输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。
例如输入12,从1到12这些整数中包含“1”的数字有1,10,11和12,其中“1”一共出现了5次。
输入: 12
输出: 5
从1到n,每增加1,weight就会加1,当weight加到9时,再加1又会回到0重新开始。那么weight从0-9的这种周期会出现多少次呢?这取决于n的高位是多少,看图:
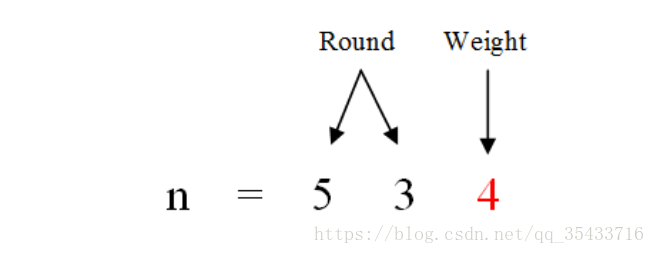
以534为例,在从1增长到n的过程中,534的个位从0-9变化了53次,记为round。每一轮变化中,1在个位出现一次,所以一共出现了53次。
再来看weight的值。weight为4,大于0,说明第54轮变化是从0-4,1又出现了1次。我们记1出现的次数为count,所以:
count = round+1 = 53 + 1 = 54
如果此时weight为0(n=530),说明第54轮到0就停止了,那么:
count = round = 53
2、十位
对于10位来说,其0-9周期的出现次数与个位的统计方式是相同的,见图:

不同点在于:从1到n,每增加10,十位的weight才会增加1,所以,一轮0-9周期内,1会出现10次。即rount*10。
再来看weight的值。当此时weight为3,大于1,说明第6轮出现了10次1,则:
count = round*10+10 = 5*10+10 = 60
如果此时weight的值等于0(n=504),说明第6轮到0就停止了,所以:
count = round*10+10 = 5*10 = 50
如果此时weight的值等于1(n=514),那么第6轮中1出现了多少次呢?很明显,这与个位数的值有关,个位数为k,第6轮中1就出现了k+1次(0-k)。我们记个位数为former,则:
count = round*10+former +1= 5*10+534%10+1 = 55
3、更高位
更高位的计算方式其实与十位是一致的,不再阐述。
4总结
则:
若weight为0,则1出现次数为round*base
若weight为1,则1出现次数为round*base+former+1
若weight大于1,则1出现次数为rount*base+base
比如:
534 = (个位1出现次数)+(十位1出现次数)+(百位1出现次数)=(53*1+1)+(5*10+10)+(0*100+100)= 214
530 = (53*1)+(5*10+10)+(0*100+100) = 213
504 = (50*1+1)+(5*10)+(0*100+100) = 201
514 = (51*1+1)+(5*10+4+1)+(0*100+100) = 207
10 = (1*1)+(0*10+0+1) = 2
public int numberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
if (n<1)
return 0;
int weight=0;
int round=n;
int base=1;
int count=0;
while (round != 0) {
weight=round%10;
round=round/10;
if (weight==0){
count+=round*base;
}else if (weight==1){
count+=round*base+n%base+1;
}else {
count+=round*base+base;
}
base*=10;
}
return count;
}