在并发控制的流程中,有一个很重要的概念,即为标题中的条件对象,条件对象对应的英文是Condition接口,我们使用ReentrantLock是,发现基于ReentrantLock可以获取到Contition接口,可以进行阻塞或者唤醒操作。本文从以下几个方面介绍。
Condition作用及用途
Condition是基于ReentrantLock使用的,我们使用Condition可以实现条件判断
Condition代码演示
演示代码1
演示Condition的基本用法,如下代码所示:
package com.yang.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 本实例测试Condition的基本用法
*/
public class ConditionDemo1 {
private ReentrantLock reentrantLock=new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition=reentrantLock.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConditionDemo1 conditionDemo1 = new ConditionDemo1();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
conditionDemo1.method2();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
conditionDemo1.method1();
}
public void method1(){
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("条件不满足,等待中");
condition.await();
System.out.println("条件满足,可以运行");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
public void method2(){
reentrantLock.lock();
try{
condition.signal();
System.out.println("条件转换为满足");
}finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
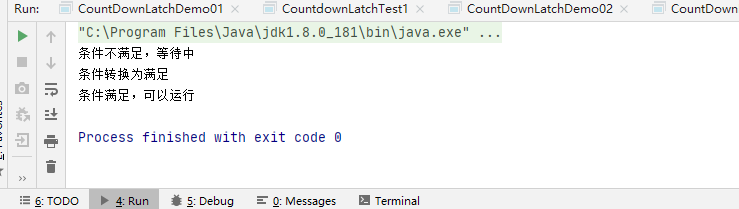
运行结果如下:
演示代码2
本代码演示用Condition实现生产者和消费者,如下实例代码所示
package com.yang.concurrent;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 此实例我们用Condition去模拟生产者和消费者的实现
*/
public class ConditionDemo2 {
private int queueSize = 10;
private PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(10);
private ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition notFull = reentrantLock.newCondition();
private Condition notEmpty = reentrantLock.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConditionDemo2 conditionDemo2 = new ConditionDemo2();
Provider provider = conditionDemo2.new Provider();
Consumer consumer=conditionDemo2.new Consumer();
provider.start();
consumer.start();
}
class Provider extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
provid();
}
private void provid() {
while (true) {
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
//一直在生产
while (queue.size() == queueSize) {
try {
System.out.println("队列满了,等待中");
notFull.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.offer(1);
notEmpty.signalAll();
System.out.println("对列中放入了一个数据,队列大小为:" + queue.size());
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
consume();
}
private void consume() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//一直在消费
while (true) {
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == 0) {
//队列空
System.out.println("队列为空,等待中");
try {
notEmpty.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.poll();
notFull.signalAll();
System.out.println("从队列中取走了一个数据,队列剩余:" + queue.size());
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果如下图所示:

Condition使用说明
当我们调用await方法后,就释放了锁。