方式1:通过XML方式指定配置文件路径,用于XML文件中属性
Book.java
@Component
@Getter
@Setter
@Data
public class Book {private String name;
}
beans.xml <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" />
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" />
<bean id="book" class="com.example.ioc.pojo.Book">
<property name="name" value="${user}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
Main.java
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Book book = applicationContext.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
方式2:@PropertySource + @Value("${xxxx}")
src/main/resouces/db.properties
user=root
使用 BeanConfig (@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties") 导入外部文件
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public Book book() {
return new Book();
}
}
Book.java @Value("${user}")
@Getter @Setter @Data public class Book { @Value("${user}") private String name; }
Main.java
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(BeanConfig.class); annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh(); Book book = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Book.class); System.out.println(book); }
说明:引入外部属性配置文件 @PropertySouce 和 @PropertySources
针对springboot:1)src/main/resouces/application.properies被自动检测到,不需要配置;2)java -jar app.jar --spring.config.location=config/*/
@Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:/annotations.properties") @PropertySource("classpath:/vehicle-factory.properties") class VehicleFactoryConfig {} 或 @Configuration @PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:/annotations.properties"), @PropertySource("classpath:/vehicle-factory.properties") }) class VehicleFactoryConfig {}
关于@Value的更多用法
1、@Value("${unknown.param:some default}") 提供默认值
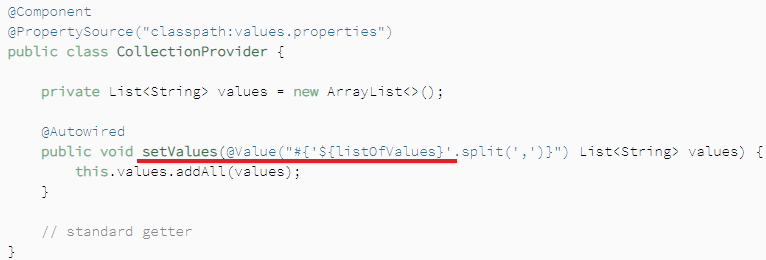
2、配置文件中value配置项value通过逗号分隔,传入数组
3、@Value("#{${valuesMap}['unknownKey']}")
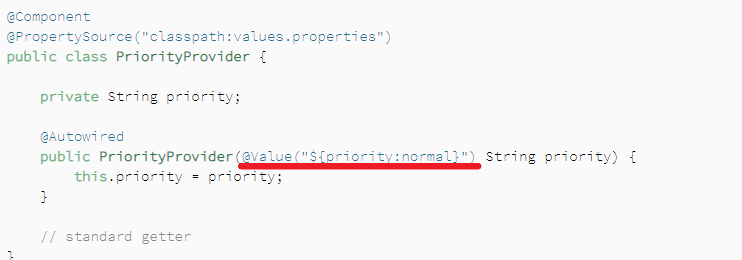
4、作为构造器注入
5、通过setter注入