1、static(静态定位):
默认值。没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, left, right 或者 z-index 声明)。参考上篇随笔。
2、relative(相对定位):
定位为relative的元素脱离正常的文档流,但其在文档流中的位置依然存在,只是视觉上相对原来的位置有移动。
通过top,bottom,left,right的设置相对于其正常(原先本身)位置进行定位。可通过z-index进行层次分级 。
.static1{ height:80px; background-color: red; } .relative{ height:80px; position:relative; top:40px; left:40px; background-color: black; } .static2{ height:80px; background-color: blue; }
</style> </head> <body> <div class="static1"></div> <div class="relative"></div> <div class="static2"></div> </body>

他是默认参照父级的原始点为原始点(父级不是必须设定position属性),无论父级存在不存在,无论有没有TRBL,均是以父级的左上角进行定位,但是父级的Padding属性会对其影响。
无父级则以文本流的顺序在上一个元素的底部为原始点
3、absolute(绝对定位):生成绝对定位的元素,相对于 static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定。可通过z-index进行层次分级。
定位为absolute的层脱离正常文档流,但与relative的区别是其在正常流中的位置不再存在。
这个属性总是有人给出误导。说当position属性设为absolute后,总是按照浏览器窗口来进行定位的,这其实是错误的。实际上,这是fixed属性的特点。
1,如果没有TRBL(top、right、bottom、left),以父级的左上角,在没有父级的时候,参照浏览器左上角。
2,如果设定TRBL,并且父级没有设定position属性(position:static;不算设定了属性),那么当前的absolute则以浏览器左上角为原始点进行定位,位置将由TRBL决定。
3,如果设定TRBL,并且父级设定position属性(无论是absolute还是relative),则以父级的左上角为原点进行定位,位置由 TRBL决定。即使父级有Padding属性,对其也不起作用。
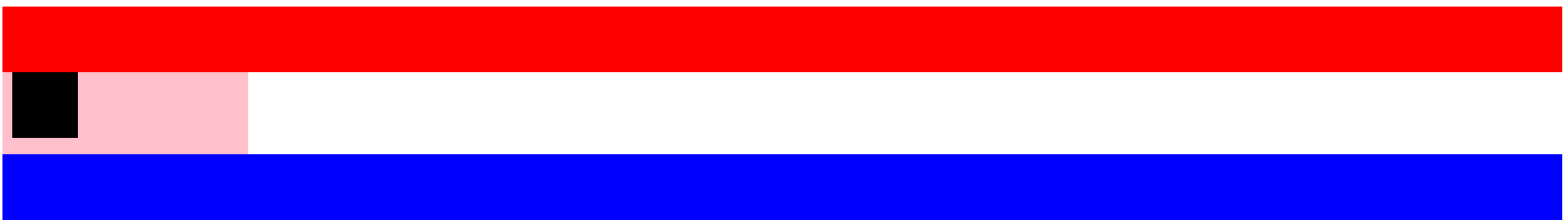
<style type="text/css"> .static1{ height:80px; background-color: red; } .father{ height:100px; background-color: pink; position:relative; left:20px; } .relative{ height:80px; width:80px; position:absolute; top:10px; left:10px; background-color: black; } .static2{ height:80px; background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="static1"></div> <div class="father"> <div class="relative"></div> </div> <div class="static2"></div>

4、fixed(固定定位):生成绝对定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定。可通过z-index进行层次分级。
1、如果没有TRBL(top、right、bottom、left),默认参照父级的原始点为原始点(父级不是必须设定position属性)。
2、如果设定TRBL,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。
<style type="text/css"> .static1{ height:80px; background-color: red; } .father{ height:100px; width:300px; background-color: pink; left:100px; top:100px; } .relative{ height:80px; width:80px; position:fixed; left:20px; background-color: black; } .static2{ height:80px; background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="static1"></div> <div class="father"> <div class="relative"></div> </div> <div class="static2"></div>
z-index属性
z-index,又称为对象的层叠顺序,它用一个整数来定义堆叠的层次,整数值越大,则被层叠在越上面,当然这是指同级元素间的堆叠,如果两个对象的此属 性具有同样的值,那么将依据它们在HTML文档中流的顺序层叠,写在后面的将会覆盖前面的。需要注意的是,父子关系是无法用z-index来设定上下关系 的,一定是子级在上父级在下。
Note:使用static 定位或无position定位的元素z-index属性是无效的。