FFT
study from:
http://www.orchidany.cf/2019/02/19/FFT1/
https://www.cnblogs.com/zwfymqz/p/8244902.html
e^iθ=cosθ+isinθ
重新写了一遍……
A(x)=F(x)*G(x)
F(x),G(x),A(x)分别为n,m,n+m次多项式
对于任意x,A(x),F(x),G(x)都是一个特定的数值。
F(x),G(x)为什么可以进行系数表示法和点值表示法的互换?
因为它们是k次多项式,如使用拉格朗日插值多项式从点值表示法转换为系数表示法。
对于A(x),同样也是如此!
为什么可以进行F(x)*G(x)点值的相乘呢?
1.无论x为多少,A(x)都等于F(x)*G(x)
2.A(x)可以用点值表示,它是n+m次多项式(感觉说了句无用的话)
那需要多少个F(x)和G(x)点值的相乘呢?
由于A(x)是n+m次多项式,则F(x),G(x)至少各需要n+m+1个点值
得到的是n+m+1个点值,然后点值表示法转系数表示法,求出A(x)这个n+m次多项式的所有系数。
关于蝴蝶操作(迭代实现)
最后的编号(一种规则)->起始
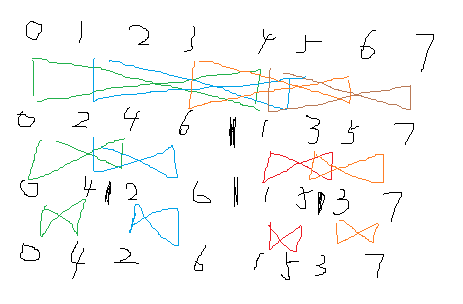
两个位置在原位置上的改动
区间1->2->4->...
P3803 【模板】多项式乘法(FFT)
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 11 const double eps=1e-8; 12 const ll inf=1e9; 13 const ll mod=1e9+7; 14 const int maxn=(1e6+10)*4; ///注意乘4[(n+m)*2] 15 const double pi=acos(-1); 16 17 struct complex 18 { 19 double x,y; 20 complex() 21 { 22 } 23 complex(double x,double y) 24 { 25 this->x=x; 26 this->y=y; 27 } 28 void init(double x,double y) 29 { 30 this->x=x; 31 this->y=y; 32 } 33 complex operator+(const complex &b) const 34 { 35 return complex(x+b.x , y+b.y); 36 } 37 complex operator-(const complex &b) const 38 { 39 return complex(x-b.x , y-b.y); 40 } 41 complex operator*(const complex &b) const 42 { 43 return complex(x*b.x-y*b.y , x*b.y+y*b.x); 44 } 45 }a[maxn],b[maxn]; 46 47 int r[maxn],n,m,tot; 48 49 void fft(complex a[maxn],int mode) 50 { 51 int i,j,pre_siz,cur_siz; 52 complex temp,value,x,y; 53 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 54 if (i<r[i]) ///just change one time 55 swap(a[i],a[r[i]]); 56 57 for (pre_siz=1;pre_siz<tot;pre_siz<<=1) 58 { 59 cur_siz=pre_siz<<1; 60 /// 2pi/cur_siz = pi/pre_siz 61 temp.init(cos(pi/pre_siz),mode*sin(pi/pre_siz)); 62 for (i=0;i<tot;i+=cur_siz) 63 { 64 value.init(1,0); 65 for (j=0;j<pre_siz;j++,value=value*temp) 66 { 67 x=a[i+j],y=value*a[i+pre_siz+j]; 68 a[i+j]=x+y; 69 a[i+pre_siz+j]=x-y; 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 int i,nm,len; 78 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 79 for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 80 scanf("%lf",&a[i].x); 81 for (i=0;i<=m;i++) 82 scanf("%lf",&b[i].x); 83 84 nm=n+m; 85 tot=1,len=0; 86 while (tot<=nm) ///2^len not less than n+m+1 87 { 88 tot<<=1; 89 len++; 90 } 91 92 ///关系 ...... 93 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 94 r[i]=(r[i>>1]>>1) | ((i&1)<<(len-1)); 95 96 ///系数表示法转点值表示法 97 fft(a,1); 98 fft(b,1); 99 100 ///a,b点值相乘 101 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 102 a[i]=a[i]*b[i]; 103 104 ///点值表示法转系数表示法,恰巧为...... 105 fft(a,-1); 106 107 for (i=0;i<=nm;i++) ///n+m 108 ///点值表示法转系数表示法,要除以的系数 109 printf("%lld%c",(ll)(a[i].x/tot+0.5),i==tot?' ':' '); /// /tot 110 111 112 return 0; 113 }
P1919 【模板】A*B Problem升级版(FFT快速傅里叶)
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 11 const double eps=1e-8; 12 const ll inf=1e9; 13 const ll mod=1e9+7; 14 const int maxn=(1e6+10)*4; ///注意乘4[(n+m)*2] 15 const double pi=acos(-1); 16 17 struct complex 18 { 19 double x,y; 20 complex() 21 { 22 } 23 complex(double x,double y) 24 { 25 this->x=x; 26 this->y=y; 27 } 28 void init(double x,double y) 29 { 30 this->x=x; 31 this->y=y; 32 } 33 complex operator+(const complex &b) const 34 { 35 return complex(x+b.x , y+b.y); 36 } 37 complex operator-(const complex &b) const 38 { 39 return complex(x-b.x , y-b.y); 40 } 41 complex operator*(const complex &b) const 42 { 43 return complex(x*b.x-y*b.y , x*b.y+y*b.x); 44 } 45 }a[maxn],b[maxn]; 46 47 int r[maxn],n,m,tot,z[maxn]; 48 49 char str[maxn]; 50 51 void fft(complex a[maxn],int mode) 52 { 53 int i,j,pre_siz,cur_siz; 54 complex temp,value,x,y; 55 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 56 if (i<r[i]) ///just change one time 57 swap(a[i],a[r[i]]); 58 59 for (pre_siz=1;pre_siz<tot;pre_siz<<=1) 60 { 61 cur_siz=pre_siz<<1; 62 /// 2pi/cur_siz = pi/pre_siz 63 temp.init(cos(pi/pre_siz),mode*sin(pi/pre_siz)); 64 for (i=0;i<tot;i+=cur_siz) 65 { 66 value.init(1,0); 67 for (j=0;j<pre_siz;j++,value=value*temp) 68 { 69 x=a[i+j],y=value*a[i+pre_siz+j]; 70 a[i+j]=x+y; 71 a[i+pre_siz+j]=x-y; 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 77 int main() 78 { 79 int i,nm,len; 80 scanf("%d",&n); ///输入样例有毒,n后面有空格 81 n--; 82 83 scanf("%s",str); 84 for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 85 a[n-i].x=str[i]-48; 86 87 scanf("%s",str); 88 for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 89 b[n-i].x=str[i]-48; 90 91 nm=n+n; 92 tot=1,len=0; 93 while (tot<=nm) ///2^len not less than n+m+1 94 { 95 tot<<=1; 96 len++; 97 } 98 99 ///关系 ...... 100 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 101 r[i]=(r[i>>1]>>1) | ((i&1)<<(len-1)); 102 103 ///系数表示法转点值表示法 104 fft(a,1); 105 fft(b,1); 106 107 ///a,b点值相乘 108 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 109 a[i]=a[i]*b[i]; 110 111 ///点值表示法转系数表示法,恰巧为...... 112 fft(a,-1); 113 114 for (i=0;i<=nm;i++) 115 { 116 ///点值表示法转系数表示法,要除以的系数 117 z[i]+=a[i].x/tot+0.5; 118 // printf("%d ",a[i].x/tot+0.5); 119 if (z[i]>=10) 120 { 121 z[i+1]+=z[i]/10; 122 z[i]%=10; 123 } 124 else if (z[i]<0) 125 { 126 z[i+1]+=z[i]/10-(z[i]!=0); 127 z[i]=(z[i]%10+10)%10; 128 } 129 } 130 while (z[i]>=10) 131 { 132 z[i+1]=z[i]/10; 133 z[i]%=10; 134 i++; 135 } 136 137 ///输入的都是正整数 138 ///前导0 139 while (z[i]==0) 140 i--; 141 142 while (i>=0) 143 printf("%d",z[i--]); 144 145 ///也可以认为结果是a[0]+a[1]*10+a[2]*10^2+... 146 147 148 return 0; 149 } 150 /* 151 2 152 12 153 13 154 155 2 156 99 157 99 158 159 3 160 199 161 299 162 163 164 10 165 9789344841 166 4839019669 167 168 169 170 另外的提高速度的方法: 171 压位 172 173 结果为: 174 a[0]+a[1]*x+a[2]*x^2 175 x=10^k 176 177 */
==================================================
NTT
https://www.cnblogs.com/Wuweizheng/p/8553155.html
百度“原根”
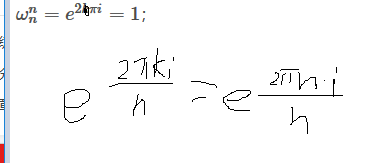

对于选取的P,可用的n最大的值与P中的2的系数有关
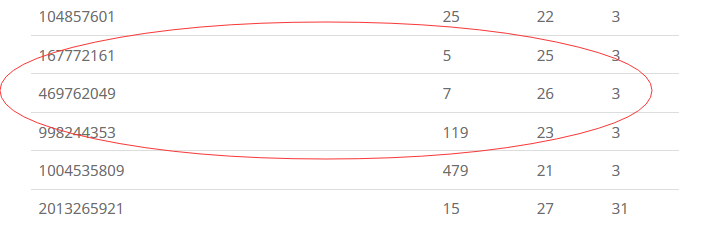
如选择998244353就优于1004535809。
如果选择框住的三个数,那么可以处理的最大的n+m为2^23=8388608。
最好模数对应的g(底数,最后一列)都相同,否则对于不同的模数,要选择不同的g。
如果题目要求除以998244353之类的满足条件的数,则可以直接用这个方法做,不用后续处理
P1919 【模板】A*B Problem升级版(FFT快速傅里叶)
结果小于等于
9[第一个数每一位的最大值]*9[第二个数每一位的最大值]*n[两个数的最大长度] = 4860000
可以使用取模998244353
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 11 const double eps=1e-8; 12 const ll inf=1e9; 13 const ll mod=998244353; 14 const int maxn=(1e5+10)*4; 15 16 ll di=3; 17 int tot,r[maxn]; 18 ll a[maxn],b[maxn],inv_siz[100],inv_rev_siz[100],c[maxn]; 19 20 char str[maxn]; 21 22 ll mul(ll a,ll b) 23 { 24 ll y=1; 25 while (b) 26 { 27 if (b&1) 28 y=y*a%mod; 29 a=a*a%mod; 30 b>>=1; 31 } 32 return y; 33 } 34 35 void ntt(ll a[maxn],int mode) 36 { 37 int i,j,cnt_pre,cnt_cur,siz; 38 ll x,y,sing,value; 39 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 40 if (i<r[i]) 41 swap(a[i],a[r[i]]); 42 43 for (cnt_pre=1,siz=1;cnt_pre<tot;cnt_pre=cnt_pre<<1,siz++) /// 44 { 45 cnt_cur=cnt_pre<<1; 46 sing=mode==1?inv_siz[siz]:inv_rev_siz[siz]; 47 for (i=0;i<tot;i+=cnt_cur) 48 { 49 value=1; 50 for (j=0;j<cnt_pre;j++,value=value*sing%mod) 51 { 52 x=a[i+j],y=value*a[i+j+cnt_pre]%mod; 53 a[i+j]=(x+y)%mod; 54 a[i+j+cnt_pre]=(x-y+mod)%mod; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 int n,m,len,nm,i,j; 63 64 // scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&p); 65 // for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 66 // scanf("%lld",&a[i]); 67 // for (i=0;i<m;i++) 68 // scanf("%lld",&b[i]); 69 70 scanf("%d",&n); 71 n--; 72 73 scanf("%s",str); 74 for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 75 a[i]=str[n-i]-48; 76 77 scanf("%s",str); 78 for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 79 b[i]=str[n-i]-48; 80 81 nm=n+n; 82 tot=1,len=0; 83 while (tot<=nm) 84 { 85 tot<<=1; 86 len++; 87 } 88 for (i=1;i<tot;i++) 89 r[i]=(r[i>>1]>>1) | ((i&1)<<(len-1)); 90 for (i=2,j=1;i<=tot;i=i<<1,j++) /// 91 { 92 inv_siz[j]=mul(di,(mod-1)/i); 93 inv_rev_siz[j]=mul(di,(mod-1)-(mod-1)/i); 94 } 95 96 97 ntt(a,1); 98 ntt(b,1); 99 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 100 a[i]=a[i]*b[i]%mod; 101 ntt(a,-1); 102 j=mul(tot,mod-2); 103 for (i=0;i<=nm;i++) 104 { 105 a[i]=a[i]*j%mod; 106 107 c[i]+=a[i]; 108 if (c[i]>=10) 109 { 110 c[i+1]+=c[i]/10; 111 c[i]%=10; 112 } 113 else if (c[i]<0) 114 { 115 c[i+1]+=c[i]/10-(c[i]!=0); 116 c[i]=(c[i]%10+10)%10; 117 } 118 } 119 while (c[i]>=10) 120 { 121 c[i+1]=c[i]/10; 122 c[i]%=10; 123 i++; 124 } 125 126 while (c[i]==0) 127 i--; 128 while (i>=0) 129 printf("%lld",c[i--]); 130 131 132 return 0; 133 } 134 /* 135 1 136 8 137 9 138 139 2 140 12 141 13 142 143 2 144 99 145 99 146 147 3 148 111 149 111 150 151 3 152 999 153 102 154 155 101898 156 */
感觉别人的代码短很多:
https://www.bbsmax.com/A/ke5jRWmO5r/
mode=-1下不同的实现方法
reverse(&a[1],&a[limit]);P4245 【模板】任意模数NTT
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/solution/P4245
https://www.cnblogs.com/Memory-of-winter/p/10223844.html

这样写的前提是取模的数之间互质,才能使用inv(模数) [inv 指的是 求逆]
可以理解为k1''=k1'+g*B
x1+k1''A=x1+(k1'+g*B)*A=(x1+k1'*A)+g*A*B
======================================
max = 10^9 * 10^9 * 10^5 = 10^23
对应若干个模数的相等大于它
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 11 const double eps=1e-8; 12 const ll inf=1e9; 13 const int maxn=(1e5+10)*4; 14 15 ll chu[3]={998244353,469762049,167772161}; ///single>10^8 all>10^24 16 ll di=3,mod,re[3][maxn]; 17 int tot,r[maxn]; 18 ll a[maxn],b[maxn],aa[maxn],bb[maxn],inv_siz[100],inv_rev_siz[100],c[maxn]; 19 20 ll mul(ll a,ll b) 21 { 22 ll y=1; 23 while (b) 24 { 25 if (b&1) 26 y=y*a%mod; 27 a=a*a%mod; 28 b>>=1; 29 } 30 return y; 31 } 32 33 ll _mul(ll a,ll b,ll c) 34 { 35 ll y=1; 36 while (b) 37 { 38 if (b&1) 39 y=y*a%c; 40 a=a*a%c; 41 b>>=1; 42 } 43 return y; 44 } 45 46 void ntt(ll a[maxn],int mode) 47 { 48 int i,j,cnt_pre,cnt_cur,siz; 49 ll x,y,sing,value; 50 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 51 if (i<r[i]) 52 swap(a[i],a[r[i]]); 53 54 for (cnt_pre=1,siz=1;cnt_pre<tot;cnt_pre=cnt_pre<<1,siz++) /// 55 { 56 cnt_cur=cnt_pre<<1; 57 sing=mode==1?inv_siz[siz]:inv_rev_siz[siz]; 58 for (i=0;i<tot;i+=cnt_cur) 59 { 60 value=1; 61 for (j=0;j<cnt_pre;j++,value=value*sing%mod) 62 { 63 x=a[i+j],y=value*a[i+j+cnt_pre]%mod; 64 a[i+j]=(x+y)%mod; 65 a[i+j+cnt_pre]=(x-y+mod)%mod; 66 } 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 71 int main() 72 { 73 int n,m,len,nm,i,j,k; 74 ll p; 75 scanf("%d%d%lld",&n,&m,&p); 76 for (i=0;i<=n;i++) 77 { 78 scanf("%lld",&aa[i]); 79 aa[i]%=p; 80 } 81 for (i=0;i<=m;i++) 82 { 83 scanf("%lld",&bb[i]); 84 bb[i]%=p; 85 } 86 87 nm=n+m; 88 tot=1,len=0; 89 while (tot<=nm) 90 { 91 tot<<=1; 92 len++; 93 } 94 for (i=1;i<tot;i++) 95 r[i]=(r[i>>1]>>1) | ((i&1)<<(len-1)); 96 for (k=0;k<3;k++) 97 { 98 memcpy(a,aa,sizeof(aa)); 99 memcpy(b,bb,sizeof(bb)); 100 ///最主要觉得一起写在ntt函数中,不好改 101 102 mod=chu[k]; 103 for (i=2,j=1;i<=tot;i=i<<1,j++) /// 104 { 105 inv_siz[j]=mul(di,(mod-1)/i); 106 inv_rev_siz[j]=mul(di,(mod-1)-(mod-1)/i); 107 } 108 109 ntt(a,1); 110 ntt(b,1); 111 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 112 a[i]=a[i]*b[i]%mod; 113 ntt(a,-1); 114 j=mul(tot,mod-2); 115 for (i=0;i<=nm;i++) 116 re[k][i]=a[i]*j%mod; 117 118 } 119 120 /** 121 取模的数之间,gcd(mod1,mod2)=1 122 **/ 123 ll x1,x2,x3,x4,A,B,C,k1,k4; 124 for (j=0;j<=nm;j++) 125 { 126 x1=re[0][j],x2=re[1][j],x3=re[2][j]; 127 A=chu[0],B=chu[1],C=chu[2]; 128 k1=(((x2-x1)%B+B)%B)*_mul(A,B-2,B)%B; 129 x4=x1+k1*A; 130 k4=(((x3-x4)%C+C)%C)*_mul(A*B%C,C-2,C)%C; ///(...%C+C)%C 131 printf("%lld%c",(x4%p+k4%p*A%p*B%p)%p,j==nm?' ':' '); ///k4%p, since k4>p 132 ///it is safe that x4%p 133 ///之后则是((x4-x5+D)%D)*mul(A*B%D*C%D,D-2,D)%D; 134 } 135 return 0; 136 } 137 /* 138 1 1 10001 139 1000000000 1000000000 140 1000000000 1000000000 141 142 1 2 10001 143 1000000000 1000000000 144 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 145 146 5 6 1000000009 147 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 148 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 149 */
看毛啸《再探快速傅里叶变换》
题目练习:
[SDOI2015]序列统计
==================================================
分治FFT
P4721 【模板】分治 FFT
https://blog.csdn.net/VictoryCzt/article/details/82939586
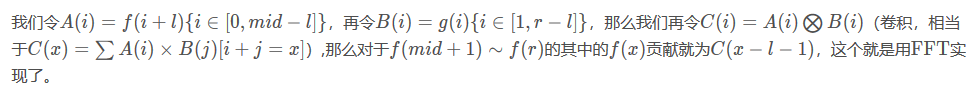
其实,C(x)是多算了一些内容,C(0)~C(mid-l-1)是无用的,但是没办法。
(r-mid)+(r-mid-1)+...+1 -> FFT len=大于等于r-l的最小的数,O(len*log(len))。
对于f(x) 其它数1-~x-1对f(x)的贡献,
通过cdq处理
类似的题 https://www.cnblogs.com/cmyg/p/11146038.html
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 11 const double eps=1e-8; 12 const ll inf=1e9; 13 const ll mod=998244353; 14 const int maxn=(1e5+10)*4; 15 16 ll f[maxn],g[maxn],a[maxn],b[maxn]; 17 ll inv_di[100],inv_rev_di[100],inv_tot[100]; 18 int tot,ind[maxn]; 19 ll di=3; 20 21 ll mul(ll a,ll b) 22 { 23 ll y=1; 24 while (b) 25 { 26 if (b&1) 27 y=y*a%mod; 28 a=a*a%mod; 29 b>>=1; 30 } 31 return y; 32 } 33 34 void ntt(ll *a,int mode) 35 { 36 int i,j,cnt_pre,cnt_cur,cnt=0; 37 ll sing,value,x,y; 38 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 39 if (i<ind[i]) 40 swap(a[i],a[ind[i]]); 41 for (cnt_pre=1,cnt=1;cnt_pre<tot;cnt_pre<<=1,cnt++) 42 { 43 cnt_cur=cnt_pre<<1; 44 sing=mode==1?inv_di[cnt]:inv_rev_di[cnt]; 45 for (i=0;i<tot;i+=cnt_cur) 46 { 47 value=1; 48 for (j=0;j<cnt_pre;j++,value=value*sing%mod) 49 { 50 x=a[i+j],y=a[i+j+cnt_pre]*value%mod; 51 a[i+j]=(x+y)%mod; 52 a[i+j+cnt_pre]=(x-y+mod)%mod; 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 void cdq(int l,int r) 59 { 60 if (l==r) 61 return; 62 63 int m=(l+r)>>1,nm,len,i; 64 cdq(l,m); 65 66 /** 67 对于[m+1,r], 68 [l,m]对它们的贡献 69 C(z)=f(l+x)*g(1+y) 70 x in [0,m-l] 71 y in [0,r-l-1] 72 73 z=x+y 74 [m-l,r-l-1] 75 **/ 76 77 tot=1,len=0; 78 nm=(m-l)+(r-l-1); 79 while (tot<=nm) 80 tot<<=1,len++; 81 for (i=1;i<tot;i++) 82 ind[i]=(ind[i>>1]>>1) | ((i&1)<<(len-1)); 83 for (i=0;i<=m-l;i++) 84 a[i]=f[l+i]; 85 for (i=m-l+1;i<tot;i++) 86 a[i]=0; 87 for (i=0;i<=r-l-1;i++) 88 b[i]=g[1+i]; 89 for (i=r-l;i<tot;i++) 90 b[i]=0; 91 ntt(a,1); 92 ntt(b,1); 93 for (i=0;i<tot;i++) 94 a[i]=a[i]*b[i]%mod; 95 ntt(a,-1); 96 97 for (i=m-l;i<=r-l-1;i++) 98 (f[i+l+1]+=a[i]*inv_tot[len])%=mod; 99 100 cdq(m+1,r); 101 } 102 103 int main() 104 { 105 int n,i,j; 106 scanf("%d",&n); 107 for (i=1;i<n;i++) 108 scanf("%lld",&g[i]); 109 f[0]=1; 110 111 for (i=1,j=0;i<=4e5;i<<=1,j++) 112 { 113 inv_tot[j]=mul(i,mod-2); 114 inv_di[j]=mul(di,(mod-1)/i); 115 inv_rev_di[j]=mul(di,(mod-1)-(mod-1)/i); 116 } 117 118 cdq(0,n); ///begin from 0 119 for (i=0;i<n;i++) 120 printf("%lld%c",f[i],i==n-1?' ':' '); 121 return 0; 122 }
快速沃尔什变换 与 快速莫比乌斯变换
https://www.cnblogs.com/cmyg/p/10424145.html