(get_width(max)) << i << setw(get_width(max*max) + 1) <<i * i << endl; } return 0; }
4-4 现在,再次修改你的求平方程序,用它来求double类型而不是int类型的值的平方。使用控制器来控制输入,让数值按列排列起来。
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<math.h> using namespace std; int get_width(double n) { return log10(n) + 1; } int main() { cout << "enter the range min to max: "; double min, max; cin >> min >> max; for(double i=min;i<=max;i++) { cout << setw(get_width(max)) << i << setw(get_width(max*max)) << i * i << endl; } return 0; }
4-5 编写一个函数来从输入流读单词,把读到的单词存储在一个向量中。利用这个函数编写一个程序来计算输入的单词的数目以及每一个单词所出现的次数。
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { vector<string> words; vector<int> counts; int sum = 0; typedef vector<string>::size_type vec_sz; cout << "Enter words: "; string s; while(cin >> s) { bool found = false; for(vec_sz i=0; i<words.size(); i++) { if(words[i] == s) { counts[i]++; found = true; } } if(!found) { words.push_back(s); counts.push_back(1); } sum++; } cout << "The total number of words are "<< sum << endl; for(vec_sz i = 0; i <= words.size(); i++) { cout << words[i] << " appears " << counts[i] << " times" << endl; } return 0; }
4-6 重写Student_info结构并使用重写后的结构来直接计算成绩,要求在程序中仅仅存储总成绩。

#include <algorithm> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> #include <string> #include <vector> #ifdef _MSC_VER //#include "../minmax.h" #else using std::max; #endif using namespace std; struct Student_info { string name; double grade; }; // note the semicolon--it's required // compute the median of a `vector<double>' // note that calling this function copies the entire argument `vector' double median(vector<double> vec) { #ifdef _MSC_VER typedef std::vector<double>::size_type vec_sz; #else typedef vector<double>::size_type vec_sz; #endif vec_sz size = vec.size(); if (size == 0) throw domain_error("median of an empty vector"); sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); vec_sz mid = size/2; return size % 2 == 0 ? (vec[mid] + vec[mid-1]) / 2 : vec[mid]; } // compute a student's overall grade from midterm and final exam grades and homework grade double grade(double midterm, double final, double homework) { return 0.2 * midterm + 0.4 * final + 0.4 * homework; } // compute a student's overall grade from midterm and final exam grades // and vector of homework grades. // this function does not copy its argument, because `median' does so for us. double grade(double midterm, double final, const vector<double>& hw) { if (hw.size() == 0) throw domain_error("student has done no homework"); return grade(midterm, final, median(hw)); } double grade(const Student_info& s) { return s.grade; } // read homework grades from an input stream into a `vector<double>' istream& read_hw(istream& in, vector<double>& hw) { if (in) { // get rid of previous contents hw.clear(); // read homework grades double x; while (in >> x) hw.push_back(x); // clear the stream so that input will work for the next student in.clear(); } return in; } istream& read(istream& is, Student_info& s) { double midterm, final; // read and store the student's name and midterm and final exam grades is >> s.name >> midterm >> final; vector<double> homework; read_hw(is, homework); // read and store all the student's homework grades if (cin) s.grade = grade(midterm, final, homework); return is; } bool compare(const Student_info& x, const Student_info& y) { return x.name < y.name; } int main() { vector<Student_info> students; Student_info record; string::size_type maxlen = 0; try { // read and store all the records, and find the length of the longest name while (read(cin, record)) { maxlen = _MAX(maxlen, record.name.size()); students.push_back(record); } } catch (domain_error e) { cout << e.what() << endl; } // alphabetize the records sort(students.begin(), students.end(), compare); #ifdef _MSC_VER for (std::vector<Student_info>::size_type i = 0; #else for (vector<Student_info>::size_type i = 0; #endif i != students.size(); ++i) { // write the name, padded on the right to `maxlen' `+' `1' characters cout << students[i].name << string(maxlen + 1 - students[i].name.size(), ' '); // compute and write the grade double final_grade = grade(students[i]); streamsize prec = cout.precision(); cout << setprecision(3) << final_grade << setprecision(prec); cout << endl; } return 0; }
4-7 编写一个程序来计算存储在一个vector<double>类型的向量中的数据的平均值。

#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <vector> #include <numeric> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Enter numbers: "; vector<double> numbers; double num; while (cin >> num) { numbers.push_back(num); } cout << "Average: " <<accumulate(numbers.begin(),numbers.end(), 0.0)/numbers.size(); return 0; }
4-8 如果下面的代码是合法的,那么对于f的返回类型我们能做出什么推断呢?
double d = f() [n];
#include<iostream> #include<conio.h> double *f() { static double value[]= {1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5}; return value; } int main () { int n = 2; double d = f() [n]; std::cout << "d = " << d <<' '; getch(); return 0; }
4-9 在C++编程中有一个相当常见的程序错误:如果我们像在4.2.3中所做的那样给setw一个字符串类型的参数,那么setw函数可能会无法正常工作。重写4.2.3中的程序,让它不用再依赖setw函数。提示(1.2): string spaces(n,' ')构造了一个含有欧n个空格的字符串。
第5章
5-0

#include "stdafx.h" #pragma warning(disable : 4786) //屏蔽4876错误 #include <vector> #include <cctype> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; vector<string> split(const string & s) { vector<string> ret; typedef string::size_type string_size; string_size i = 0; while(i!=s.size()) { while(i!=s.size() && isspace(s[i])) ++i; string_size j = i; while(j != s.size() && !isspace(s[j])) //书中这里错误写的i ++j; if(i!=j) { ret.push_back(s.substr(i,j-i)); i=j; } } return ret; } int main() { string s; while(getline(cin,s)) { vector<string> v =split(s); for(vector<string>::size_type i=0; i!=v.size(); ++i) cout<<v[i]<<endl; } return 0; }
参考
[1]https://blog.csdn.net/u013706695/article/details/19493443
[2]https://github.com/bitsai/book-exercises/tree/master/Accelerated%20C%2B%2B
