(请观看本人博文——《详解 字节流》)
数据输入输出流
对于数据输入输出流,本人要提的一点就是:
这个流是保证按照什么顺序录入,就要按照什么顺序读出的流。
也就是说,读取的数据的类型,和取出的数据的类型,在顺序上要保持一致,否则就会出现“乱码”
DataOutputStream:
(输出流)
概念:
允许应用程序以与机器无关方式从底层输入流中读取基本 Java 数据类型。
应用程序可以使用数据输出流写入稍后由数据输入流读取的数据。
DataInputStream 对于多线程访问不一定是安全的。 线程安全是可选的,它由此类方法的使用者负责。
这个类的构造方法只有一种:
构造方法:
DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) :
创建一个新的数据输出流,将数据写入指定基础输出流
现在,本人呢来展示下这个类的常用API:
- void flush()
清空此数据输出流缓冲区- int size()
返回计数器 written 的当前值,即到目前为止写入此数据输出流的字节数- void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入基础输出流- void write(int b)
将指定字节(参数 b 的八个低位)写入基础输出流- void writeBoolean(boolean v)
将一个 boolean 值以 1-byte 值形式写入基础输出流- void writeByte(int v)
将一个 byte 值以 1-byte 值形式写出到基础输出流中- void writeBytes(String s)
将字符串按字节顺序写出到基础输出流中- void writeChar(int v)
将一个 char 值以 2-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节。- void writeChars(String s)
将字符串按字符顺序写入基础输出流- void writeDouble(double v)
使用 Double 类中的 doubleToLongBits 方法将 double 参数转换为一个 long 值,然后将该 long 值以 8-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节- void writeFloat(float v)
使用 Float 类中的 floatToIntBits 方法将 float 参数转换为一个 int 值,然后将该 int 值以 4-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节- void writeInt(int v)
将一个 int 值以 4-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节- void writeLong(long v)
将一个 long 值以 8-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节- void writeShort(int v)
将一个 short 值以 2-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节- void writeUTF(String str)
以与机器无关方式使用 UTF-8 修改版编码将一个字符串写入基础输出流
DataInputStream:
(输入流)
概念:
数据输出流允许应用程序以适当方式将基本 Java 数据类型写入输出流中。
然后,应用程序可以使用数据输入流将数据读入。
此类的构造方法也只有一个:
DataInputStream(InputStream in) :
使用指定的底层 InputStream 创建一个 DataInputStream。
现在,本人来展示下这个类的API:
- int read(byte[] b)
从包含的输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将它们存储到缓冲区数组 b 中- int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
从包含的输入流中将最多 len 个字节读入一个 byte 数组中- boolean readBoolean()
读取一个输入字节,如果该字节不是零,则返回 true,如果是零,则返回 false- byte readByte()
读取并返回一个输入字节- char readChar()
读取两个输入字节并返回一个 char 值- double readDouble()
读取八个输入字节并返回一个 double 值- float readFloat()
读取四个输入字节并返回一个 float 值- void readFully(byte[] b)
从输入流中读取一些字节,并将它们存储在缓冲区数组 b 中- void readFully(byte[] b, int off, int len)
从输入流中读取 len 个字节- int readInt()
读取四个输入字节并返回一个 int 值- String readLine()
从输入流中读取下一文本行- long readLong()
读取八个输入字节并返回一个 long 值- short readShort()
读取两个输入字节并返回一个 short 值- int readUnsignedByte()
读取一个输入字节,将它左侧补零 (zero-extend) 转变为 int 类型,并返回结果,所以结果的范围是 0 到 255- int readUnsignedShort()
读取两个输入字节,并返回 0 到 65535 范围内的一个 int 值- String readUTF()
读入一个已使用 UTF-8 修改版格式编码的字符串- int skipBytes(int n)
试图在输入流中跳过数据的 n 个字节,并丢弃跳过的字节
那么,现在,本人来展示下这两个类的使用:
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
writeData();
readData();
}
private static void readData() throws IOException {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
boolean b = in.readBoolean();
double v = in.readDouble();
int i = in.readInt();
String s = in.readUTF();
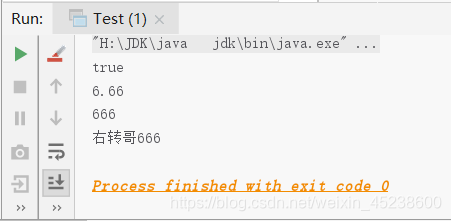
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(v);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(s);
//释放资源
in.close();
}
private static void writeData() throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt"));
out.writeBoolean(true);
out.writeDouble(6.66);
out.writeInt(666);
out.writeUTF("右转哥666");
out.close();
}
}
现在,本人来展示下运行结果:
(本人《详解 字节流》博文链接:https:////www.cnblogs.com/codderYouzg/p/12418463.html)
(本人 I/O流总集篇 博文链接:https:////www.cnblogs.com/codderYouzg/p/12418404.html)