Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
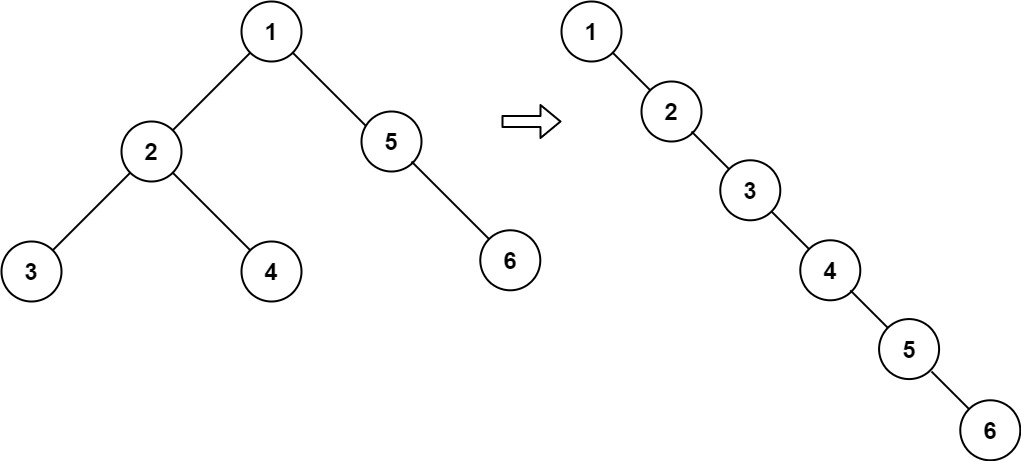
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
二叉树展开为链表。
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
这里我给出迭代的做法,会用到stack。照着例子看来,最后的输出是按照先序遍历的顺序来的。所以用stack先右后左地塞入每个节点,但是在弹出的时候需要注意一些细节,在重连right指针的时候,先不要把那个对应的右节点从stack中pop出来,否则就会出错。具体的参见代码注释。
时间O(n)
空间O(n) - stack
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public void flatten(TreeNode root) { 12 // corner case 13 if (root == null) { 14 return; 15 } 16 17 // normal case 18 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); 19 stack.push(root); 20 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 21 TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); 22 if (cur.right != null) { 23 stack.push(cur.right); 24 } 25 if (cur.left != null) { 26 stack.push(cur.left); 27 } 28 if (!stack.isEmpty()) { 29 // if pop here, the result will be wrong 30 // at this step, you get the right node, this node will be poped out in the next round 31 cur.right = stack.peek(); 32 } 33 cur.left = null; 34 } 35 } 36 }
JavaScript实现
1 /** 2 * @param {TreeNode} root 3 * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead. 4 */ 5 var flatten = function (root) { 6 // corner case 7 if (root == null) { 8 return; 9 } 10 11 // normal case 12 let stack = []; 13 stack.push(root); 14 while (stack.length) { 15 let cur = stack.pop(); 16 if (cur.right != null) { 17 stack.push(cur.right); 18 } 19 if (cur.left != null) { 20 stack.push(cur.left); 21 } 22 if (stack.length) { 23 cur.right = stack[stack.length - 1]; 24 } 25 cur.left = null; 26 } 27 };
另一种不用额外空间的迭代思路,参考这个帖子的解法一
时间O(n)
空间O(1)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public void flatten(TreeNode root) { 18 while (root != null) { 19 // 如果左子树为空,直接去看右子树 20 if (root.left == null) { 21 root = root.right; 22 } else { 23 // 找到左子树的最右孩子 24 TreeNode pre = root.left; 25 while (pre.right != null) { 26 pre = pre.right; 27 } 28 // 把右子树接到左子树的最右孩子 29 pre.right = root.right; 30 root.right = root.left; 31 root.left = null; 32 root = root.right; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 }
相关题目
114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List