本文分别从线程池的组成部分和原理方面进行讲解。
线程池的组成部分
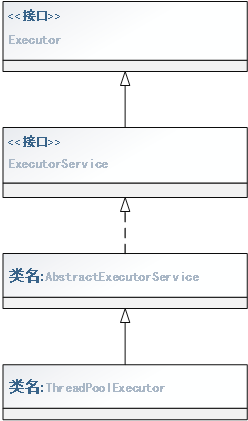
主要包含:Executor、ExecutorService、Executors、AbstracExecutorService、ThreadPoolExecutor等,下文从集成关系方面进行说明。
线程池的原理
重点讲解线程池如何去实现线程复用的原理,即就是我们使用相同的线程去处理不同任务的,固定的线程去取不同的任务。我们从execute看起
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
从上面我们可以看到有corepoolSize的判断,addWorker是具体实现模块。实现见下图,while中不停的获取task,进行执行,达到线程复用的目的。
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}