Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; }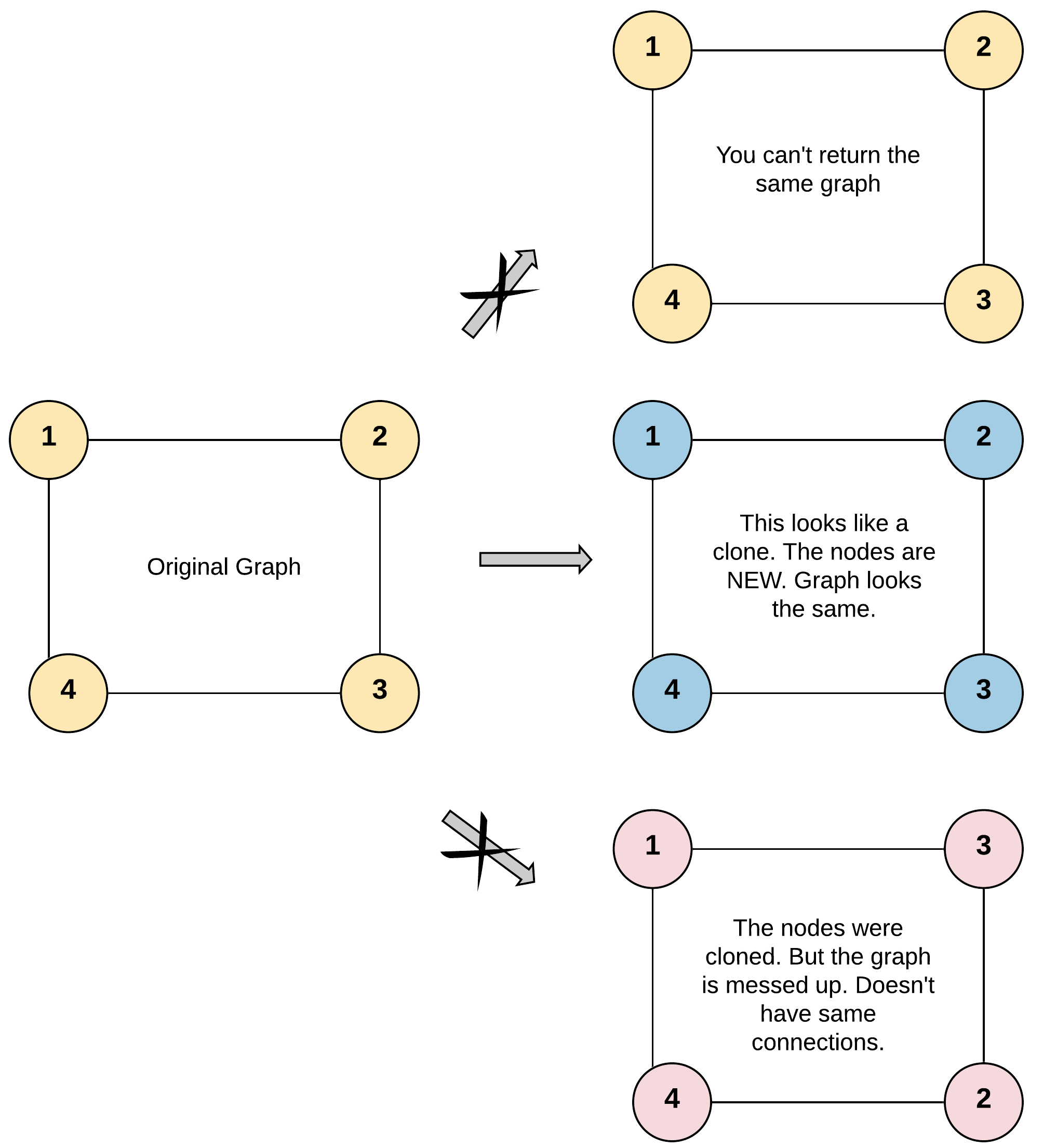 Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
克隆图。
题目就是题意,对一个图做深度复制。这里需要被复制的内容不光是图上的每个节点,同时也需要为每个节点的邻接点做深度复制。
既然是克隆/复制一个数据结构,一定涉及到两点,一是遍历,二是记录。图的遍历无非就是BFS或者DFS,记录基本都会用到hashmap,除了链表的复制也许可以不需要用到hashmap,因为可以把复制出来的节点加在原节点之后。参见138题。
这个题也可以用DFS做但是我个人觉得BFS比较好记。具体的做法是创建一个visited hashmap记住<原来的node,新的node>之间的对应关系,和一个queue。
一开始,先把当前唯一的节点node加入queue并且把当前节点当做key存入hashmap,map的value是一个有着相同node.val但是只有一个空的邻接表(neighbors)的node;
然后从queue中开始弹出元素,每弹出一个元素cur,判断这个node的每一个邻居是否存在于hashmap,将不存在的邻居加入hashmap,同时也将这些刚刚加入hashmap中的邻居再次加入queue进行下一轮遍历;如果有某一个邻居已经存在于hashmap了,则往cur的邻接表里面添加这个已经存在的邻居的copy。
BFS
时间O(V + E)
空间O(n) - queue
Java实现
/* class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val, ArrayList<Node> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } } */ class Solution { public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { // corner case if (node == null) { return null; } // normal case HashMap<Node, Node> visited = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(node); // <oldNode, newNode> visited.put(node, new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>())); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = queue.poll(); for (Node neighbor : cur.neighbors) { if (!visited.containsKey(neighbor)) { visited.put(neighbor, new Node(neighbor.val, new ArrayList())); queue.offer(neighbor); } // add a copy of this neighbor to the copy of cur visited.get(cur).neighbors.add(visited.get(neighbor)); } } return visited.get(node); } }
DFS
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 class Solution { 2 public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { 3 HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); 4 return dfs(node, map); 5 } 6 7 private Node dfs(Node node, HashMap<Node, Node> map) { 8 if (node == null) { 9 return null; 10 } 11 if (map.containsKey(node)) { 12 return map.get(node); 13 } 14 Node clone = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>()); 15 map.put(node, clone); 16 for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) { 17 clone.neighbors.add(dfs(neighbor, map)); 18 } 19 return clone; 20 } 21 }
相关题目
138. Copy List with Random Pointer