深度优先搜索( DFS, Depth-First Search) 是搜索的手段之一。它从某个状态开始,不断地转移状态直到无法转移,然后回退到前一步的状态 ,继续转移到其他状态,如此不断重复,直至找到最终的解。例如求解数独,首先在某个格子内填人适当的数字,然后再继续在下一个格子内填入数字,如此继续下去。如果发现某个格子无解了,就放弃前一个格 子上选择的数字,改用其他可行的数字。根据深度优先搜索的特点,采用递归函数实现比较简单。

上诉状态转移顺序和二叉树的前序遍历一致,二叉树的前序遍历就是dfs。上面这颗二叉树的前序遍历是:12345678910
题目:
给定n个整数a1、a2、.......an,判断是否可以从中选出若干数,使它们的和恰好为K。
输入:
n=4
a={1,2,4,7}
k=13
输出:
Yes(13=2+4+7)
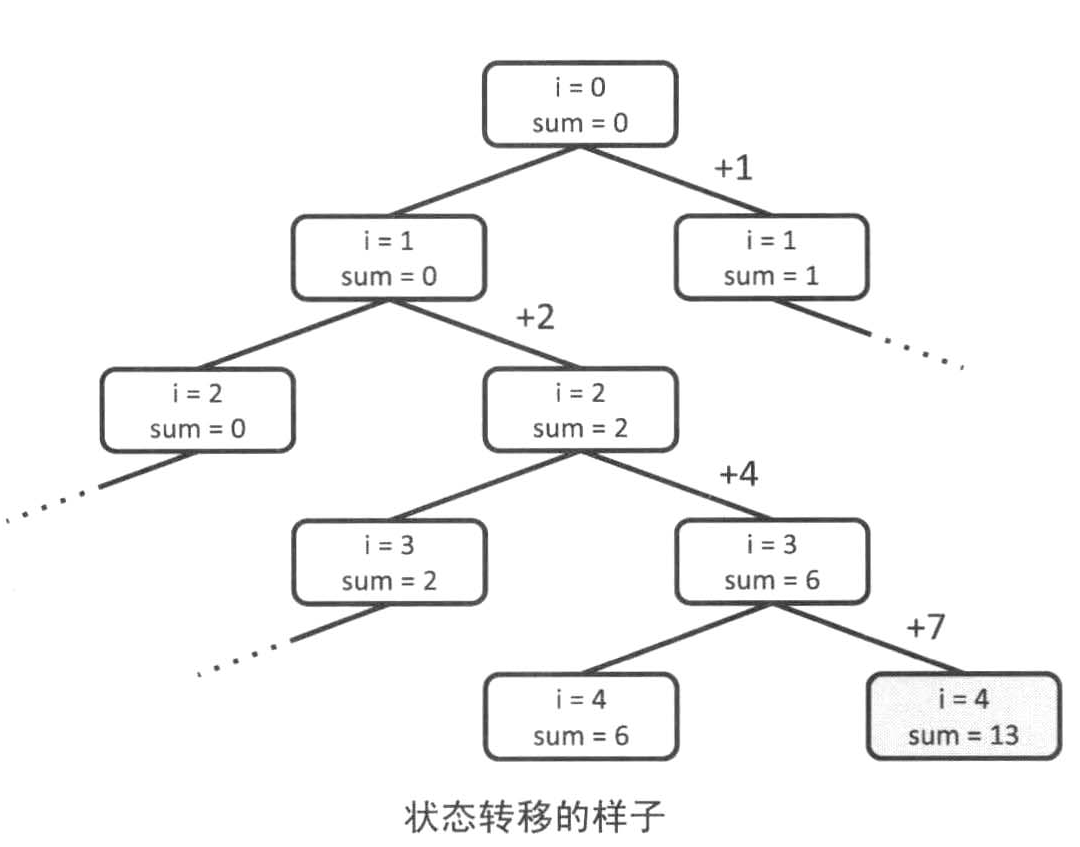
上述转移状态中二叉树的每一层都是相同的数字,第一层是a[1],第二层是a[2],第三层是a[3]......
java版本解法:
package dfs;
public class Main {
static int []a;
static int n,k;//一共n个数;若干个数和为k
static boolean dfs(int i,int sum){
if (i==n) {
return k==sum;
}
boolean x=dfs(i+1,sum+a[i]);
boolean y= dfs(i+1,sum);
return x||y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
n=4;
a=new int[]{1,2,4,7};
k=16;
System.out.println(dfs(0,0));
}
}
c++解法:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=20+10;
int arr[maxn];
int n,sum,k;
bool dfs(int i,int sum)
{
if(i==n) return sum==k;
if(dfs(i+1,sum)) return true;
if(dfs(i+1,sum+arr[i])) return true;
return false;
}
int solve()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>arr[i];
}
cin>>k;
if(dfs(0,0))
cout<<"Yes
";
else
cout<<"No
";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0);
solve();
}
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
百 度了一下,原来而cin,cout之所以效率低,是因为先把要输出的东西存入缓冲区,再输出,导致效率降低,而这段语句可以来打消iostream的输入 输出缓存,可以节省许多时间,使效率与scanf与printf相差无几,还有应注意的是scanf与printf使用的头文件应是stdio.h而不是 iostream。
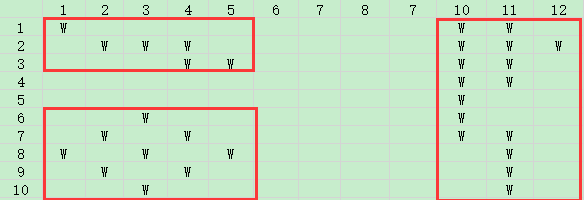
有一个大小为NXM的园子,雨后积起了水。八连通的积水被认为是连接在一-起的。请求出:园子里总共有多少水洼?(八连通指的是下图中相对W的*的部分)
***
*w*
Sample Input
10 12
W........WW.
.WWW.....WWW
....WW...WW.
.........WW.
.........W..
..W......W..
.W.W.....WW.
W.W.W.....W.
.W.W......W.
..W.......W.
Sample Output
3
分析:因为是八联通,所以对角线的水也能够互相流通。如第一个水洼。
解析:
从任意的w开始,不停地把邻接的部分用' . '代替。1次DFS后与初始的这个w连接的所有w就都被替换成了' . ',因此直到图中不再存在w为止,总共进行DFS的次数就是答案了(感染法)。8个方向共对应了8种状态转移,每个格子作为DFS的参数至多被调用1次,所以复杂度为0(8 xNx M)=O(Nx M)。
[-1,0,1]
[-1,0,1]
两个for循环取这两个数组的值一共有9种可能,包括元素所在的位置偏移量(0,0),所以是可以遍历w周围的8个方向。
c++版本解法:
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 110;
int n, m,res;
char field[MAX_N][MAX_N];
void dfs(int x, int y) {
//将w感染成 .
field[x][y] = '.';
//判断八个方向上是否有w
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
int nx = x + dx;
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
int ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && field[nx][ny] == 'W')
dfs(nx, ny);
}
}
}
void solve() {
res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(field[i][j] == 'W') {
dfs(i, j);
res++;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
getchar(); //吃掉换行符
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
scanf("%c", &field[i][j]);
}
getchar();
}
solve();
printf("%d
", res);
return 0;
}
Java版本解法:
package dfs;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main1 {
static String[][] field;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int m=sc.nextInt();
field=new String[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String tmp=sc.next();
String tmps[]= tmp.split("");
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
field[i][j]=tmps[j+1];
}
}
System.out.println(solve());
}
private static int solve() {
int res=0;
for (int i = 0; i < field.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < field[0].length; j++) {
if(field[i][j].equals("W")) {
dfs(i, j);
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private static void dfs(int x, int y) {
int n=field.length;
int m=field[0].length;
//将w感染成 .
field[x][y] = ".";
//判断八个方向上是否有w
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
int nx = x + dx;
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
int ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && field[nx][ny].equals("W"))
dfs(nx, ny);
}
}
}
}