元注解(meta-annotation):an annotation that can be applied to another one.
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext: register(xxConfig.class,xxConfig.class) ->refresh() -> getBean
Spring Core注解: https://www.baeldung.com/spring-core-annotations
@Autowired: 构造器注入、setter注入、字段注入三种方式
@Bean、@Qualifier、@DependOn、@Lazy、@Primary、@Scope、
@Import: specific @Configuration classes without component scanning https://www.cnblogs.com/yichunguo/p/12122598.html
第一种用法:@Import({ 要导入的容器中的组件,可以是configuration,也可以是一个具体的类数组 } ):容器会自动注册这个组件,id默认是全类名
第二种用法:ImportSelector接口实现类:返回需要导入的组件的全类名数组,springboot底层用的特别多【重点 】
第三种用法:ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar:手动注册bean到容器
@Profile
@Configuration
@ImportResource(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) 导入bean XML文件,连同@Configuration使用
@Value: 构造器注入、setter注入、字段注入,需要配合@PropertyResource使用
@PropertySources 导入多个
@Alias:样例ComponentScan注解的定义
@ComponentScan vs @EnableAutoConfiguration (SpringBoot)
@ComponentScan scans for annotated Spring components -- 对应spring,扫描service、controller等
@EnableAutoConfiguration is used to enable the auto-configuration --- 对应springboot,自动发现和注册bean
SpringBoot注解
@SpringBootApplication:mark the main class of a Spring Boot application,内部封装了@Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan
@EnableAutoConfiguration,: Spring Boot looks for auto-configuration beans on its classpath and automatically applies them.
Auto-Configuration Conditions:@Conditional(判断指定类中match()结果)、@ConditionalOnClass(xx.class)、@ConditionalOnMissingClass... 作用在@Configuration类 或@Bean方法上
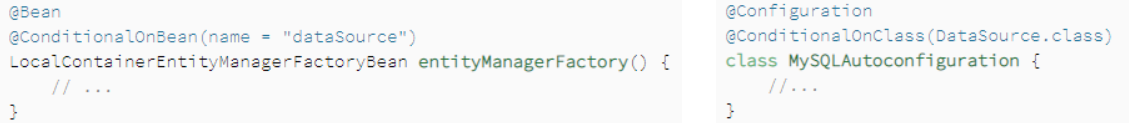
条件注解:根据指定条件是否match,来决定bean是否创建,作用在bean注册上(@Config、@Bean、@Component、@Service。。。)参考最后的样例
@Condtional:条件注解,根据指定的类中match方法返回true和false,决定是否初始化bean
@ConditionalOnProperty:依赖指定属性是否满足指定条件,如(value="logging.enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnExpression:依赖表达式是否成立,如"${logging.enabled:true} and '${logging.level}'.equals('DEBUG')"
@ConditionalOnBean(CustomLoggingConfiguration.class):依赖指定bean是否已被创建
@ConditionalOnClass(CustomLogger.class):依赖classpath下有无指定class
@ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.EIGHT):当前jdk是否1.8版本
自定义扩展:class XXXCondition implements Condition + @Conditional(XXXCondition.class)
组合条件注解:AnyNestedCondition(或)、与(多个condition联合使用)
Condtion接口:定义matcher方法,返回boolean
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
/**
* All {@link Condition} classes that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match}
* in order for the component to be registered.
*/
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}

属性读取:
1、Spring:
@PropertySource("classpath:foo.properties")、 @PropertySources(定义多个属性文件):作用在类上,从名字可知,不支持导入yaml格式
@Value( "${jdbc.url}" ): 读取参数,SPEL表达式; 更复杂场景参考下面Value专区
2、SpringBoot:
1)自动检测并读取 src/main/resouces/application.properties或yml ,所以只需将属性放入该文件,不需指定文件
2)手工指定 java -jar app.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:/another-location.properties 或 config/*/
3) @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server.default"):如果属性是一组,如jdbc,自动映射这些属性到Java对象中 POJO(非Bean)
https://www.baeldung.com/configuration-properties-in-spring-boot 映射list、map等复杂元素

通过如下方式,注册Java Bean;或通过下面的EnableConfigurationProperties实现

复杂的YAML解析样例