
% MTSP Fix_GA固定多个旅行商问题(M-TSP)遗传算法(GA) % 通过设置找到MTSP变体的(近似)最优解 %通过GA搜索最短路线(每个推销员从起始位置到个别城市并返回原始起点所需的最短距离) % 说明: % 1.每个推销员从第一个点开始,到第一个点结束,但前往一组中唯一的城市 % 2. 除了第一个,每个城市只有一个推销员访问 % % 注意:固定的起始/结束位置被认为是第一个XY点。 % % Input: % - XY(浮点)是城市位置的Nx2矩阵,其中N是城市的数量 % -DMAT(浮点)是城市到城市距离或成本的NxN矩阵 % - NSALESMEN(整数)是访问城市的推销员数量 % - MINTOUR(整数)是任何销售人员的最小旅行长度,不包括起点/终点 % - POPSIZE(整数)是总体的大小(应该可以被8整除) % - NUMITER(整数)是算法运行所需迭代次数 % - 如果为真,则SHOWPROG(标量逻辑)显示GA进度 % - 如果为真,则SHOWRESULT(标量逻辑)显示GA结果 % - 如果为真, SHOWWAITBAR(标量逻辑)显示等待栏 % % 输入注释: % 1. 不是传入包含这些字段的结构,而是可以以任何顺序将任何/所有这些输入作为参数/值对传递。 % 2. 字段/参数名称不区分大小写,但必须完全匹配。 % % Output: % RESULTSTRUCT(结构)包含以下字段:(除了算法配置的记录) % - OPTROUTE(整数数组)是算法找到的最佳路径 % OPTBREAK(整数数组)是路由断点的列表(这些指定了索引用于获取各个推销员路线的路线) % - MINDIST(标量浮点数)是销售人员行进的总距离 % % Route / Breakpoint详细信息: % 如果有10个城市和3个推销员,一个可能的路线/突破 % 组合可能是:RTE=[ 5 6 9 9 4 2 8 10 3 7 ],BRKS=[3 7 ]综合起来,这些表示解[1 5 6 6 9][ 1 4 2 8 10 1 ][1 3 7 1]; % 指定3名推销员的路线如下: % 推销员1从城市1到5旅行到6到9回到1 % 推销员2从城市1到4旅行到2到8到10回到1 % 推销员3从城市1到3到7,回到1 % % Example: % % 让函数创建实例问题求解 % mtspf_ga; % Example: % % 从求解器请求输出结构 % resultStruct = mtspf_ga; % Example: % % 将用户定义的XY点的随机集合传递给求解器 % userConfig = struct('xy',10*rand(35,2)); % resultStruct = mtspf_ga(userConfig); % % Example: % % 向解算器传递一组更有趣的XY点 % n = 50; % phi = (sqrt(5)-1)/2; % theta = 2*pi*phi*(0:n-1); % rho = (1:n).^phi; % [x,y] = pol2cart(theta(:),rho(:)); % xy = 10*([x y]-min([x;y]))/(max([x;y])-min([x;y])); % userConfig = struct('xy',xy); % resultStruct = mtspf_ga(userConfig); % % Example: 三维寻路 % % 将一组随机的3D(XYZ)点传递给求解器 % xyz = 10*rand(35,3); % userConfig = struct('xy',xyz); % resultStruct = mtspf_ga(userConfig); % % Example: % % 改变遗传算法种群大小和迭代次数的缺省值 % userConfig = struct('popSize',200,'numIter',1e4); % resultStruct = mtspf_ga(userConfig); % % See also: mtsp_ga, mtspo_ga, mtspof_ga, mtspofs_ga, mtspv_ga, distmat % % Author: Joseph Kirk % Email: jdkirk630@gmail.com % Release: 2.0 % Release Date: 05/01/2014 function varargout = mtspf_ga(varargin) % Initialize default configuration defaultConfig.xy = 10*rand(40,2); defaultConfig.dmat = []; % N*N距离矩阵 defaultConfig.nSalesmen = 3; defaultConfig.minTour = 10; defaultConfig.popSize = 500; defaultConfig.numIter = 5e3; defaultConfig.showProg = true; defaultConfig.showResult = true; defaultConfig.showWaitbar = false; % Interpret user configuration inputs if ~nargin userConfig = struct(); elseif isstruct(varargin{1}) userConfig = varargin{1}; else try userConfig = struct(varargin{:}); catch error('Expected inputs are either a structure or parameter/value pairs'); end end % Override default configuration with user inputs configStruct = get_config(defaultConfig,userConfig); % Extract configuration xy = configStruct.xy; dmat = configStruct.dmat; nSalesmen = configStruct.nSalesmen; minTour = configStruct.minTour; popSize = configStruct.popSize; numIter = configStruct.numIter; showProg = configStruct.showProg; showResult = configStruct.showResult; showWaitbar = configStruct.showWaitbar; if isempty(dmat) nPoints = size(xy,1); a = meshgrid(1:nPoints); dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),nPoints,nPoints); end % Verify Inputs 验证输入 [N,dims] = size(xy); [nr,nc] = size(dmat); if N ~= nr || N ~= nc error('Invalid XY or DMAT inputs!') end n = N - 1; % Separate Start/End City % Sanity Checks nSalesmen = max(1,min(n,round(real(nSalesmen(1))))); minTour = max(1,min(floor(n/nSalesmen),round(real(minTour(1))))); popSize = max(8,8*ceil(popSize(1)/8)); numIter = max(1,round(real(numIter(1)))); showProg = logical(showProg(1)); showResult = logical(showResult(1)); showWaitbar = logical(showWaitbar(1)); % Initializations for Route Break Point Selection 路径断点选择的初始化 nBreaks = nSalesmen-1; dof = n - minTour*nSalesmen; % degrees of freedom addto = ones(1,dof+1); for k = 2:nBreaks addto = cumsum(addto); end cumProb = cumsum(addto)/sum(addto); % Initialize the Populations popRoute = zeros(popSize,n); % population of routes popBreak = zeros(popSize,nBreaks); % population of breaks popRoute(1,:) = (1:n) + 1; popBreak(1,:) = rand_breaks(); for k = 2:popSize popRoute(k,:) = randperm(n) + 1; popBreak(k,:) = rand_breaks(); end % Select the Colors for the Plotted Routes 所画路径的颜色 pclr = ~get(0,'DefaultAxesColor'); clr = [1 0 0; 0 0 1; 0.67 0 1; 0 1 0; 1 0.5 0]; if nSalesmen > 5 clr = hsv(nSalesmen); end % Run the GA globalMin = Inf; totalDist = zeros(1,popSize); distHistory = zeros(1,numIter); tmpPopRoute = zeros(8,n); tmpPopBreak = zeros(8,nBreaks); newPopRoute = zeros(popSize,n); newPopBreak = zeros(popSize,nBreaks); if showProg figure('Name','MTSPF_GA | Current Best Solution','Numbertitle','off'); hAx = gca; end if showWaitbar hWait = waitbar(0,'Searching for near-optimal solution ...'); end for iter = 1:numIter % Evaluate Members of the Population 人口评估 for p = 1:popSize d = 0; pRoute = popRoute(p,:); pBreak = popBreak(p,:); rng = [[1 pBreak+1];[pBreak n]]'; for s = 1:nSalesmen d = d + dmat(1,pRoute(rng(s,1))); % Add Start Distance for k = rng(s,1):rng(s,2)-1 d = d + dmat(pRoute(k),pRoute(k+1)); end d = d + dmat(pRoute(rng(s,2)),1); % Add End Distance end totalDist(p) = d; end % Find the Best Route in the Population [minDist,index] = min(totalDist); distHistory(iter) = minDist; if minDist < globalMin globalMin = minDist; optRoute = popRoute(index,:); optBreak = popBreak(index,:); rng = [[1 optBreak+1];[optBreak n]]'; if showProg % Plot the Best Route 实时展示最优路径 for s = 1:nSalesmen rte = [1 optRoute(rng(s,1):rng(s,2)) 1]; if dims > 2, plot3(hAx,xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); else plot(hAx,xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); end hold(hAx,'on'); end if dims > 2, plot3(hAx,xy(1,1),xy(1,2),xy(1,3),'o','Color',pclr); else plot(hAx,xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'o','Color',pclr); end title(hAx,sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f, Iteration = %d',minDist,iter)); hold(hAx,'off'); drawnow; end end % Genetic Algorithm Operators randomOrder = randperm(popSize); for p = 8:8:popSize rtes = popRoute(randomOrder(p-7:p),:); brks = popBreak(randomOrder(p-7:p),:); dists = totalDist(randomOrder(p-7:p)); [ignore,idx] = min(dists); %#ok bestOf8Route = rtes(idx,:); bestOf8Break = brks(idx,:); routeInsertionPoints = sort(ceil(n*rand(1,2))); I = routeInsertionPoints(1); J = routeInsertionPoints(2); for k = 1:8 % Generate New Solutions tmpPopRoute(k,:) = bestOf8Route; tmpPopBreak(k,:) = bestOf8Break; switch k case 2 % Flip tmpPopRoute(k,I:J) = tmpPopRoute(k,J:-1:I); case 3 % Swap tmpPopRoute(k,[I J]) = tmpPopRoute(k,[J I]); case 4 % Slide tmpPopRoute(k,I:J) = tmpPopRoute(k,[I+1:J I]); case 5 % Modify Breaks tmpPopBreak(k,:) = rand_breaks(); case 6 % Flip, Modify Breaks tmpPopRoute(k,I:J) = tmpPopRoute(k,J:-1:I); tmpPopBreak(k,:) = rand_breaks(); case 7 % Swap, Modify Breaks tmpPopRoute(k,[I J]) = tmpPopRoute(k,[J I]); tmpPopBreak(k,:) = rand_breaks(); case 8 % Slide, Modify Breaks tmpPopRoute(k,I:J) = tmpPopRoute(k,[I+1:J I]); tmpPopBreak(k,:) = rand_breaks(); otherwise % Do Nothing end end newPopRoute(p-7:p,:) = tmpPopRoute; newPopBreak(p-7:p,:) = tmpPopBreak; end popRoute = newPopRoute; popBreak = newPopBreak; % Update the waitbar if showWaitbar && ~mod(iter,ceil(numIter/325)) waitbar(iter/numIter,hWait); end end if showWaitbar close(hWait); end if showResult % Plots 画图 figure('Name','MTSPF_GA | Results','Numbertitle','off'); subplot(2,2,1); if dims > 2, plot3(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),xy(:,3),'.','Color',pclr); else plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'.','Color',pclr); end title('City Locations'); subplot(2,2,2); imagesc(dmat([1 optRoute],[1 optRoute])); title('Distance Matrix'); subplot(2,2,3); rng = [[1 optBreak+1];[optBreak n]]'; for s = 1:nSalesmen rte = [1 optRoute(rng(s,1):rng(s,2)) 1]; if dims > 2, plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); else plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); end title(sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f',minDist)); hold on; end if dims > 2, plot3(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),xy(1,3),'o','Color',pclr); else plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'o','Color',pclr); end subplot(2,2,4); plot(distHistory,'b','LineWidth',2); title('Best Solution History'); set(gca,'XLim',[0 numIter+1],'YLim',[0 1.1*max([1 distHistory])]); end % Return Output if nargout resultStruct = struct( ... 'xy', xy, ... 'dmat', dmat, ... 'nSalesmen', nSalesmen, ... 'minTour', minTour, ... 'popSize', popSize, ... 'numIter', numIter, ... 'showProg', showProg, ... 'showResult', showResult, ... 'showWaitbar', showWaitbar, ... 'optRoute', optRoute, ... 'optBreak', optBreak, ... 'minDist', minDist); varargout = {resultStruct}; end % Generate Random Set of Break Points function breaks = rand_breaks() if minTour == 1 % No Constraints on Breaks tmpBreaks = randperm(n-1); breaks = sort(tmpBreaks(1:nBreaks)); else % Force Breaks to be at Least the Minimum Tour Length nAdjust = find(rand < cumProb,1)-1; spaces = ceil(nBreaks*rand(1,nAdjust)); adjust = zeros(1,nBreaks); for kk = 1:nBreaks adjust(kk) = sum(spaces == kk); end breaks = minTour*(1:nBreaks) + cumsum(adjust); end end end % Subfunction to override the default configuration with user inputs % 将输入初始化,什么都不输入,就用这个应该是 function config = get_config(defaultConfig,userConfig) % Initialize the configuration structure as the default config = defaultConfig; % Extract the field names of the default configuration structure defaultFields = fieldnames(defaultConfig); % Extract the field names of the user configuration structure userFields = fieldnames(userConfig); nUserFields = length(userFields); % Override any default configuration fields with user values for i = 1:nUserFields userField = userFields{i}; isField = strcmpi(defaultFields,userField); if nnz(isField) == 1 thisField = defaultFields{isField}; config.(thisField) = userConfig.(userField); end end end

n = 100; phi = (sqrt(5)-1)/2; theta = 2*pi*phi*(0:n-1); rho = (1:n).^phi; [x,y] = pol2cart(theta(:),rho(:)); xy = 10*([x y]-min([x;y]))/(max([x;y])-min([x;y])); userConfig = struct('xy',xy); resultStruct = mtspf_ga(userConfig);
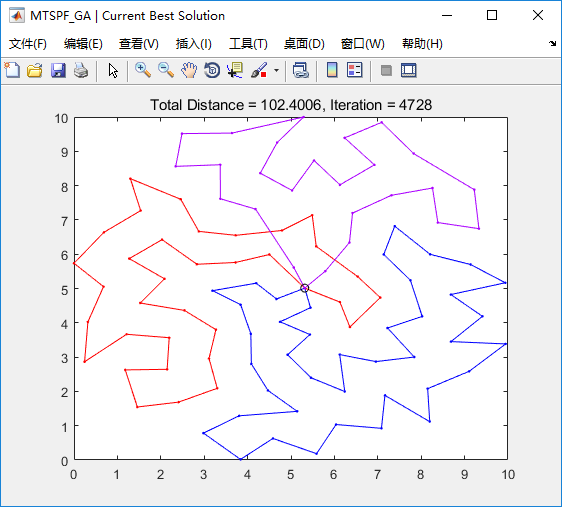
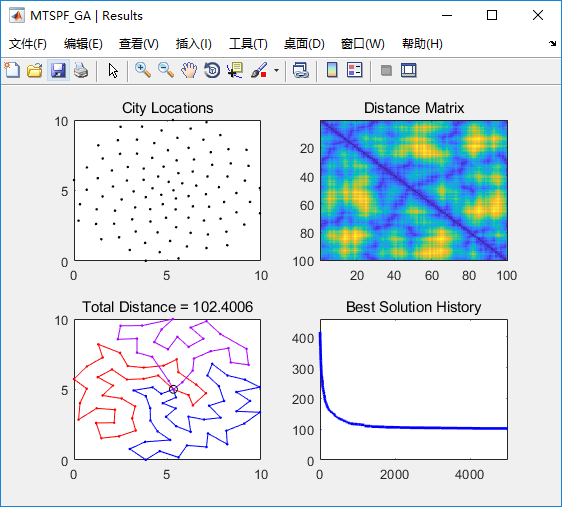
以上是 定起点定终点的多旅行商问题,其中的城市坐标数据是随机的。

function [min_dist,best_tour,generation] = mdmtspv_ga(xy,max_salesmen,depots,CostType,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,show_prog,show_res,dmat) % MDMTSPV_GA Multiple Depots Multiple Traveling Salesmen Problem (M-TSP) % with Variable number of salesmen using Genetic Algorithm (GA) % Finds a (near) optimal solution to a variation of the M-TSP (that has a % variable number of salesmen) by setting up a GA to search for the % shortest route (least distance needed for the salesmen to travel to % each city exactly once and return to their starting locations). The % salesmen originate from a set of fixed locations, called depots. % This algorithm is based on Joseph Kirk's MTSPV_GA, but adds the % following functionality: % 1. Depots at which each salesman originates and ends its tour. % 2. Two possible cost functions, that allow to find minimum sum of all % tour lengths (as in the original version) and to find the minimum % longest tour. The latter problem is sometimes called MinMaxMDMTSP. % % Summary: % 1. Each salesman travels to a unique set of cities and completes the % route by returning to the depot he started from % 2. Each city is visited by exactly one salesman % % Input: % XY (float) is an Nx2 matrix of city locations, where N is the number of cities % max_salesmen (scalar integer) is the maximum number of salesmen % depots (float) ia an Mx2 matrix of the depots used by salesmen, M=max_salesmen % CostType (integer) defines which cost we use. If 1 - sum of all route lengths, if 2 - maximum route length% MIN_TOUR (scalar integer) is the minimum tour length for any of the salesmen % POP_SIZE (scalar integer) is the size of the population (should be divisible by 16) % NUM_ITER (scalar integer) is the number of desired iterations for the % algorithm to run after a new best solution is found. Don't worry the % algorithm will always stop. % SHOW_PROG (scalar logical) shows the GA progress if true % SHOW_RES (scalar logical) shows the GA results if true % DMAT (float) is an NxN matrix of point to point distances or costs % % Output: % MIN_DIST (scalar float) is the best cost found by the algorithm % BEST_TOUR (matrix integer) is an MxL matrix, each row is an agent tour % Generation (scalar integer) is the number of generations required by % the algorithm to find the solution % % Route/Breakpoint Details: % The algorithm uses a data structure in which RTE lists the cities in % a route and BRKS lists break points that divide RTE between agents. % If there are 10 cities and 3 salesmen, a possible route/break % combination might be: rte = [5 6 9 1 4 2 8 10 3 7], brks = [3 7] % Taken together, these represent the solution [5 6 9][1 4 2 8][10 3 7], % which designates the routes for the 3 salesmen as follows: % . Salesman 1 travels from city 5 to 6 to 9 and back to 5 % . Salesman 2 travels from city 1 to 4 to 2 to 8 and back to 1 % . Salesman 3 travels from city 10 to 3 to 7 and back to 10 % Note that the salesman's depot will be taken into accout, so the % complete routes returned by the algorithm will be: % For agent 1: [1 5 6 9 1] - from depot 1 along the route and back % For agent 2: [2 1 4 2 8 2] - from depot 2 along the route and back % For agent 3: [3 10 3 7 3] - from depot 3 along the rout and back % % 2D Example: % n = 35; % xy = 10*rand(n,2); % max_salesmen = 5; % depots = 10*rand(max_salesmen,2); % CostType=1; %- total length, use 2 to minimize the longest tour % min_tour = 3; % pop_size = 80; % num_iter = 1e3; % a = meshgrid(1:n); % dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),n,n); % [min_dist,best_tour,generation] = mdmtspv_ga(xy,max_salesmen,depots,CostType,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,1,1,dmat) % % 3D Example: % n = 35; % xy = 10*rand(n,3); % max_salesmen = 5; % depots = 10*rand(max_salesmen,3); % CostType=1; %- total length, use 2 to minimize the longest tour % min_tour = 3; % pop_size = 80; % num_iter = 1e3; % a = meshgrid(1:n); % dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),n,n); % [min_dist,best_tour,generation] = mdmtspv_ga(xy,max_salesmen,depots,CostType,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,1,1,dmat) % % See also: mtsp_ga, mtspf_ga, mtspo_ga, mtspof_ga, mtspofs_ga, distmat % % Author: Elad Kivelevitch % Based on: Joseph Kirk's MTSPV_GA (see MATLAB Central for download) % Release: 1.0 % Release Date: June 15, 2011 % Process Inputs and Initialize Defaults nargs = 10; for k = nargin:nargs-1 switch k case 0 xy = 10*rand(40,2); case 1 max_salesmen=10; case 2 depots = 10*rand(max_salesmen,2); case 3 CostType = 2; case 4 min_tour = 1; case 5 pop_size = 80; case 6 num_iter = 1e3; case 7 show_prog = 1; case 8 show_res = 1; case 9 N = size(xy,1); a = meshgrid(1:N); dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),N,N); otherwise end end Epsilon=1e-10; % Distances to Depots %Assumes that each salesman is located at a different depot and there are %enough depots [NumOfCities,Dimensions]=size(xy); for i=1:max_salesmen for j=1:NumOfCities D0(i,j)=norm(depots(i,:)-xy(j,:)); end end % Verify Inputs [N,dims] = size(xy); [nr,nc] = size(dmat); if N ~= nr || N ~= nc error('Invalid XY or DMAT inputs!') end n = N; % Sanity Checks min_tour = max(1,min(n,round(real(min_tour(1))))); pop_size = max(8,8*ceil(pop_size(1)/8)); num_iter = max(1,round(real(num_iter(1)))); show_prog = logical(show_prog(1)); show_res = logical(show_res(1)); % Initialize the Populations pop_rte = zeros(pop_size,n); % population of routes pop_brk = cell(pop_size,1); % population of breaks for k = 1:pop_size pop_rte(k,:) = randperm(n); pop_brk{k} = randbreak(max_salesmen,n,min_tour); end % Select the Colors for the Plotted Routes %clr = hsv(ceil(n/min_tour)); clr = hsv(max_salesmen); % Run the GA global_min = Inf; total_dist = zeros(1,pop_size); dist_history = zeros(1,num_iter); tmp_pop_rte = zeros(8,n); tmp_pop_brk = cell(8,1); new_pop_rte = zeros(pop_size,n); new_pop_brk = cell(pop_size,1); if show_prog pfig = figure('Name','MTSPV_GA | Current Best Solution','Numbertitle','off'); end iter=0; iter2go=0; while iter2go < num_iter iter2go=iter2go+1; iter=iter+1; % Evaluate Each Population Member (Calculate Total Distance) for p = 1:pop_size d = []; p_rte = pop_rte(p,:); p_brk = pop_brk{p}; salesmen = length(p_brk)+1; rng=CalcRange(p_brk,n); for sa = 1:salesmen if rng(sa,1)<=rng(sa,2) Tour=[sa p_rte(rng(sa,1):rng(sa,2)) sa]; indices=length(Tour)-1; d(sa)=CalcTourLength(Tour,dmat,D0,indices); else Tour=[sa sa]; d(sa)=0; end end if CostType==1 total_dist(p) = sum(d); elseif CostType==2 total_dist(p) = max(d)+Epsilon*sum(d); end end % Find the Best Route in the Population [min_dist,index] = min(total_dist); dist_history(iter) = min_dist; if min_dist < global_min iter2go=0; generation=iter; global_min = min_dist; opt_rte = pop_rte(index,:); opt_brk = pop_brk{index}; salesmen = length(opt_brk)+1; rng=CalcRange(opt_brk,n); if show_prog % Plot the Best Route figure(pfig); clf for s = 1:salesmen if dims==2 plot(depots(s,1),depots(s,2),'s','Color',clr(s,:)); else plot3(depots(s,1),depots(s,2),depots(s,3),'s','Color',clr(s,:)); end if rng(s,1)<=rng(s,2) rte = opt_rte([rng(s,1):rng(s,2)]); hold on; if ~isempty(rte) && dims == 2 plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); plot([depots(s,1),xy(rte(1),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(1),2)],'Color',clr(s,:)); plot([depots(s,1),xy(rte(end),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(end),2)],'Color',clr(s,:)); elseif ~isempty(rte) && dims == 3 plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); plot3([depots(s,1),xy(rte(1),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(1),2)],[depots(s,3),xy(rte(1),3)],'Color',clr(s,:)); plot3([depots(s,1),xy(rte(end),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(end),2)],[depots(s,3),xy(rte(end),3)],'Color',clr(s,:)); end end title(sprintf(['Total Distance = %1.4f, Salesmen = %d, ' ... 'Iteration = %d'],min_dist,salesmen,iter)); hold on end pause(0.02) hold off end end % Genetic Algorithm Operators rand_grouping = randperm(pop_size); ops=16; for p = ops:ops:pop_size rtes = pop_rte(rand_grouping(p-ops+1:p),:); brks = pop_brk(rand_grouping(p-ops+1:p)); dists = total_dist(rand_grouping(p-ops+1:p)); [ignore,idx] = min(dists); best_of_8_rte = rtes(idx,:); best_of_8_brk = brks{idx}; rte_ins_pts = sort(ceil(n*rand(1,2))); I = rte_ins_pts(1); J = rte_ins_pts(2); for k = 1:ops % Generate New Solutions tmp_pop_rte(k,:) = best_of_8_rte; tmp_pop_brk{k} = best_of_8_brk; switch k case 2 % Flip tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = fliplr(tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J)); case 3 % Swap tmp_pop_rte(k,[I J]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[J I]); case 4 % Slide tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1:J I]); case 5 % Change Breaks tmp_pop_brk{k} = randbreak(max_salesmen,n,min_tour); case 6 % Flip, Change Breaks tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = fliplr(tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J)); tmp_pop_brk{k} = randbreak(max_salesmen,n,min_tour); case 7 % Swap, Change Breaks tmp_pop_rte(k,[I J]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[J I]); tmp_pop_brk{k} = randbreak(max_salesmen,n,min_tour); case 8 % Slide, Change Breaks tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1:J I]); tmp_pop_brk{k} = randbreak(max_salesmen,n,min_tour); case 9 l=random('unid',min(n-J-1,floor(sqrt(n)))); if isnan(l) l=0; end temp1=tmp_pop_rte(k,I:I+l); temp2=tmp_pop_rte(k,J:J+l); tmp_pop_rte(k,I:I+l)=temp2; tmp_pop_rte(k,I:I+l)=temp1; % case 9 %Choose agent % m=length(tmp_pop_brk{k}); % l=random('unid',m); % temp=[ones(1,l), n*ones(1,m-l)]; % tmp_pop_brk{k} = temp; case 12 % Remove tasks from agent l=random('unid',max_salesmen-1,1,1); temp=tmp_pop_brk{k}; temp=[temp(1:l-1) temp(l+1:end) n]; tmp_pop_brk{k}=temp; case 13 l=random('unid',max_salesmen-1,1,1); temp=tmp_pop_brk{k}; temp=[1 temp(1:l-1) temp(l+1:end)]; tmp_pop_brk{k}=temp; otherwise %swap close points if I<n tmp_pop_rte(k,[I I+1]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1 I]); end end end new_pop_rte(p-ops+1:p,:) = tmp_pop_rte; new_pop_brk(p-ops+1:p) = tmp_pop_brk; end pop_rte = new_pop_rte; pop_brk = new_pop_brk; end if show_res % Plots figure('Name','MTSPV_GA | Results','Numbertitle','off'); subplot(2,2,1); if dims == 3 plot3(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),xy(:,3),'k.'); hold on; for s=1:max_salesmen plot3(depots(s,1),depots(s,2),depots(s,3),'s','Color',clr(s,:)); end else plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'k.'); hold on; for s=1:max_salesmen plot(depots(s,1),depots(s,2),'s','Color',clr(s,:)); end end title('City / Depots Locations'); subplot(2,2,2); imagesc(dmat(opt_rte,opt_rte)); title('Distance Matrix'); salesmen = length(opt_brk)+1; subplot(2,2,3); rng=CalcRange(opt_brk,n); for s = 1:salesmen if dims==3 plot3(depots(s,1),depots(s,2),depots(s,3),'s','Color',clr(s,:)); hold on; if rng(s,2)>=rng(s,1) rte = opt_rte([rng(s,1):rng(s,2)]); plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); if ~isempty(rte) plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); plot3([depots(s,1),xy(rte(1),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(1),2)],[depots(s,3),xy(rte(1),3)],'Color',clr(s,:)); plot3([depots(s,1),xy(rte(end),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(end),2)],[depots(s,3),xy(rte(end),3)],'Color',clr(s,:)); end end else plot(depots(s,1),depots(s,2),'s','Color',clr(s,:)); hold on; if rng(s,2)>=rng(s,1) rte = opt_rte([rng(s,1):rng(s,2)]); if ~isempty(rte) plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); plot([depots(s,1),xy(rte(1),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(1),2)],'Color',clr(s,:)); plot([depots(s,1),xy(rte(end),1)],[depots(s,2),xy(rte(end),2)],'Color',clr(s,:)); end end end title(sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f',min_dist)); hold on; end subplot(2,2,4); plot(dist_history,'b','LineWidth',2) title('Best Solution History'); set(gca,'XLim',[0 num_iter+1],'YLim',[0 1.1*max([1 dist_history])]); end % Return Outputs for i=1:max_salesmen if rng(i,1)<=rng(i,2) best_tour(i,1:(rng(i,2)-rng(i,1)+3))=[i,opt_rte([rng(i,1):rng(i,2)]),i]; else best_tour(i,1:2)=[i i]; end best_tour %generation=iter; end %========================================================================== %Additional functions called during the run function VehicleTourLength=CalcTourLength(Tour,d,d0,indices) VehicleTourLength=d0(Tour(1),Tour(2)); for c=2:indices-1 VehicleTourLength=VehicleTourLength+d(Tour(c+1),Tour(c)); end VehicleTourLength=VehicleTourLength+d0(Tour(indices+1),Tour(indices)); function rng=CalcRange(p_brk,n) flag=1; for i=1:length(p_brk) if flag==1 && p_brk(i)>1 rng(i,:)=[1 p_brk(i)]; flag=0; elseif flag==1 rng(i,:)=[1 0]; elseif p_brk(i)<=p_brk(i-1) rng(i,:)=[p_brk(i-1) p_brk(i)]; elseif i<length(p_brk) rng(i,:)=[p_brk(i-1)+1 p_brk(i)]; else rng(i,:)=[p_brk(i-1)+1 p_brk(i)]; end end if p_brk(end)<n && p_brk(end)~=1 rng(i+1,:)=[p_brk(end)+1 n]; elseif p_brk(end)<n && p_brk(end)==1 rng(i+1,:)=[p_brk(end) n]; else rng(i+1,:)=[p_brk(end) n-1]; end function breaks = randbreak(max_salesmen,n,min_tour) num_brks = max_salesmen - 1; breaks = sort(random('unid',n,1,num_brks)); % % 通过设置GA来搜索最短路径(所需的最短距离或销售人员前往每个城市只需一次,并找到M-TSP的变体(具有可变数量的推销员)的(近)最优解决方案回到他们的起始位置)。销售人员来自一组固定的位置,称为仓库。 % 该算法基于Joseph Kirk的MTSPV_GA,但增加了以下功能: % 1。每个销售人员发起并结束其旅程的仓库。 % 2.两种可能的成本函数,允许找到所有游览长度的最小总和(如在原始版本中)并找到最小的最长游览。后一个问题有时被称为MinMaxMDMTSP。 % % 摘要: % 1。每个推销员前往一组独特的城市,并通过返回他开始的仓库完成路线。 % 每个城市都由一位推销员访问。 % % 输入: % * XY(浮点)是城市位置的Nx2矩阵,其中N是城市数量 % * max_salesmen(标量整数)是销售员 % *仓库(浮动)的最大数量,是销售人员使用的 仓库的Mx2矩阵, M = max_salesmen % * CostType(整数)定义我们使用的成本。如果1 - 所有路由长度的总和,如果2 - 最大路由长度 % * MIN_TOUR(标量整数)是任何销售人员的最小游览长度 % * POP_SIZE(标量整数)是总体的大小(应该可以被16整除) % * NUM_ITER(标量整数)是在找到新的最佳解决方案后算法运行所需的迭代次数。不要担心算法会一直停止。 % * SHOW_PROG(标量逻辑)显示GA进度,如果为true % * SHOW_RES(标量逻辑)显示GA结果,如果为真 % * DMAT(float)是点到点距离或成本的NxN矩阵 % % 输出: % * MIN_DIST(标量浮点)是算法找到的最佳成本,具体取决于所使用的成本函数。 % * BEST_TOUR(矩阵整数)是一个MxL矩阵,每一行都是一个代理游览 % *生成(标量整数)是算法找到解决方案所需的代数

n = 100; xy = 10*rand(n,2); max_salesmen = 5; depots = 10*rand(max_salesmen,2); CostType=2; %- total length, use 2 to minimize the longest tour min_tour = 5; pop_size = 80; num_iter = 1e3; a = meshgrid(1:n); dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),n,n); [min_dist,best_tour,generation] = mdmtspv_ga(xy,max_salesmen,depots,CostType,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,1,1,dmat)
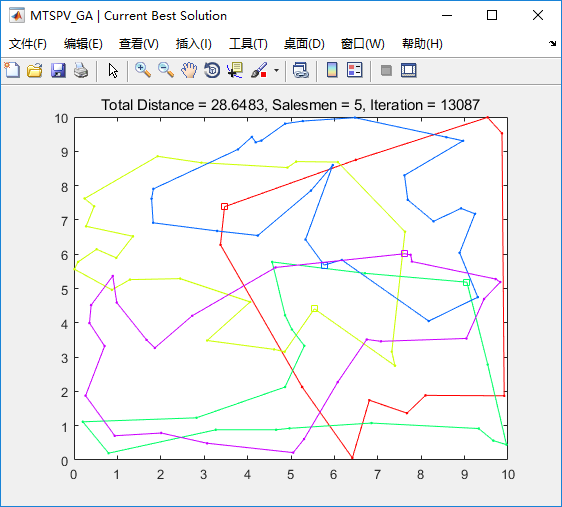
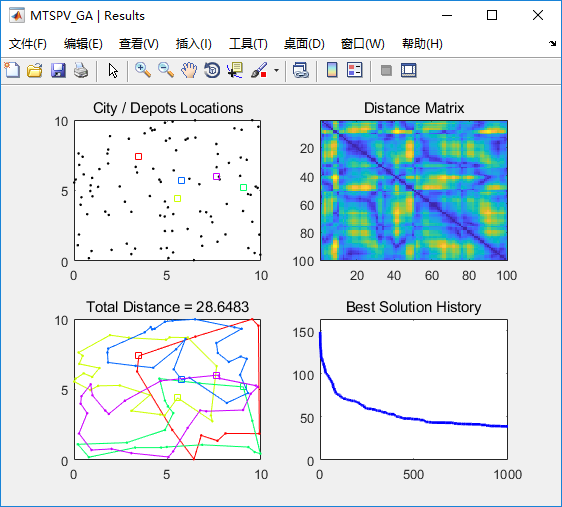
以上是 多起点的多旅行商问题,其中的城市坐标数据是随机的。 具体参数调试可以更优
