
基本知识点:
概念:
Restful就是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格
不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格
基于这个风格 设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制
现在,本人对上文中的两个名词做下解释:
名词解释:
- 资源:
互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源- 资源操作:
使用 POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,等不同方法对资源进行操作
(分别对应数据的 添加、 删除、修改、查询)
RestFul 风格 与 普通风格 的区别:
区别:
- 在我们按照以前的方式去访问一个网站,可能键入的路径为:
localhost:8080/hello/name=youzg&comment=666- 而当我们使用 RestFul 风格 后,就可以按照这样的方式去键入路径来代替上述路径:
localhost:8080/hello/youzg/666
语法:
使用@RequestMapping注解:
在@RequestMapping注解中,增加如下参数:
@RequestMapping("/访问的路径名/{参数名1}/{参数名2}")
通过@PathVariable注解来注入相应的参数:
在被该注解标识的方法中,就可以通过@PathVariable注解来注入相应的参数:
- 若参数名称 与 请求参数 同名,
直接使用@PathVariable注解标记该参数即可
例如:
package edu.youzg.about_spring_mvc.controllor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @Author: Youzg
* @CreateTime: 2020-05-13 10:41
* @Description: 带你深究Java的本质!
*/
@Controller
public class RestfulController {
@RequestMapping("/query/{name}/{age}")
public String query(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable int age, Model model) {
String res = name + ":" + age;
model.addAttribute("inf", res);
return "info";
}
}
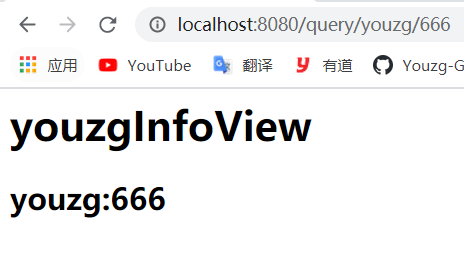
那么,当我们访问如下路径 localhost:8080/query/youzg/666 时,
youzg和666将作为上面的方法中的name和age参数传入并执行该方法
因此,浏览器就会显示如下界面:
2. 若参数名称 与 请求参数 不同名,
使用@PathVariable注解的value属性来指定要进行注入的请求参数
例如:
@RequestMapping("/hello/{uid}")
public String hello(@PathVariable("uid") Integer id){
System.out.println("hello springMVC"+id);
return "index";
}
注意:
@PathVariable指定的请求参数,
必须在@RequestMapping中的value属性中存在
否则无法获取!
在上文中,本人说了 RestFul 风格 可以处理不同的资源操作 请求
(POST、DELETE、PUT、GET等)
那么,在特定的情况下,可能会出现这样的情况:
同样是访问了一个网址(譬如:),
但是,回显的页面却是不一样的
这就是因为网页的制作者可能使用了 @RequestMapping注解 的 method属性
来为某方法指定要处理的请求类型:
指定 请求类型:
法一 —— 使用@RequestMapping注解 的 method属性:
首先,本人来展示下 @RequestMapping注解 的源码:
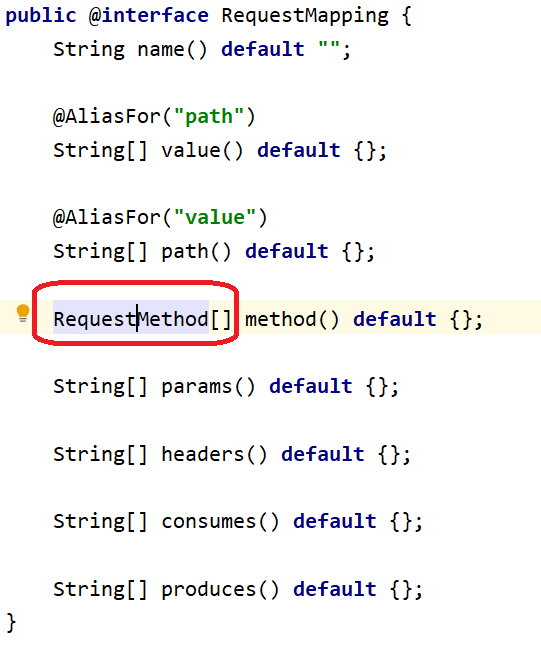
能够看到:method属性的类型为 RequestMethod枚举
那么,本人再来展示下RequestMethod枚举 的部分源码:
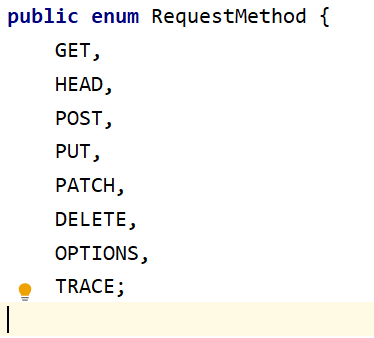
可以看到,RequestMethod枚举一共提供了8种请求方式的枚举,
分别用于处理8种请求方式
例如:
package edu.youzg.about_spring_mvc.controllor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* @Author: Youzg
* @CreateTime: 2020-05-13 10:41
* @Description: 带你深究Java的本质!
*/
@Controller
public class RestfulController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/query/{name}/{age}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String query(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable int age, Model model) {
System.out.println("query进来了");
String res = name + ":" + age;
model.addAttribute("inf", res);
return "info";
}
}
(注意:
虽然我们能够在此处配置某方法的请求类型,
但是 所有的地址栏请求 默认 按照 Get方式 请求服务器 !)
通过 @RequestMapping注解 中的 method属性 来指定目标请求方式
法二 —— 使用@RequestMapping注解 的 5种衍生注解:
springMVC框架为了简化我们的操作,
提供了5个@RequestMapping注解的子注解:
- @GetMapping
- @PostMapping
- @PutMapping
- @DeleteMapping
- @PatchMapping
本人就拿 @DeleteMapping注解 作为例子,来讲解这6个注解:
@DeleteMapping注解 == @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
下面,本人来展示下部分源码: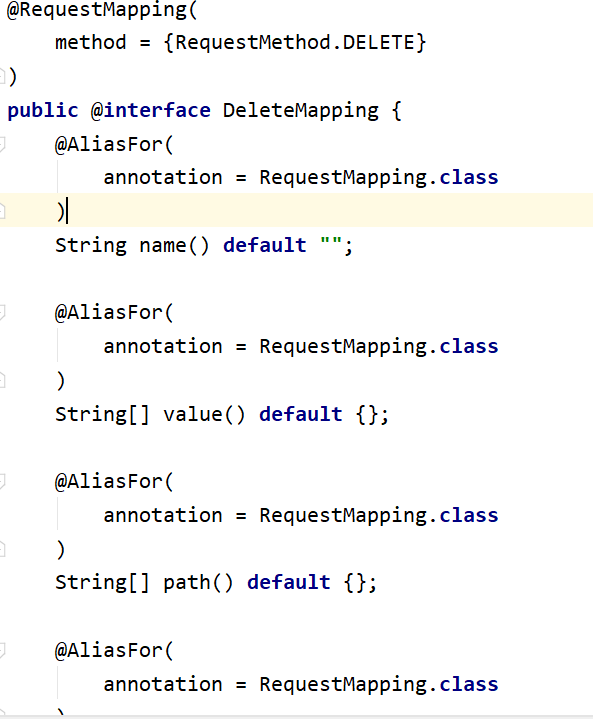
可以理解为 @RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.DELETE) 的 快捷方式!
url风格:
@RequestMapping还存在一个url风格的问题
还支持ant配置
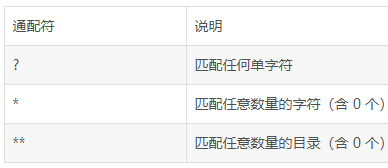
@RequestMapping("/user/?") // 匹配类似: /user/a /user/b
@RequestMapping("/user/*") // 匹配类似:/user/abc /user/abaddd
@RequestMapping("/user/**/save") // 匹配类似:/user/a/b/c/save user/a/save
不过这种风格使用较少,所以本人在此处不进行过多的解释!